
Organic Chemistry
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781118875766
Author: T. W. Graham Solomons, Craig B. Fryhle, Scott A. Snyder
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter SRP, Problem 27P
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The structure of the intermediate compound from A to M is to be written and the intermediate formed by the reaction of compound D with N-Bromo succinimide, the stereoisomer of Dianeackerone, are to be represented.
Concept introduction:
Dianeackerone consists of nineteen atoms of carbon, thirty atoms of hydrogen and one tom of oxygen due to which its molecular formula is 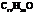 . The IUPAC name of this compound is
. The IUPAC name of this compound is 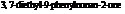 . It is a natural product and has a volatile behavior. It has both
. It is a natural product and has a volatile behavior. It has both 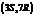 and
and 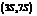 stereoisomers.
stereoisomers.
N-Bromo succinimide, also known as NBS, is a type of brominating agent, which is used as a source of bromine in many reactions.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please help me answer these three questions. Required info should be in data table.
Draw the major organic substitution product or products for (2R,3S)-2-bromo-3-methylpentane reacting with the given
nucleophile. Clearly drawn the stereochemistry, including a wedged bond, a dashed bond and two in-plane bonds at each
stereogenic center. Omit any byproducts.
Bri
CH3CH2O-
(conc.)
Draw the major organic product or products.
Tartaric acid (C4H6O6) is a diprotic weak acid. A sample of 875 mg tartaric acid are dissolved in 100 mL water and titrated with 0.994 M NaOH.
How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the first equivalence point?
How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the second equivalence point?
Chapter SRP Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. SRP - 1. Arrange the compounds of each of the following...Ch. SRP - 2. Arrange the compounds of each of the following...Ch. SRP - Predict the final product from each of the...Ch. SRP - Prob. 4PCh. SRP - Write detailed mechanisms for each of the...Ch. SRP - Prob. 6PCh. SRP - Prob. 7PCh. SRP - Prob. 8PCh. SRP - Prob. 9PCh. SRP - Give stereochemical structures for compounds AD:
Ch. SRP - Prob. 11PCh. SRP - The remaining steps in the industrial synthesis of...Ch. SRP - Prob. 13PCh. SRP - Prob. 14PCh. SRP - Prob. 15PCh. SRP - Prob. 16PCh. SRP - 17. Show how you would modify the synthesis given...Ch. SRP - Prob. 18PCh. SRP - Give structures for compounds AD. Compound D gives...Ch. SRP - The tranquilizing drug meprobamate (Equanil or...Ch. SRP - Prob. 21PCh. SRP - 22. Outlined here is the synthesis of a central...Ch. SRP - 23. What are compounds A and B? Compound B has a...Ch. SRP - Prob. 24PCh. SRP - 25. The Dow process for synthesizing phenol, which...Ch. SRP - Prob. 26PCh. SRP - Prob. 27PCh. SRP - 28. Compound Y shows prominent IR absorption...Ch. SRP - Prob. 29PCh. SRP - Consider this reaction involving peracetic acid:...Ch. SRP - 31. A compound (N) with the molecular formula...Ch. SRP - 32. Compound X is insoluble in aqueous sodium...Ch. SRP - Write the structures of the three products...Ch. SRP - Compound C (C9H11NO) gives a positive Tollens test...Ch. SRP - A compound X (C10H14O) dissolves in aqueous sodium...Ch. SRP - Compound Z (C5H10O) decolorizes bromine. The IR...Ch. SRP - 37. Compound W was isolated from a marine annelid...Ch. SRP - 38. Phenols generally are not changed on treatment...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Including activity, calculate the solubility of Pb(IO3)2 in a matrix of 0.020 M Mg(NO3)2.arrow_forwardIncluding activity coefficients, find [Hg22+] in saturated Hg2Br2 in 0.00100 M KBr.arrow_forwardIncluding activity, calculate the pH of a 0.010 M HCl solution with an ionic strength of 0.10 M.arrow_forward
- Can I please get the graph 1: Concentration vs. Density?arrow_forwardOrder the following series of compounds from highest to lowest reactivity to electrophilic aromatic substitution, explaining your answer: 2-nitrophenol, p-Toluidine, N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide, 4-methylbenzonitrile, 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile.arrow_forwardOrdene la siguiente serie de compuestos de mayor a menor reactividad a la sustitución aromática electrofílica, explicando su respuesta: ácido bencenosulfónico, fluorobenceno, etilbenceno, clorobenceno, terc-butilbenceno, acetofenona.arrow_forward
- Can I please get all final concentrations please!arrow_forwardState the detailed mechanism of the reaction of benzene with isopropanol in sulfuric acid.arrow_forwardDo not apply the calculations, based on the approximation of the stationary state, to make them perform correctly. Basta discard the 3 responses that you encounter that are obviously erroneous if you apply the formula to determine the speed of a reaction. For the decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): 2 N2O5(g) · 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 -> NO2 + NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 →> N2O5 (k-1) → NO2 + NO3 → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5 → NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) Give the expression for the acceptable rate. (A). d[N₂O] dt = -1 2k,k₂[N205] k₁+k₂ d[N₂O5] (B). dt =-k₁[N₂O₂] + k₁[NO2][NO3] - k₂[NO2]³ (C). d[N₂O] dt =-k₁[N₂O] + k₁[N205] - K3 [NO] [N205] (D). d[N2O5] =-k₁[NO] - K3[NO] [N₂05] dtarrow_forward
- A 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 20.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forwardFor the decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 NO2 + NO3 (K1) | NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) | NO2 + NO3 NO2 + O2 + NO (k2) | NO + N2O51 NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) → Give the expression for the acceptable rate. → → (A). d[N205] dt == 2k,k₂[N₂O₂] k₁+k₁₂ (B). d[N2O5] =-k₁[N₂O] + k₁[NO₂] [NO3] - k₂[NO₂]³ dt (C). d[N2O5] =-k₁[N₂O] + k [NO] - k₂[NO] [NO] d[N2O5] (D). = dt = -k₁[N2O5] - k¸[NO][N₂05] dt Do not apply the calculations, based on the approximation of the stationary state, to make them perform correctly. Basta discard the 3 responses that you encounter that are obviously erroneous if you apply the formula to determine the speed of a reaction.arrow_forwardFor the decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 NO2 + NO3 (K1) | NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) | NO2 + NO3 NO2 + O2 + NO (k2) | NO + N2O51 NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) → Give the expression for the acceptable rate. → → (A). d[N205] dt == 2k,k₂[N₂O₂] k₁+k₁₂ (B). d[N2O5] =-k₁[N₂O] + k₁[NO₂] [NO3] - k₂[NO₂]³ dt (C). d[N2O5] =-k₁[N₂O] + k [NO] - k₂[NO] [NO] d[N2O5] (D). = dt = -k₁[N2O5] - k¸[NO][N₂05] dt Do not apply the calculations, based on the approximation of the stationary state, to make them perform correctly. Basta discard the 3 responses that you encounter that are obviously erroneous if you apply the formula to determine the speed of a reaction.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
