
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The geometry around the nitrogen and boron centers in the addition compound,
Concept Introduction:
VSEPR or valence shell electron pair repulsion theory predicts the shape of the molecules with the use of arrangement of electrons around the central metal atom. Its postulates are as follows:
1. The shape of the molecules is governed by the repulsion between electron pairs situated in the outermost or valence shell of the atoms.
2. A distortion is observed in the shape of the molecules if lone pairs are present in it. These are the electron pairs that do not participate in the
3. The order of repulsion of electron pairs is as follows:
4. Multiple bonds create more repulsion as compared to single bonds.
5. The following table shows the various molecular shapes that match to different number of electron pairs:
The geometry of the molecule is predicted with the help of steric number. The formula to calculate the steric number is as follows:
The least electronegative atom is usually taken to be the central atom.
Answer to Problem 1PQ
Option (A) is the correct one.
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct option:
The formation of
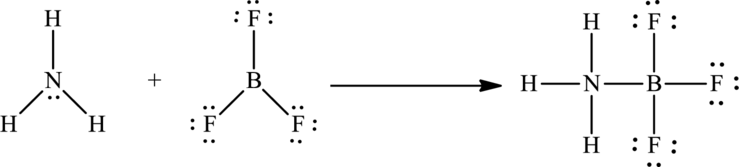
Substitute 4 for atoms bonded to the central atom and 1 for number of lone pairs on the central atom in equation (1) to calculate the steric number of
So the number of electron pairs around nitrogen atom is 4 and no lone pairs are present on it. Therefore the geometry around this atom is tetrahedral according to the VSEPR theory.
Substitute 4 for atoms bonded to the central atom and 1 for number of lone pairs on the central atom in equation (1) to calculate the steric number of
So the number of electron pairs around boron atom is 4 and no lone pairs are present on it. Therefore the geometry around this atom is also tetrahedral according to the VSEPR theory.
Therefore the geometry around both the nitrogen and boron atoms in the addition compound
Reason for incorrect option:
Since geometry around both
The geometry around the nitrogen and boron centers in the addition compound
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter MS Solutions
Preparing for your ACS examination in general chemistry
- Each of the highlighted carbon atoms is connected to hydrogen atoms.arrow_forwardく Complete the reaction in the drawing area below by adding the major products to the right-hand side. If there won't be any products, because nothing will happen under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. Note: if the products contain one or more pairs of enantiomers, don't worry about drawing each enantiomer with dash and wedge bonds. Just draw one molecule to represent each pair of enantiomers, using line bonds at the chiral center. More... No reaction. Explanation Check O + G 1. Na O Me Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2. H + 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility 000 Ar Parrow_forwardDraw a tetramer of this alternating copolymer.arrow_forward
- H I T H HH H -H C. H- Identify and select all structures below that represent a constitutional isomer(s) of the compound shown above. H- H CIH H H H HHHH H H 0 ·H H– 冊 CH CHI HH C- H- H H- H H A. H H C H H- -H HH H B. H- -H D. H H H H • H -H E. -H H H HICH T HHH F. H-arrow_forwardPolylactic acid (shown below) is a biodegradable polymer used for food packaging. Identify the monomer(s) used in the production of this polymer using a condensation process.arrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore small byproducts that would evaporate pleasearrow_forward
- Poly(ethylene adipate) is a biodegradable polyester (shown below). Identify the type of polymerization process used in the production of this polymer.arrow_forwardPolymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. draw two repeat units(dimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. assume there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the dimer. ignore inorganic byproducts pleasearrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction shown below. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forward
- Draw the product of this reaction please. Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardOne of the pi molecular orbitals of 1,3-butadiene (CH2=CHCH=CH2) is shown below. Please identify the number of nodal planes perpendicular to the bonding axisarrow_forwardDraw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer please.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





