
Concept explainers
Guiding your reasoning by retrosynthetic analysis, show how you could prepare each of the following compounds from the given starting material and any necessary organic or inorganic reagents. All require more than one synthetic step.
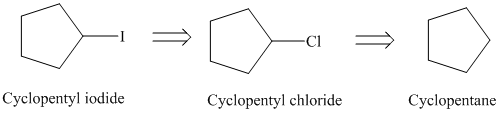
Cyclopentyl iodide from cyclopentane
from
from
Butyl methyl ether
from

Interpretation:
Each of the given compounds from the given starting material and any necessary organic or inorganic reagents are to be prepared by using retrosynthetic analysis with more than one synthetic step.
Concept Introduction:
The alkane, on chlorination, forms the corresponding alkyl chloride.
Alkyl halide, in presence of a strong base, undergoes
Alkene, on bromination, undergoes trans addition of bromine across the double bond and forms the corresponding vicinal dihalide.
The reaction of alkene with hydrogen halide forms the corresponding alkyl halide.
The primary alkyl halide, on reaction with sodium alkoxide, undergoes substitution and forms the corresponding ether.
The alkynes, on hydrogenation with catalyst Lindlar palladium, form a cis alkene.
The conjugate base of alkyne acts as a good nucleophile, on reaction with primary alkyl halide undergoes a substitution reaction.
The alkyne, on hydrogenation by a Group 1 metal (lithium, sodium, or potassium) in liquid ammonia, undergoes trans addition of
The alkene, on reaction with hydrogen bromide in presence of peroxide, undergoes an addition reaction in a way that the hydrogen bonds to a more substituted carbon of double bond and bromine bonds to a less substituted carbon of double bond. This is called anti-Markovnikov rule.
Answer to Problem 30P
Solution:
a)
Retrosynthesis:
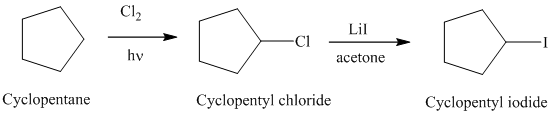
Synthesis:
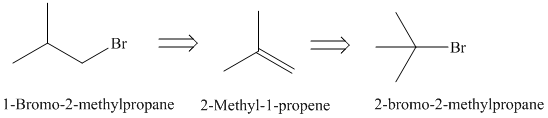
b)
Retrosynthesis:
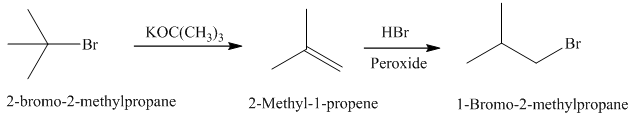
Synthesis:
c)
Retrosynthesis:
Synthesis:
d)
Retrosynthesis:
Synthesis:
e)
from
Retrosynthesis:
Synthesis:
f)
Retrosynthesis:
Synthesis:
g)
Retrosynthesis:
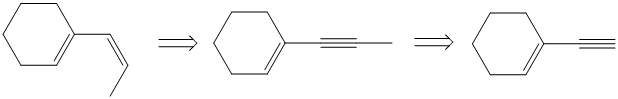
Synthesis:
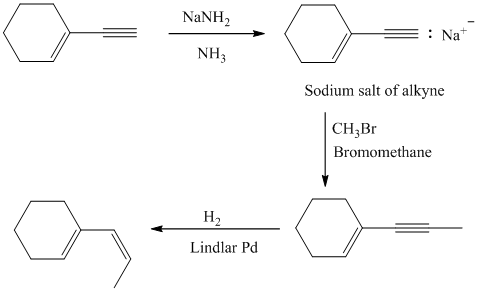
Explanation of Solution
a)
The retrosynthetic analysis for the preparation of

Cyclopentyl iodide can be prepared from cyclopentyl chloride by a substitution reaction.
The cyclopentyl chloride can be prepared from cyclopentane by chlorination in presence of light.
The actual synthetic route for the above retrosynthetic analysis is as follows:

Cyclopentane is a symmetrical cycloalkane. Reaction of cyclopentane with chlorine in presence of light will produce cyclopentyl chloride.
b)
The retrosynthetic analysis for the preparation of

Elimination reaction of
The actual synthetic route for the above retrosynthetic analysis is as follows:

to the
takes place according to a regioselectivity opposite to that of Markovnikov’s rule.
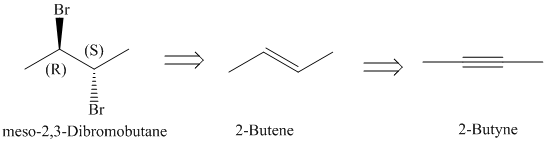
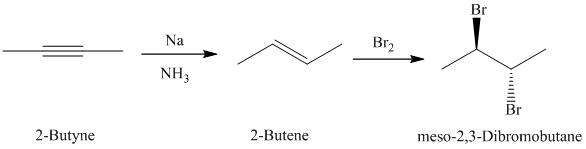
c)
The retrosynthetic analysis for the preparation of

The actual synthetic route for the above retrosynthetic analysis is as follows:

upon partial reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia produces trans
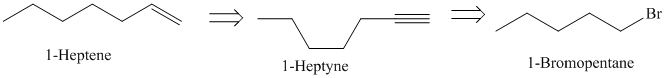
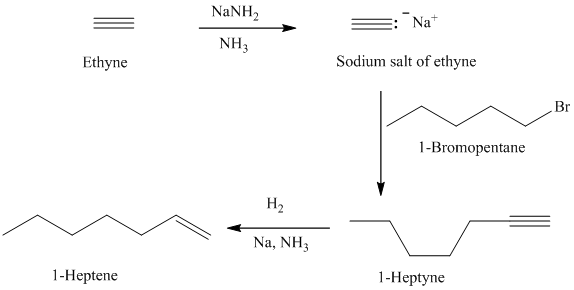
d)
The retrosynthetic analysis for the preparation of

can be prepared by the partial reduction of
The actual synthetic route for the above retrosynthetic analysis is as follows:

Ethyne upon reaction with a strong base sodium amide produces the acetylide anion. It acts as a nucleophile and reacts with the primary alkyl halide
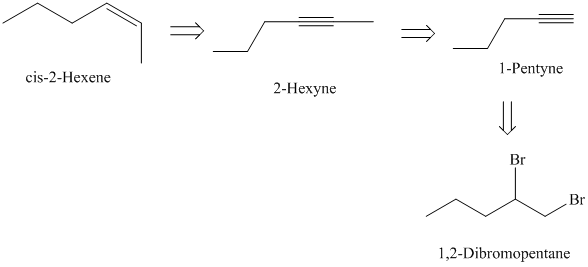
e)
from
The retrosynthetic analysis for the preparation of

The actual synthetic route for the above retrosynthetic analysis is as follows:

is a vicinal dibromide. Reaction of it with excess sodium amide will result in double dehydrohalogenation producing
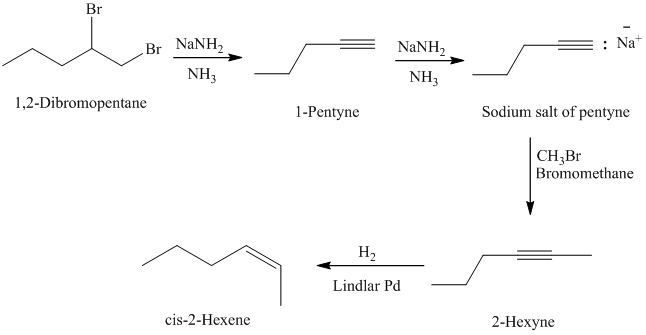
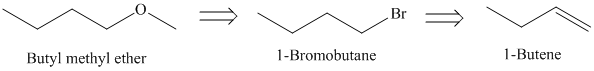
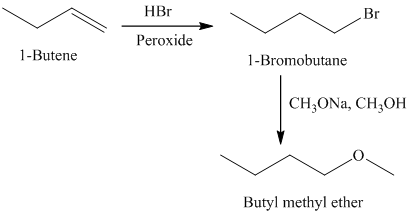
f)
The retrosynthetic analysis for the preparation of

Butyl methyl ether can be prepared by the reaction of
The actual synthetic route for the above retrosynthetic analysis is as follows:
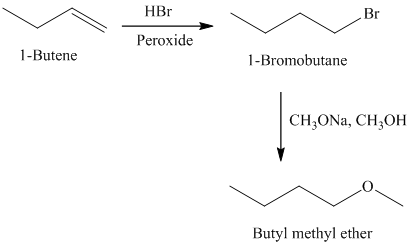
Addition of
type of reaction.
g) The given starting material is shown below.
The retrosynthetic analysis for the preparation of the given compound from the given starting material is shown below:

The double inside the cyclohexane ring is intact in the reactant and product. The double bond in the side chain can be prepared by the partial reduction of a triple bond. The triple bond can be produced by the reaction of the given terminal alkyne with sodium amide followed by methyl bromide.
The actual synthetic route for the above retrosynthetic analysis is as follows:

The terminal triple bond has an acidic proton. Reaction of this terminal alkyne with sodium amide will produce the corresponding anion. Reaction of this anion with methyl bromide will produce an internal alkyne. This can be reduced partially to a cis double bond upon reaction with Lindlar catalyst.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)-W/SOLN.>CUSTOM<
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
