
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The given ball and stick model of estragole to a skeletal structure has to be drawn and
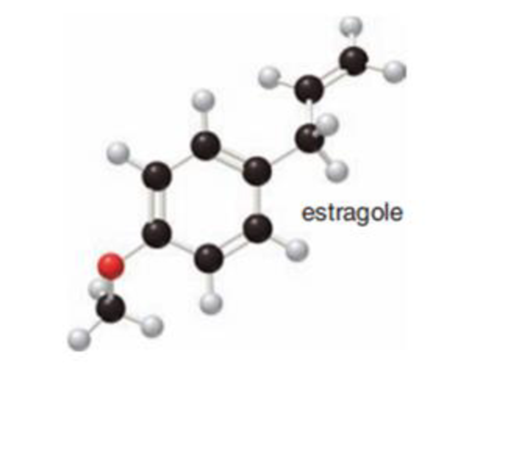
Concept Introduction:
Skeletal structures
Skeletal structures are used for representing the organic structures in diagrammatic form. The carbon atom must have four bonds. The heteroatom should not contain its lone pair of electrons. The double bond and triple bond has to be drawn. The hydrogen bonded directly to heteroatom has to be drawn. The carbon and hydrogen present in ring or chain compound has to be omitted.
Functional group:
Functional group contains particular atom or group of atoms bonded in a molecule which has specific chemical and physical properties. Adding any specific functional group to compound can form a new product it is known as functionalization. The functional group contains heteroatoms and a multiple bond in a compound.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Connect 1-Semester Online Access for Principles of General, Organic & Biochemistry
- Relative Transmittance 0.995 0.99 0.985 0.98 Please draw the structure that is consistent with all the spectral data below in the box and alphabetically label the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc ....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. Label the absorption bands in the IR spectrum indicated by the arrows. INFRARED SPECTRUM 1 0.975 3000 2000 Wavenumber (cm-1) 1000 Structure with assigned H peaks 1 3 180 160 140 120 100 f1 (ppm) 80 60 40 20 0 C-13 NMR note that there are 4 peaks between 120-140ppm Integral values equal the number of equivalent protons 10.0 9.0 8.0 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 fl (ppm)arrow_forwardCalculate the pH of 0.0025 M phenol.arrow_forwardIn the following reaction, the OH- acts as which of these? NO2-(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ OH-(aq) + HNO2(aq)arrow_forward
- Using spectra attached, can the unknown be predicted? Draw the predicition. Please explain and provide steps. Molecular focrmula:C16H13ClOarrow_forwardCalculate the percent ionization for 0.0025 M phenol. Use the assumption to find [H3O+] first. K = 1.0 x 10-10arrow_forwardThe Ka for sodium dihydrogen phosphate is 6.32 x 10-8. Find the pH of a buffer made from 0.15 M H2PO4- and 0.25 M HPO42- .arrow_forward
- The Ka for lactic acid is 1.4 x 10-4. Find the pH of a buffer made from 0.066 M lactic acid and 0.088 M sodium lactate.arrow_forwardZaitsev's Rule 3) (a) Rank the following alkenes in order of decreasing stability. most stable A B C D > > > (b) Rank the following carbocations in order of decreasing stability least stable B C Darrow_forwardCalculate the pH of 0.25 M acetic acid.arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





