
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 29P
Figure 10-32 shows an early method of measuring the
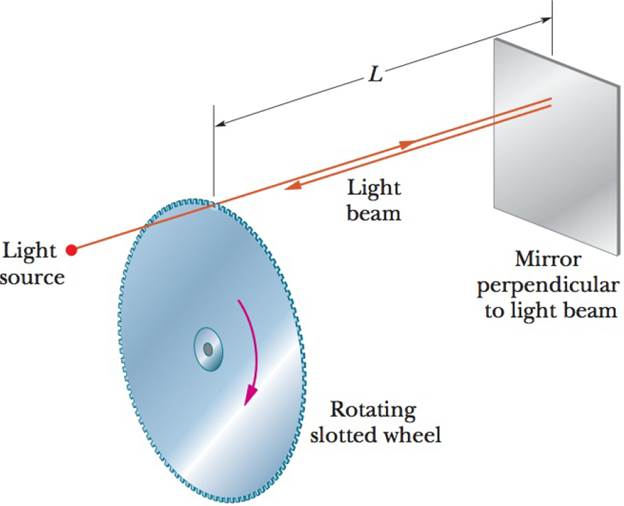
Figure 10-32 Problem 29.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
suggest a reason ultrasound cleaning is better than cleaning by hand?
Checkpoint 4
The figure shows four orientations of an electric di-
pole in an external electric field. Rank the orienta-
tions according to (a) the magnitude of the torque
on the dipole and (b) the potential energy of the di-
pole, greatest first.
(1)
(2)
E
(4)
What is integrated science.
What is fractional distillation
What is simple distillation
Chapter 10 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 10 - Figure 10-20 is a graph of the angular velocity...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-21 shows plots of angular position ...Ch. 10 - A force is applied to the rim of a disk that can...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-22b is a graph of the angular position...Ch. 10 - In Fig. 10-23, two forces F1 and F2 act on a disk...Ch. 10 - In the overhead view of Fig. 10-24, five forces of...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-25a is an overhead view of a horizontal...Ch. 10 - Figure l0-25b shows an overhead view of a...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-26 shows a uniform metal plate that had...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-27 shows three flat disks of the same...
Ch. 10 - Figure 10-28a shows a meter stick, hall wood and...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-29 shows three disks, each with a...Ch. 10 - A good baseball pitcher can throw a baseball...Ch. 10 - What is the angular speed of a the second hand, b...Ch. 10 - When a slice of buttered toast is accidentally...Ch. 10 - The angular position of a point on a rotating...Ch. 10 - ILW A diver makes 2.5 revolutions on the way from...Ch. 10 - The angular position of a point on the rim of a...Ch. 10 - The wheel in Fig. 10-30 has eight equally spaced...Ch. 10 - The angular acceleration of a wheel is = 6.0t4 ...Ch. 10 - A drum rotates around its central axis at an...Ch. 10 - Starting from rest, a disk rotates about its...Ch. 10 - A disk, initially rotating at 120 rad/s, is slowed...Ch. 10 - The angular speed of an automobile engine is...Ch. 10 - ILW A flywheel turns through 40 rev as it slows...Ch. 10 - GO A disk rotates about its central axis starling...Ch. 10 - SSM Starting from rest, a wheel has constant =...Ch. 10 - A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular...Ch. 10 - At t = 0, a flywheel has an angular velocity of...Ch. 10 - A pulsar is a rapidly rotating neutron star that...Ch. 10 - What are the magnitudes of a the angular velocity,...Ch. 10 - An object rotates about a fixed axis, and the...Ch. 10 - Between 1911 and 1990, the top of the leaning bell...Ch. 10 - An astronaut is tested in a centrifuge with radius...Ch. 10 - SSM WWW A flywheel with a diameter of 1.20 m is...Ch. 10 - A vinyl record is played by rotating the record so...Ch. 10 - SSM a What is the angular speed about the polar...Ch. 10 - The flywheel of a steam engine runs with a...Ch. 10 - A seed is on a turntable rotating at 3313 rev/min,...Ch. 10 - In Fig. 10-31, wheel A of radius rA = 10 cm is...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-32 shows an early method of measuring...Ch. 10 - A gyroscope flywheel of radius 2.83 cm is...Ch. 10 - GO A disk, with a radius of 0.25 m. is to be...Ch. 10 - A car starts from rest and moves around a circular...Ch. 10 - SSM Calculate the rotational inertia of a wheel...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-33 gives angular speed versus time for a...Ch. 10 - SSM Two uniform solid cylinders, each rotating...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-34a shows a disk that can rotate about...Ch. 10 - SSM Calculate the rotational inertia of a meter...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-35 shows three 0.0100 kg particles that...Ch. 10 - Trucks can be run on energy stored in a rotating...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-36 shows an arrangement of 15 identical...Ch. 10 - GO In Fig. 10-37, two particles, each with mass m...Ch. 10 - The masses and coordinates of four particles are...Ch. 10 - SSM WWW The uniform solid block in Fig. 10-38 has...Ch. 10 - Four identical particles of mass 0.50 kg each are...Ch. 10 - SSM ILW The body in Fig. 10-39 is pivoted at O,...Ch. 10 - The body in Fig. 10-40 is pivoted at O. Three...Ch. 10 - SSM A small ball of mass 0.75 kg is attached to...Ch. 10 - The length of a bicycle pedal arm is 0.152 m, and...Ch. 10 - SSM ILW During the launch from a board, a divers...Ch. 10 - If a 32.0 N m torque on a wheel causes angular...Ch. 10 - Prob. 51PCh. 10 - GO In Fig. 10-42, a cylinder having a mass of 2.0...Ch. 10 - GO Figure 10-43 shows a uniform disk that can...Ch. 10 - In a judo foot-sweep move, you sweep your...Ch. 10 - In Fig. 10-45a, an irregularly shaped plastic...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-46 shows particles 1 and 2, each of mass...Ch. 10 - GO A pulley, with a rotational inertia of 1.0 103...Ch. 10 - a IF R= 12 cm, M = 400 g, and m = 50 g in Fig....Ch. 10 - An automobile crankshaft transfers energy from the...Ch. 10 - A thin rod of length 0.75 m and mass 0.42 kg is...Ch. 10 - A 32.0 kg wheel, essentially a thin hoop with...Ch. 10 - In Fig. 10-35, three 0.0100 kg particles have been...Ch. 10 - SSM ILW A meter stick is held vertically with one...Ch. 10 - A uniform cylinder of radius 10 cm and mass 20 kg...Ch. 10 - GO A tall, cylindrical chimney fall;; over when...Ch. 10 - GO A uniform spherical shell of mass M = 4.5 kg...Ch. 10 - GO Figure 10-48 shows a rigid assembly of a thin...Ch. 10 - Prob. 68PCh. 10 - Prob. 69PCh. 10 - A wheel, starling from rest, rotates with a...Ch. 10 - SSM In Fig. 10-50, two 6.20 kg blocks are...Ch. 10 - Prob. 72PCh. 10 - A uniform helicopter rotor blade is 7.80 m long,...Ch. 10 - Prob. 74PCh. 10 - Prob. 75PCh. 10 - Starting from rest at t = 0, a wheel undergoes a...Ch. 10 - SSM A record turntable rotating at 3313 rev/min...Ch. 10 - Prob. 78PCh. 10 - Prob. 79PCh. 10 - A disk rotates al constant angular acceleration,...Ch. 10 - GO The thin uniform rod in Fig. 10-53 has length...Ch. 10 - Prob. 82PCh. 10 - Prob. 83PCh. 10 - At 7:14 A.M. on June 30, 1908, a huge explosion...Ch. 10 - A golf ball is launched at an angle of 20 to the...Ch. 10 - Prob. 86PCh. 10 - GO IN Fig. 10-55, a wheel of radius 0.20 m is...Ch. 10 - A thin spherical shell has a radius of 1.90 m. An...Ch. 10 - Prob. 89PCh. 10 - The flywheel of an engine is rotating at 25.0...Ch. 10 - SSM In Fig. 10-19a, a wheel of radius 0.20 m is...Ch. 10 - Our Sun is 23 104 ly light-years from the center...Ch. 10 - SSM A wheel of radius 0.20 m is mounted on a...Ch. 10 - If an airplane propeller rotates at 2000 rev/min...Ch. 10 - The rigid body shown in Fig. 10-57 consists of...Ch. 10 - Beverage engineering. The pull tab was a major...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-58 shows a propeller blade that rotates...Ch. 10 - A yo-yo-shaped device mounted on a horizontal...Ch. 10 - Prob. 99PCh. 10 - Two thin rods each of mass 0.20 kg are joined...Ch. 10 - In Fig. 10-61, four pulleys are connected by two...Ch. 10 - Prob. 102PCh. 10 - In Fig. 10-63, a thin uniform rod mass 3.0 kg,...Ch. 10 - Prob. 104PCh. 10 - Prob. 105PCh. 10 - A point on the rim of a 0.75-m-diameler grinding...Ch. 10 - A pulley wheel that is 8.0 cm in diameter has a...Ch. 10 - A vinyl record on a turntable rotates at 3313...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 19:39 · C Chegg 1 69% ✓ The compound beam is fixed at Ę and supported by rollers at A and B. There are pins at C and D. Take F=1700 lb. (Figure 1) Figure 800 lb ||-5- F 600 lb بتا D E C BO 10 ft 5 ft 4 ft-—— 6 ft — 5 ft- Solved Part A The compound beam is fixed at E and... Hình ảnh có thể có bản quyền. Tìm hiểu thêm Problem A-12 % Chia sẻ kip 800 lb Truy cập ) D Lưu of C 600 lb |-sa+ 10ft 5ft 4ft6ft D E 5 ft- Trying Cheaa Những kết quả này có hữu ích không? There are pins at C and D To F-1200 Egue!) Chegg Solved The compound b... Có Không ☑ ||| Chegg 10 וחarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardair is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forward
- Calculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardCan you help me solve the questions pleasearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Moment of Inertia; Author: Physics with Professor Matt Anderson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZrGhUTeIlWs;License: Standard Youtube License