
Concept explainers
Carbon–carbon bond dissociation enthalpies have been measured for many
Without referring to Table
has the lower carbon–carbon bond-dissociation enthalpy, and explain the reason for your
choice.
Ethane or propane
Propane or
Cyclobutane or cyclopentane
Interpretation:
In each of the given pairs, the alkane having lower carbon-carbon bond dissociation enthalpy is to be identified and the reason for this is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
Species that contain unpaired electrons are called free radicals.
Alkyl radicals are described by the presence of carbon with three bonds. The alkyl radicals are classified as primary, secondary or tertiary on the basis of the number of carbon atoms directly attached to the carbon atom bearing unpaired electron.
Similar to carbocation’s, free radicals are stabilized by alkyl substituents. The stability order of alkyl radicals is
In a hemolytic cleavage, each atom of the bond keeps one of the electrons in the bond.
The bond dissociation energy represents the stability of radical formed.
Answer to Problem 16P
Solution:
a) Propane has the lower carbon-carbon bond dissociation enthalpy because it produces more stable free radicals.
b)
c)
d) Cyclopentane has the lower carbon-carbon bond dissociation enthalpy because it produces more stable free radicals.
Explanation of Solution
a) The given alkanes are ethane and propane.
The cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond in propane produces one methyl radical and one ethyl radical.
The ethyl radical is a primary radical and is more stable than the methyl radical. Hence propane produces more stable radicals than ethane upon homolytic cleavage. Lower energy is required to generate free radicals in propane. Thus, propane has a lower bond dissociation enthalpy than ethane.
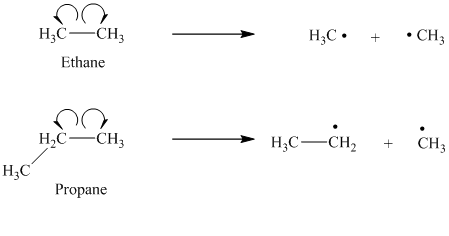
b) The given alkanes are propane and
The homolytic cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond in propane produces one methyl radical and one ethyl radical. The homolytic cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond in
The isopropyl radical is a secondary radical and is more stable than the ethyl radical, which is a primary radical. Hence
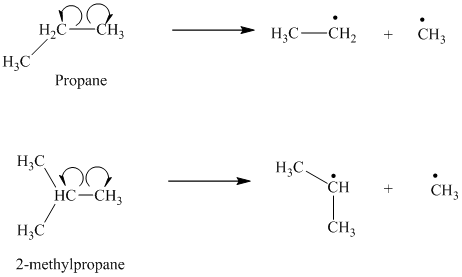
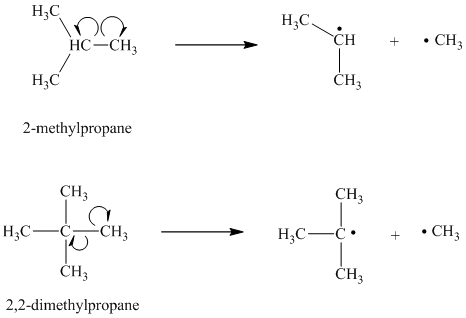
c) The given alkanes are
The homolytic cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond in
The tertiary butyl radical is a tertiary radical and is more stable than the isopropyl radical, which is a secondary radical. Hence
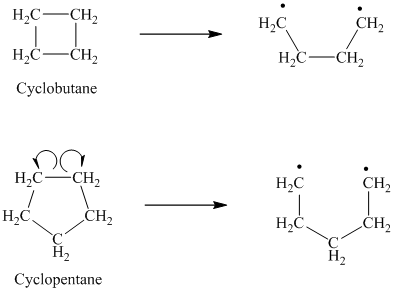
d) The given alkanes are cyclobutane and cyclopentane.
The homolytic cleavage of cyclobutane produces two radicals, which are attached to each other. Both the unpaired electrons are present on primary carbon atoms.
The homolytic cleavage of cyclopentane also produces two radicals, which are attached to each other. Both the unpaired electrons are present on primary carbon atoms.
In the radicals produced by cyclopentane, there is one alkyl substituent more as compared to the radicals in cyclobutane. The more the alkyl substituents, the more stable is the radical. Hence, in cyclopentane, the radicals are slightly more stable as compared to cyclobutane. Hence, cyclopentane has a lower bond dissociation enthalpy than cyclobutane.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)-W/SOLN.>CUSTOM<
- Determine the distance between the metal and the OHP layer using the Helm- holtz model when the electrode's differential capacitance is 145 μF cm². DATA: dielectric constant of the medium for the interfacial zone &r= lectric constant of the vacuum &0 = 8.85-10-12 F m-1 = 50, die-arrow_forwardDescribe a sequence of photophysical processes that can be followed by radiation adsorbed by a molecule in the ground state to give rise to phosphorescent emission.arrow_forwardState two similarities between fluorescence and phosphorescence.arrow_forward
- State three photophysical processes that can be related to the effects of incident radiation on a molecule in its ground state. Consider that radiation can give rise to fluorescent emission, but not phosphorescent emission.arrow_forwardIn a photochemical reaction, how is the rate of the process related to its quantum yield?arrow_forwardPrimary and global quantum yields in photochemistry. Define them and give their formulas. Differentiate between them.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





