
Concept explainers
Gretchen’s Kitchen is a fast-food restaurant located in an ideal spot near the local high school. Gretchen Lowe must prepare an annual staffing plan. The only menu items are hamburgers, chili, soft drinks, shakes, and French fries. A sample of 1,000 customers taken at random revealed that they purchased 2,100 hamburgers, 200 pints of chili, 1,000 soft drinks and shakes, and 1,000 bags of French fries. Thus, for purposes of estimating staffing requirements, Lowe assumes that each customer purchases 2.1 hamburgers, 0.2 pint of chili, 1 soft drink or shake, and 1 bag of French fries. Each hamburger requires 4 minutes of labor, a pint of chili requires 3 minutes, and a soft drink or shake and a bag of fries each take 2 minutes of labor.
The restaurant currently has 10 part-time employees who work 80 hours a month on staggered shifts. Wages are $400 per month for regular time amid $7.50 per hour for overtime. Hiring amid training costs are $250 new employee, and layoff costs are $50 per employee.
Lowe realizes that building up seasonal inventories of hamburgers (or any of the products) would not be wise because of shelf-life considerations. Also, any demand not satisfied is a lost sale amid must be avoided. Three strategies come to mind.
- Use a level strategy relying on overtime and under time, with up to 20 percent of regular-time capacity on overtime.
- Maintain a base of 10 employees, hiring and laying off as needed to avoid any overtime.
- Utilize a chase strategy, hiring and laying off employees as demand changes to avoid overtime.
When performing her calculations, Lowe always rounds to the next highest integer for the number of employees. She also follows a policy of not using an employee more than 80 hours per month, except when overtime is needed. The projected demand by month (number of customers) for next year is as follows:
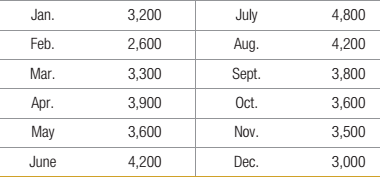
- Develop the
schedule of service requirements (hours per month) for the next year. - Which strategy is most effective?
- Suppose that an arrangement with the high school enables the manager to identify good prospective employees without having to advertise in the local newspaper. This source reduces the hiring cost to $50, which is mainly the cost of charred hamburgers during training. If cost is her only concern, will this method of hiring change Gretchen Lowe’s strategy? Considering other objectives that may be appropriate, do you think she should change strategies?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains (11th Edition)
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
Intermediate Accounting (2nd Edition)
Gitman: Principl Manageri Finance_15 (15th Edition) (What's New in Finance)
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Principles of Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management (10th Edition)
Fundamentals of Cost Accounting
- The oasis outpost of Abu Ilan, in the heart of the Negev desert, has a population of 20 Bedouin tribesmen and 20 Farima tribesmen. El Kamin, a nearby oasis, has a population of 32 Bedouins and 8 Farima. A lost Israeli soldier, accidentally separated from his army unit, is wandering through the desert and arrives at the edge of one of the oases. The soldier has no idea which oasis he has found, but the first person he spots at a distance is a Bedouin. 1. What is the probability that he wandered into Abu Ilan? 2. What is the probability that he is in El Kamin?arrow_forward2-22 The lost Israeli soldier mentioned in Problem 2-21 decides to rest for a few minutes before entering the desert oasis he has just found. Closing his eyes, he dozes off for 15 minutes, wakes, and walks toward the center of the oasis. The first person he spots this time he again recognizes as a Bedouin. What is the posterior probability that he is in El Kamin?*Note* 2-21 The oasis outpost of Abu Ilan, in the heart of the Negev desert, has a population of 20 Bedouin tribesmen and 20 Farima tribesmen. El Kamin, a nearby oasis, has a population of 32 Bedouins and 8 Farima. A lost Israeli soldier, accidentally separated from his army unit, is wandering through the desert and arrives at the edge of one of the oases. The soldier has no idea which oasis he has found, but the first person he spots at a distance is a Bedouin. What is the probability that he has wandered into Abu Ilan? What is the probability that he is in El Kamin?arrow_forwardHello, please make an excel of this. Show all the cells thanks. some replied with a paper answer thank you I just cant understand the way the did it. Can someone show me all screenshots o fthis problem solved and in excel? i need to solver too for the constraints. I seen multiple times across other platforms that one of the chairs optimal solutions is 0 but they both have to be higher than 1 The Heinrich Company manufactures two types of plastic hangerracks (Foldaways and Straightaways) especially suited for mountingnear clothes dryers. Because permanent press clothing must be hungon hangers immediately after removal from the dryer, these items havebeen especially popular. However, there is some concern that thePreppie movement (popularized by its own handbook) will extinguishpolyester clothing; Heinrich is terribly interested in doing the best withthe resources it has while its products are still in demand. The firsttype of hanger rack, the Foldaway, requires 10 ounces of…arrow_forward
- Review the Profit Ratio by Product chart again. What information is uncovered when the data is less aggregated than the data in Profit Ratio by Category chart?arrow_forwardWhat is the correlation between Measure A and Measure B in this example?arrow_forward1) View the video ON Unveils ‘Lightspray’ Technology (4.55 mins, Ctrl+Click in the link), and The Secret of Lightspray (8.27 mins, Ctrl+Click in the link), answer the following questions: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wjmeaC-wlZs a) What is new about the design of ON’s shoes? b) How will ON’s new manufacturing technique affect location planning for footwear firms? c) How does ON focus on it sustainability strategy? Note: As a rough guideline, please try to keep the written submission to one or two paragraphs for each of the questions. 2) Unimed Hospital currently processes patient admissions through three admitting clerks who are set up to work in series, with respective reliabilities of 0.96, 0.95, and 0.90 (see figure below). a) Find the reliability of the current admission process. Due to rising patient complaints, the hospital administrator, Chimeg Ganbaatar, has decided to improve the reliability of the admission process by providing backup clerks for two of the…arrow_forward
- + < Question 21 of 39 What is the correct common name for the compound shown here? 2-methoxyprop ane | 3-1-2- n-tert- iso sec- eth prop meth methoxy propoxy ethoxy yl acid ether ester ane Reset ☑ Submitarrow_forward(25 Marks) Discuss how you would "reset the store estate" to remain competitive and relevant in the market?arrow_forwardHello, please make an excel of this. Show all the cells thanks The Heinrich Company manufactures two types of plastic hangerracks (Foldaways and Straightaways) especially suited for mountingnear clothes dryers. Because permanent press clothing must be hungon hangers immediately after removal from the dryer, these items havebeen especially popular. However, there is some concern that thePreppie movement (popularized by its own handbook) will extinguishpolyester clothing; Heinrich is terribly interested in doing the best withthe resources it has while its products are still in demand. The firsttype of hanger rack, the Foldaway, requires 10 ounces of plasticmaterial and 0.3 hours of labor. Plastic costs Heinrich 10 cents anounce; labor costs Heinrich $20 per hour. The second type of hangerrack, the Straightaway, requires 15 ounces of plastic and 0.175 hoursof labor. The prices of these resources are the same as those for theFoldaway. Under current market conditions, Heinrich can sell…arrow_forward
- FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT 1 Read the article below and answer ALL the questions Pick n Pay reveals strategy to restore its business 27 May 2024 [100 MARKS] Following a disappointing full year performance for FY24, Pick n Pay CEO Sean Summers has unveiled the new board- approved six-point strategy to restore the Group's core Pick n Pay supermarket business to profitability. PHASED APPROACH IMPLEMENTATION Leverage strength of partnerships Leadership and people 2 Reset the store estate 3 Improve offer to drive sales 4 Optimise operating model Leverage strength of partnerships Recapitalisation Pick n Pay Prod FY26 FY27 Before Tax break-even FY25 Halve Group H2 FY24 H1 FY25 H2 FY25 H1 FY26 H2 FY26 HI FY27 H2 FY27 KEY IMPACT AND/OR TARGETED OUTCOMES Appointing the right people, in the optimal roles, to Directly and indirectly impact revenue growth drivers and 1 drive sales and realise margin improvement 5 enhances gross and operating margins 2 Expected notable associated savings/loss avoidance…arrow_forwardWith an enormous amount of data stored in databases and data warehouses, it is increasinglyimportant to develop powerful tools for analysis of such data and mining interestingknowledge from it. Data mining is a process of inferring knowledge from such huge data. Themain problem related to the retrieval of information from the World Wide Web is theenormous number of unstructured documents and resources, i.e., the difficulty of locating andtracking appropriate sources. Your company is considering investing in a Human Resource Information System (HRIS).Briefly explain the strategies for justifying HRIS investments.arrow_forwardYour company is considering investing in a Human Resource Information System (HRIS).Briefly explain the strategies for justifying HRIS investments.arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning





