
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the structure is to be given.
Concept introduction:
In the
Answer to Problem A.30P
The correct IUPAC name for the structure is
Explanation of Solution
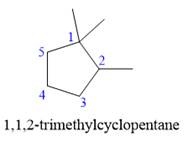
The given structure is
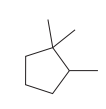
In the structure above, the ring has more carbon atoms than any of the straight chain groups. Hence, the root name of this structure is “cyclopentane.” The carbon atom of this ring, which is attached to two methyl groups, will be numbered as
The correct IUPAC name for the given structure is
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the structure is to be given.
Concept introduction:
In the IUPAC nomenclature, the longest continuous carbon chain or the largest carbon ring is considered as the parent chain. The name of this corresponding parent chain/ring will be the root of the molecule’s name. Identify the substituents and add the name of the substituent as a prefix to the left of the root. The number assigned to the carbon that is bonded to the substituent is called the locator number or locant. In case of two or more different substituents, the alphabetical order is considered. Number each carbon atom of the chain sequentially, beginning with
Answer to Problem A.30P
The correct IUPAC name for the structure is
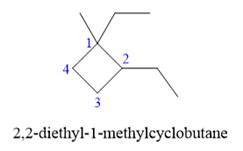
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is
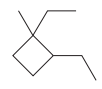
In the above structure, the ring has more carbon atoms than any of the straight chain groups. Hence, the root name of this structure is “cyclobutane.” The carbon atom of this ring, which is attached to two substituents, will be numbered as
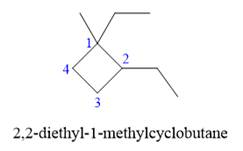
The correct IUPAC name for the given structure is
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the structure is to be given.
Concept introduction:
In the IUPAC nomenclature, the longest continuous carbon chain or the largest carbon ring is considered as the parent chain. The name of this corresponding parent chain/ring will be the root of the molecule’s name. Identify the substituents and add the name of the substituent as a prefix to the left of the root. The number assigned to the carbon that is bonded to the substituent is called the locator number or locant. In case of two or more different substituents, the alphabetical order is considered. Number each carbon atom of the chain sequentially, beginning with
Answer to Problem A.30P
The correct IUPAC name for the structure is
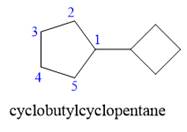
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is
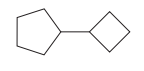
In the structure above, two rings are present. The ring on the left has more number of carbon atoms than the ring on the right; hence the root name of this compound is “cyclopentane.” The carbon atom of this cyclopentane ring to which the cyclobutane ring is attached will be numbered as

The correct IUPAC name for the given structure is
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the structure is to be given.
Concept introduction:
In the IUPAC nomenclature, the longest continuous carbon chain or the largest carbon ring is considered as the parent chain. The name of this corresponding parent chain/ring will be the root of the molecule’s name. Identify the substituents and add the name of the substituent as a prefix to the left of the root. The number assigned to the carbon that is bonded to the substituent is called the locator number or locant. In case of two or more different substituents, the alphabetical order is considered. Number each carbon atom of the chain sequentially, beginning with
Answer to Problem A.30P
The correct IUPAC name for the structure is
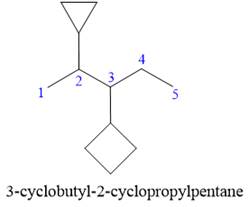
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is
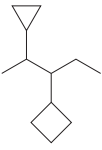
In the structure above, there are two rings and a straight chain of carbon atoms. Out of these, the straight continuous carbon chain has more atoms than any of the rings. Hence, the straight chain carbon will serve as the parent, and the two rings will serve as substituents. Thus, the root name of this structure is “pentane.” The numbering of this parent chain should start from the left as the substituent encountered receives the lowest possible locator number. The two substituents are attached on the
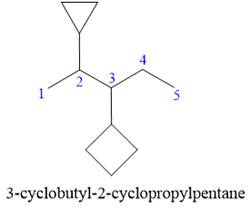
The correct IUPAC name for the given structure is
(e)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the structure is to be given.
Concept introduction:
In the IUPAC nomenclature, the longest continuous carbon chain or the largest carbon ring is considered as the parent chain. The name of this corresponding parent chain/ring will be the root of the molecule’s name. Identify the substituents and add the name of the substituent as a prefix to the left of the root. The number assigned to the carbon that is bonded to the substituent is called the locator number or locant. In case of two or more different substituents, the alphabetical order is considered. Number each carbon atom of the chain sequentially, beginning with
Answer to Problem A.30P
The correct IUPAC name for the structure is
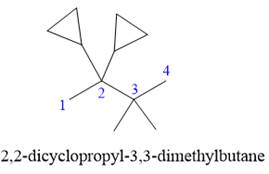
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is
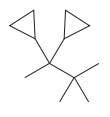
In the structure above, the straight continuous chain of carbon atoms will serve as the parent as it contains the highest number of carbon atoms than the rings. Hence, the root name of this structure is “butane.” There are two types of substituents attached- cyclopropyl and methyl. As the prefix “cyclo” is considered while naming, it will appear first in the IUPAC name. Thus, the numbering will also start from the left so that the carbon atom with two cyclopropyl rings will get the lowest possible locator numbers. The prefix di will be used for both the substituents as they appear twice. Thus, the IUPAC name for this structure is
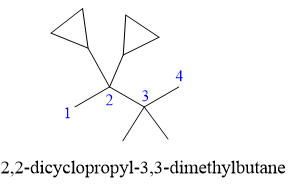
The correct IUPAC name for the given structure is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter A Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms: Study Guide/solutions Manual (second)
- Assign these C-NMR and H-NMR Spectrumarrow_forwardPredict the product of this organic reaction: IZ + HO i P+H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of P. If there is no reasonable possibility for P, check the No answer box under the drawing area. No Answer Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ☐ :arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: 0 O ----- A + KOH ? CH3-CH2-C-O-CH2-C-CH3 Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. X ⑤ èarrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: O CH3 + H2O + HCI A A? CH3-CH2-C-N-CH3 Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No Reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? R+ HO-C-CH2-CH3 0= CH3 CH3 —CH, C−NH—CH CH3 + H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume no products other than those shown above are formed. No Answer Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. €arrow_forward个 CHEM&131 9267 - $25 - Intro to Mail - Hutchison, Allison (Student x Aktiv Learnin https://app.aktiv.com Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. + Na2Cr2O7 Acetone, H2SO4 Type here to search Dryng OH W Prarrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: OH + NaOH A? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ✓ Sarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: CH3-C-O-CH2-CH2-C-CH3 + H₂O ? A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. :☐ darrow_forwardDE d. Draw an arrow pushing mechanism for the following IN O CI N fo 人 P Polle DELL prt sc home end ins F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12arrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: + H₂O H* ? A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No Reaction Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardPredict the major organic products of the reaction below and draw them on right side of the arrow. If there will be no significant reaction, check the box below the drawing area instead. C Cl CH, OH There will be no significant reaction. + pyridine G Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? H R+ H2O Δ OH 0= CH3-CH-O-CH3 + CH3-C-OH Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. No Answer Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. dyarrow_forward
