
University Physics Volume 3
17th Edition
ISBN: 9781938168185
Author: William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 1.2CYU
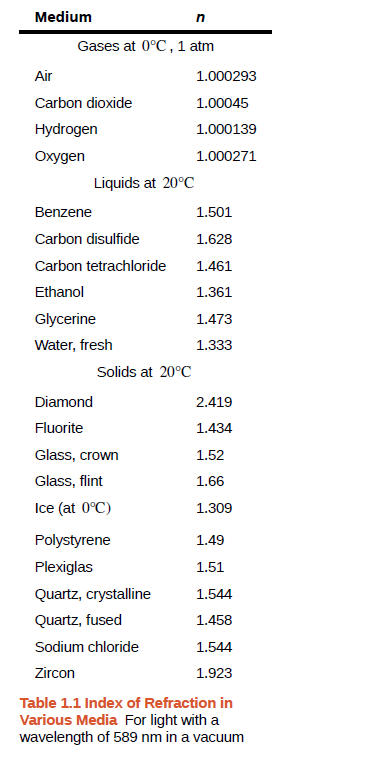
Check Your Understanding In Table 1.1, the solid with the next highest index of refraction after diamond is zircon. If the diamond in Example 1.3 were replaced with a piece of zircon, what would be the
new angle of refraction?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Imagine you are out for a stroll on a sunny day when you encounter a lake. Unpolarized light from the sun is reflected off the lake into your eyes. However, you notice when you put on your vertically polarized sunglasses, the light reflected off the lake no longer reaches your eyes. What is the angle between the unpolarized light and the surface of the water, in degrees, measured from the horizontal? You may assume the index of refraction of air is nair=1 and the index of refraction of water is nwater=1.33 . Round your answer to three significant figures. Just enter the number, nothing else.
Deduce what overvoltage is like in reversible electrodes.
pls help on these
Chapter 1 Solutions
University Physics Volume 3
Ch. 1 - Check Your Understanding Table 1.1 shows that...Ch. 1 - Check Your Understanding In Table 1.1, the solid...Ch. 1 - Check Your Understanding At the surface between...Ch. 1 - Check Your Understanding In the preceding example....Ch. 1 - Check Your Understanding in Example 1.6, we had...Ch. 1 - Check Your Understanding Although we did no...Ch. 1 - Check Your Understanding What happens at...Ch. 1 - Under what conditions can light be modeled like a...Ch. 1 - Why is the index of refraction always greater than...Ch. 1 - Does the fact that the light flash from lightning...
Ch. 1 - Speculate as to s1at physical process might be...Ch. 1 - Using the law of reflection, explain how powder...Ch. 1 - Diffusion by reflection from a rough surface is...Ch. 1 - Will 1igt change direction toward or away from the...Ch. 1 - Exp1ain why an object in water always appears to...Ch. 1 - Explain why a person’s legs appear very short when...Ch. 1 - Explain why an oar that is partially submerged in...Ch. 1 - A ring with a colorless gemstone is dropped into...Ch. 1 - The most common type of mirage is an illusion that...Ch. 1 - How can you use total internal reflection to...Ch. 1 - Is it possible that total internal reflection...Ch. 1 - A high-quality diamond may be quite clear and...Ch. 1 - How do wave effects depend on the size of the...Ch. 1 - Does Huygens’s principle apply to all types of...Ch. 1 - If diffraction is observed for some phenomenon, it...Ch. 1 - Can a sound wave in air be polarized? Explain.Ch. 1 - No light passes through two perfect polarizing...Ch. 1 - Explain what happens to the energy carried by...Ch. 1 - When particles scattering light are much smaller...Ch. 1 - Using the information given in the preceding...Ch. 1 - When light is reflected at Brewster’s angle from a...Ch. 1 - If you lie on a beach looking at the water with...Ch. 1 - What is the speed of light in water? In glycerine?Ch. 1 - What is the speed of light in air? In crown glass?Ch. 1 - Calculate the index of refraction for a medium in...Ch. 1 - In what substance in Table 1.1 is the speed of...Ch. 1 - There was a major collision of an asteroid with...Ch. 1 - Components of some computers communicate with each...Ch. 1 - Compare the time it takes for light to travel 1000...Ch. 1 - How far does light travel underwater during a time...Ch. 1 - Suppose a man stands in front of a mm-or as show...Ch. 1 - Show that when light reflects from two mirrors...Ch. 1 - On the Moon’s surface, lunar astronauts placed a...Ch. 1 - A flat mirror Is neither converging nor diverging....Ch. 1 - A light beam in air has an angle of incidence of...Ch. 1 - A light beam in air is incident on the surface of...Ch. 1 - When a light ray crosses from water into glass, it...Ch. 1 - A pencil flashlight submerged in water sends a...Ch. 1 - Light rays from the Sun make a 30° angle to the...Ch. 1 - The path of a light beam in air goes from an angle...Ch. 1 - A scuba diver training in a pool looks at his...Ch. 1 - (a) Using information in the preceding problem,...Ch. 1 - Verify that the critical angle for light going...Ch. 1 - (a) At the end of Example 1.4, it was stated that...Ch. 1 - An optical fiber uses flint glass clad with crown...Ch. 1 - At that minimum angle will you get total internal...Ch. 1 - Suppose you are using total internal reflection to...Ch. 1 - You can determine the index of refraction of a...Ch. 1 - A ray of light, emitted beneath the surface of an...Ch. 1 - Light rays fall normally on the vertical surface...Ch. 1 - (a) What is the ratio of the speed of red light to...Ch. 1 - A beam of white light goes from air into water at...Ch. 1 - By how much do the critical angles for red (660...Ch. 1 - (a) A narrow beam of light containing yellow (580...Ch. 1 - A parallel beam of light containing orange (610...Ch. 1 - A ray of 610-nm light goes from air into fused...Ch. 1 - A narrow beam of light containing red (660 nm) and...Ch. 1 - A narrow beam of white light enters a prism made...Ch. 1 - What angle is needed between the direction of...Ch. 1 - The angle been the axes of two polarizing filters...Ch. 1 - Two polarizing sheets P1 and P2 are placed...Ch. 1 - Suppose that in the preceding problem the light...Ch. 1 - If you have completely polarized light of...Ch. 1 - What angle would the axis of a polarizing filter...Ch. 1 - At the end of Example 17, it was stated that the...Ch. 1 - Show that if you have three polarizing filters,...Ch. 1 - Three polarizing sheets are placed together such...Ch. 1 - In order to rotate the polarization axis of a beam...Ch. 1 - It is found that when light traveling in water...Ch. 1 - At what angle ill lig1t reflected from diamond be...Ch. 1 - What is Brewster’s angle for light traveling in...Ch. 1 - A scuba diver sees light reflected from the...Ch. 1 - From his measurements, Roemer estimated that it...Ch. 1 - Cornu performed Fizeau’s measurement of the speed...Ch. 1 - Suppose you have an unknown clear substance...Ch. 1 - Shown below is a ray of light going from air...Ch. 1 - Considering the previous problem, show that 3is...Ch. 1 - At what angle is light inside crown glass...Ch. 1 - Light reflected at 55.6° from a window is...Ch. 1 - (a) Light reflected at 62.5° from a gemstone in a...Ch. 1 - If bis Brewster’s angle for light reflected from...Ch. 1 - Unreasonable results Suppose light travels from...Ch. 1 - Unreasonable results Light traveling from water to...Ch. 1 - If a polarizing filter reduces the intensity of...Ch. 1 - Suppose you put on two pairs of polarizing...Ch. 1 - (a) On a day when the intensity of sunlight is...Ch. 1 - Light shows staged with lasers use moving mirrors...Ch. 1 - Consider sunlight entering Earth’s atmosphere at...Ch. 1 - A light ray entering an optical fiber surrounded...Ch. 1 - A light ray falls on the left face of a prism (see...Ch. 1 - If the apex angle in the previous problem is 20.0°...Ch. 1 - The light incident on polarizing sheet P1is...Ch. 1 - Prove that if I is the intensity of light...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
51. I A tennis player hits a ball 2.0 m above the ground. The ball leaves his racquet with a speed of 20.0 m/s ...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
2. Whether an allele is dominant or recessive depends on
a. how common the allele is, relative to other alleles...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
4. Three groups of nonvascular plants are _______, ______, and _______. Three groups of seedless vascular plant...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Your bore cells, muscle cells, and skin cells look different because a. different kinds of genes are present in...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
What percentage of Earths land surface do glaciers presently cover? ____________
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
1. Why is the quantum-mechanical model of the atom important for understanding chemistry?
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- pls help on thesearrow_forward20. Two small conducting spheres are placed on top of insulating pads. The 3.7 × 10-10 C sphere is fixed whie the 3.0 × 107 C sphere, initially at rest, is free to move. The mass of each sphere is 0.09 kg. If the spheres are initially 0.10 m apart, how fast will the sphere be moving when they are 1.5 m apart?arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward
- 19. Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain above sea level, has a peak of 8849 m above sea level. Assume that sea level defines the height of Earth's surface. (re = 6.38 × 106 m, ME = 5.98 × 1024 kg, G = 6.67 × 10 -11 Nm²/kg²) a. Calculate the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point at the peak of Mount Everest. b. What is the ratio of the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point 644416m below the surface of the Earth to a point at the top of Mount Everest? C. A tourist watching the sunrise on top of Mount Everest observes a satellite orbiting Earth at an altitude 3580 km above his position. Determine the speed of the satellite.arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward
- 6. As the distance between two charges decreases, the magnitude of the electric potential energy of the two-charge system: a) Always increases b) Always decreases c) Increases if the charges have the same sign, decreases if they have the opposite signs d) Increases if the charges have the opposite sign, decreases if they have the same sign 7. To analyze the motion of an elastic collision between two charged particles we use conservation of & a) Energy, Velocity b) Momentum, Force c) Mass, Momentum d) Energy, Momentum e) Kinetic Energy, Potential Energyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Convex and Concave Lenses; Author: Manocha Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CJ6aB5ULqa0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY