
Concept explainers
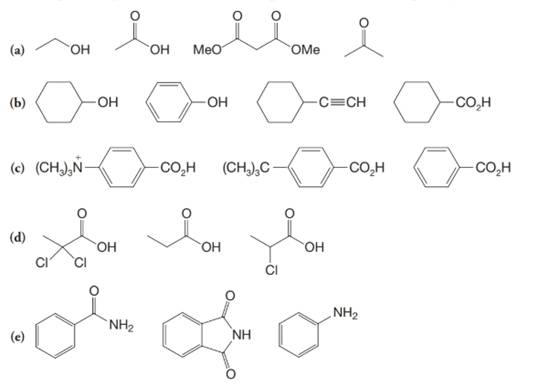
Arrange the compounds of each of the following series in order of increasing acidity:
Interpretation:
The compounds of each of the given series are to be arranged in order of increasing acidity.
Concept introduction:
Acidity depends on the
Resonance structures are the structures in which two or more possible electron structures are drawn. In the resonance structure, the position of the atoms is the same but position of the electrons is different.
Resonance causes delocalization of electron pairs, which increases the stability of the base.
Answer to Problem 1P
Solution:
(a)
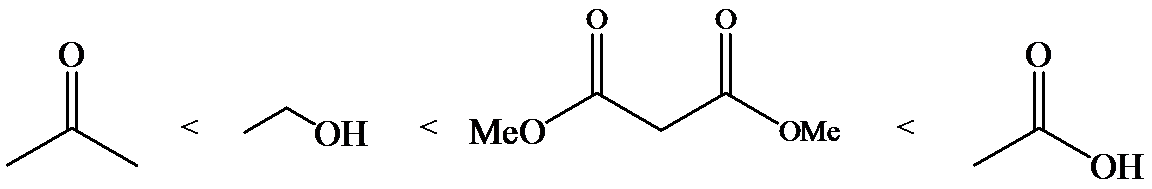
(b)
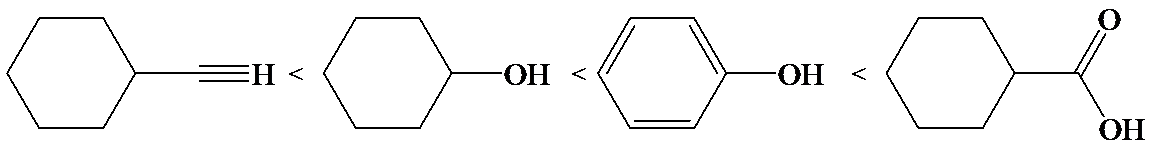
(c)

(d)
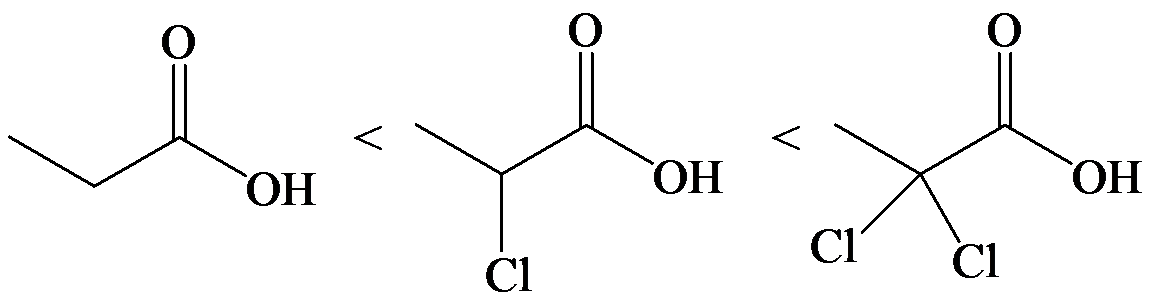
(e)
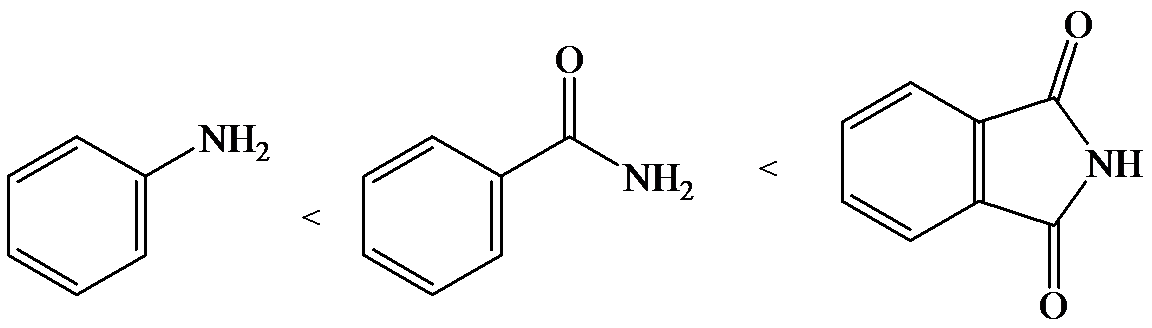
Explanation of Solution
a)
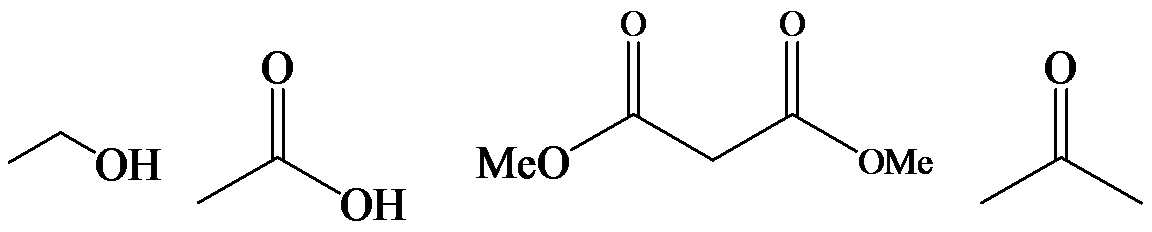
The α-hydrogen atoms of carbonyl groups are acidic. The acidity arises from the electron withdrawing effect of the carbonyl and resonance stabilization of its conjugate base. The electron donating effect of 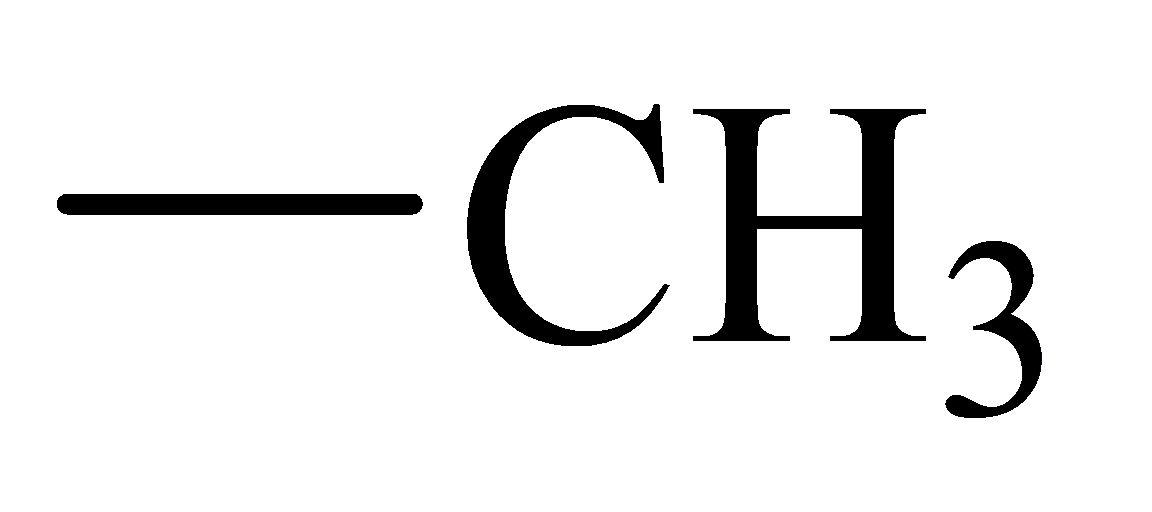 groups tends to destabilize anions. In diketone, there is an active methylene, adjacent to two carbonyl groups. This indicates more resonance stabilization. The charge of anion can be delocalized to both oxygen atoms. The hydroxyl proton in carboxylic acid is an α-proton. On comparing the acidity of carboxylic acids and alcohols, alcohol is less acidic than carboxylic acid.
groups tends to destabilize anions. In diketone, there is an active methylene, adjacent to two carbonyl groups. This indicates more resonance stabilization. The charge of anion can be delocalized to both oxygen atoms. The hydroxyl proton in carboxylic acid is an α-proton. On comparing the acidity of carboxylic acids and alcohols, alcohol is less acidic than carboxylic acid.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:
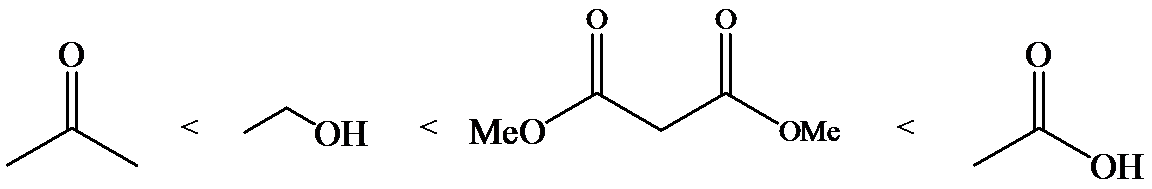
b)
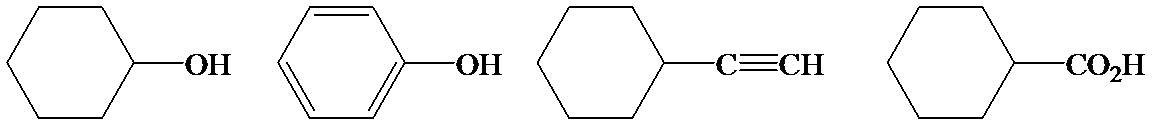
Phenol is more acidic than cyclohexanol because the resonance stabilization in both is different.
In the case of cyclohexane carboxylic acid, negative charge is shared between two different oxygen atoms making it more stabilized than phenoxide. Hence, the removal of proton from cyclohexane carboxylic acid is easier than phenol, making it more acidic than phenol.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:
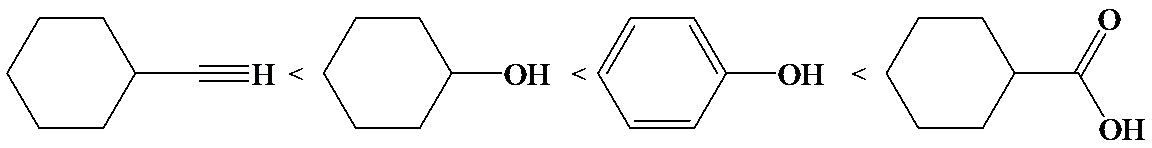
c)
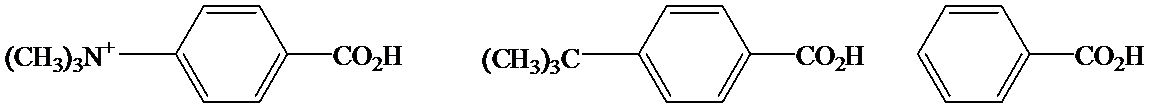
In the case of carboxylic acids, electron substituents increase acidity by inductive electron donation. The electron-donating tert-butyl group destabilizes the conjugate base of benzoic acid, making it less acidic.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:

d)
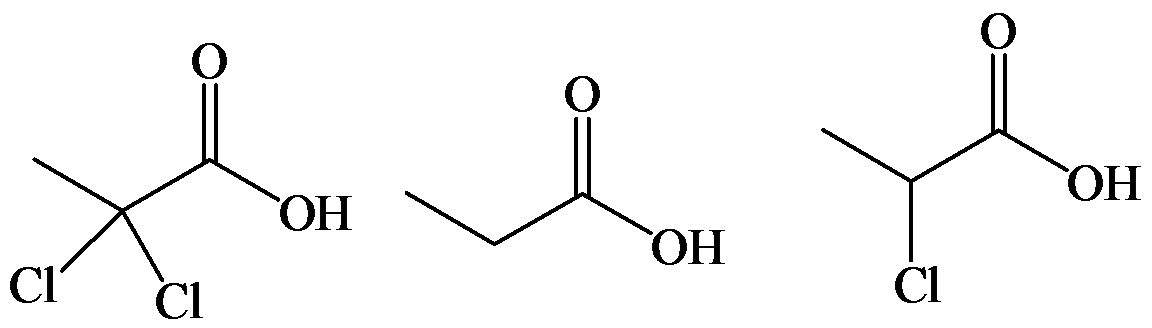
The electron-withdrawing chloro groups increase the acidity of carboxylic acid by increasing the stability of the carboxylate ion. Hence, the carboxylic acid with more chloro groups is more acidic.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:
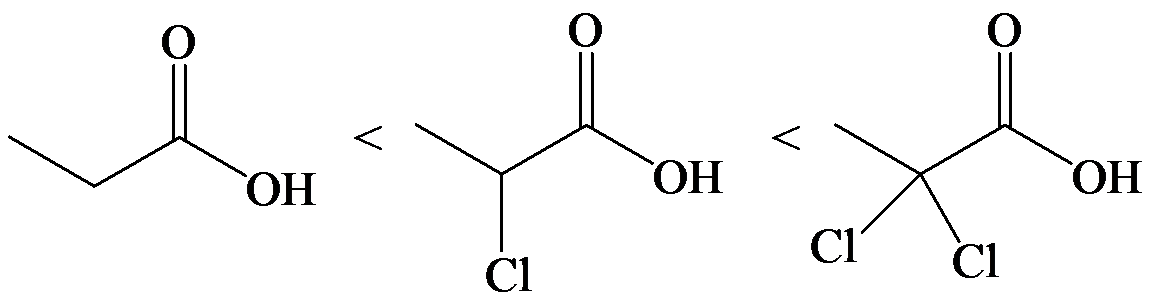
e)

The lone pair electron in aniline is localized on the nitrogen atom, whereas onbenzamide, it is delocalized between oxygen and nitrogen via resonance. Therefore, benzamide is more acidic than aniline.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:
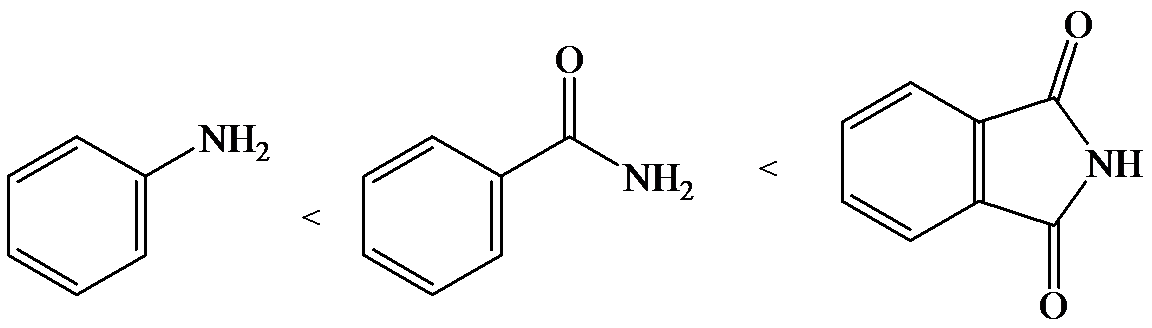
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter SRP Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- V Biological Macromolecules Drawing the Haworth projection of an aldose from its Fischer projection Draw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H C=O HO H HO H H OH CH₂OH Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardComplete the mechanismarrow_forwardComplete the mechanismarrow_forward
- 8 00 6 = 10 10 Decide whether each of the molecules in the table below is stable, in the exact form in which it is drawn, at pH = 11. If you decide at least one molecule is not stable, then redraw one of the unstable molecules in its stable form below the table. (If more than unstable, you can pick any of them to redraw.) Check OH stable HO stable Ounstable unstable O OH stable unstable OH 80 F6 F5 stable Ounstable X Save For Later Sub 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C ཀྭ་ A F7 매 F8 F9 4 F10arrow_forwardJust try completing it and it should be straightforward according to the professor and TAs.arrow_forwardThe grading is not on correctness, so if you can just get to the correct answers without perfectionism that would be great. They care about the steps and reasoning and that you did something. I asked for an extension, but was denied the extension.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

