
Concept explainers
A healthy couple with a history of three previous spontaneous abortions has just had a child with
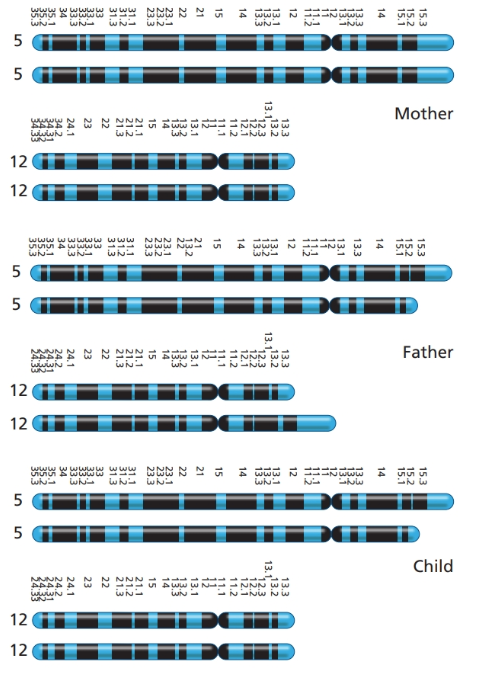
Are the chromosomes in the child consistent with those expected in a case of
Which parent has an abnormal karyotype? How can you tell? What is the nature of the abnormality?
Why does this parent have a normal
Diagram the pairing of the abnormal chromosomes.
What segregation pattern occurred to produce the gamete involved in fertilization of the child with
What is the approximate probability that the next child of this couple will have
Do the karyotypes of the parents help explain the occurrence of the three previous spontaneous abortions? Explain.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
- 1. Match each vocabulary term to its best descriptor A. affinity B. efficacy C. inert D. mimic E. how drugs move through body F. how drugs bind Kd Bmax Agonist Antagonist Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamicsarrow_forward50 mg dose of a drug is given orally to a patient. The bioavailability of the drug is 0.2. What is the volume of distribution of the drug if the plasma concentration is 1 mg/L? Be sure to provide units.arrow_forwardDetermine Kd and Bmax from the following Scatchard plot. Make sure to include units.arrow_forward
- Choose a catecholamine neurotransmitter and describe/draw the components of the synapse important for its signaling including synthesis, packaging into vesicles, receptors, transporters/degradative enzymes. Describe 2 drugs that can act on this system.arrow_forwardThe following figure is from Caterina et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature, 1997. Black boxes indicate capsaicin, white circles indicate resinferatoxin. a) Which has a higher potency? b) Which is has a higher efficacy? c) What is the approximate Kd of capsaicin in uM? (you can round to the nearest power of 10)arrow_forwardWhat is the rate-limiting-step for serotonin synthesis?arrow_forward
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





