
Effect of Paternal Grandmother’s Food Supply on Infant Mortality Researchers are investigating long- reaching epigenetic effects of starvation, in part because historical data on periods of famine are widely available. Before the industrial revolution, a failed harvest in one autumn typically led to severe food shortages the following winter. A retrospective study has correlated female infant mortality at certain ages with the abundance of food during the paternal grandmother’s childhood. FIGURE 10.12 shows some of the results of this study.
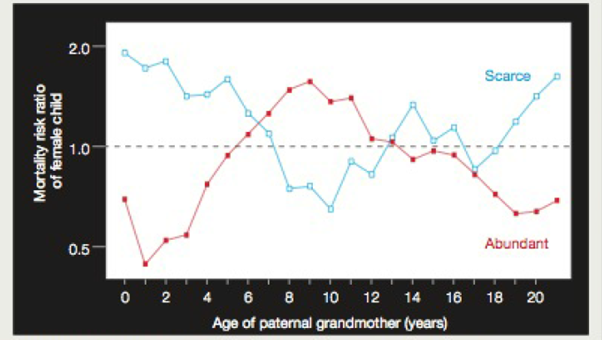
FIGURE 10.12 Graph showing the relative risk of early death of a female child, correlated with the age at which her paternal grandmother experienced a winter with a food supply that was scarce (blue) or abundant (red) during childhood. The dotted line represents no difference in risk of morality. A value above the line means an increases risk; one below the line indicates a reduced risk.
1. Compare the mortality of girls whose paternal grandmothers ate well at age 2 with that of those who experienced famine at the same age. Which girl was more likely to die early? How much more likely was she to die?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
- Molecular Biology Question. Please help solve. Thanks. Please draw how two nucleotide triphosphates are linked together to form a dinucleotide, and label the 5' and 3' ends of the resulting dinucleotide.arrow_forwardWhat is a reversion in molecular biology?arrow_forwardWhat is a gain of function mutation?arrow_forward
- Molecular Biology Question: Please help. Thank you Is Southern hybridization's purpose detecting specific nucleotide sequences? How so?arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the question(s) below. Martin Wikelski and L. Michael Romero (Body size, performance and fitness in Galápagos marine iguanas, Integrative and Comparative Biology 43 [2003]:376-86) measured the snout-to-vent (anus) length of Galápagos marine iguanas and observed the percent survival of different-sized animals, all of the same age. The graph shows the log snout-vent length (SVL, a measure of overall body size) plotted against the percent survival of these different size classes for males and females. Survival (%) 100- 80- 60- 40- 20- 0+ 1.9 T 2 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 Log SVL (mm) 19) Examine the figure above. What type of selection for body size appears to be occurring in these marine iguanas? A) directional selection B) stabilizing selection C) disruptive selection D) You cannot determine the type of selection from the above information. 3arrow_forward24) Use the following information to answer the question below. Researchers studying a small milkweed population note that some plants produce a toxin and other plants do not. They identify the gene responsible for toxin production. The dominant allele (T) codes for an enzyme that makes the toxin, and the recessive allele (t) codes for a nonfunctional enzyme that cannot produce the toxin. Heterozygotes produce an intermediate amount of toxin. The genotypes of all individuals in the population are determined (see table) and used to determine the actual allele frequencies in the population. TT 0.49 Tt 0.42 tt 0.09 Refer to the table above. Is this population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? A) Yes. C) No; there are more homozygotes than expected. B) No; there are more heterozygotes than expected. D) It is impossible to tell.arrow_forward
- 30) A B CDEFG Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the following forms a monophyletic group? A) A, B, C, and D B) C and D C) D, E, and F D) E, F, and Garrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question. Please help with step solution and explanation. Thank you: The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) reaction consists of three steps denaturation, hybridization, and elongation. Please describe what occurs in the annealing step of the PCR reaction. (I think annealing step is hybridization). What are the other two steps of PCR, and what are their functions? Next, suppose the Tm for the two primers being used are 54C for Primer A and 67C for Primer B. Regarding annealing step temperature, I have the following choices for the temperature used during the annealing step:(a) 43C (b) 49C (c) 62C (d) 73C Which temperature/temperatures should I choose? What is the corresponding correct explanation, and why would I not use the other temperatures? Have a good day!arrow_forwardUsing the data provided on the mean body mass and horn size of 4-year-old male sheep, draw a scatterplot graph to examine how body mass and horn size changed over time.arrow_forward
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning





