
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780073398242
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., David Mazurek, Phillip J. Cornwell, Brian Self
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9.5, Problem 9.116P
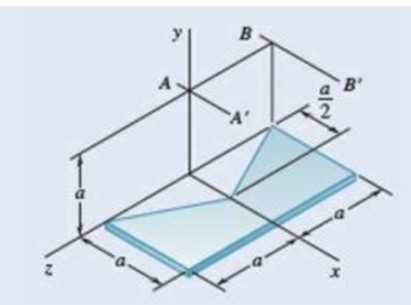
Fig. P9.115 and P9.116
9.116 A piece of thin, uniform sheet metal is cut to form the machine component shown. Denoting the mass of the component by m, determine its mass moment of inertia with respect to (a) the axis AA′, (b) the axis BB′, where the AA′ and BB′ axes are parallel to the x axis and lie in a plane parallel to and at a distance a above the xz plane.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
turbomachienery
auto controls
auto controls
Chapter 9 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Ch. 9.1 - 9.1 through 9.4 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.1 - 9.1 through 9.4 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 9.3PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 9.4PCh. 9.1 - 9.5 through 9.8 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.1 - 9.5 through 9.8 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 9.7PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 9.8PCh. 9.1 - 9.9 through 9.11 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 9.10P
Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 9.11PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 9.12PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 9.13PCh. 9.1 - 9.12 through 9.14 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 9.15PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 9.16PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 9.17PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 9.18PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 9.19PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 9.20PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 9.21PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 9.22PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 9.23PCh. 9.1 - 9.23 and 9.24 Determine the polar moment of...Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 9.25PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 9.26PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 9.27PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 9.28PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 9.29PCh. 9.1 - Prove that the centroidal polar moment of inertia...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 9.31PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.32PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.33PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.34PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.35PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.36PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.37PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.38PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.39PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.40PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.41PCh. 9.2 - 9.41 through 9.44 Determine the moments of inertia...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 9.43PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.44PCh. 9.2 - 9.45 and 9.46 Determine the polar moment of...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 9.46PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.47PCh. 9.2 - 9.47 and 9.48 Determine the polar moment of...Ch. 9.2 - 9.49 Two channels and two plates are used to form...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 9.50PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.51PCh. 9.2 - Two 20-mm steel plates are welded to a rolled S...Ch. 9.2 - A channel and a plate are welded together as shown...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 9.54PCh. 9.2 - Two L76 76 6.4-mm angles are welded to a C250 ...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 9.56PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.57PCh. 9.2 - 9.57 and 9.58 The panel shown forms the end of a...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 9.59PCh. 9.2 - 9.60 The panel shown forms the end of a trough...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 9.61PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.62PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.63PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.64PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.65PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9.66PCh. 9.3 - 9.67 through 9.70 Determine by direct integration...Ch. 9.3 - Prob. 9.68PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 9.69PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 9.70PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 9.71PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 9.72PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 9.73PCh. 9.3 - 9.71 through 9.74 Using the parallel-axis theorem,...Ch. 9.3 - Prob. 9.75PCh. 9.3 - 9.75 through 9.78 Using the parallel-axis theorem,...Ch. 9.3 - Prob. 9.77PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 9.78PCh. 9.3 - Determine for the quarter ellipse of Prob. 9.67...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the moments of inertia and the product...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the moments of inertia and the product...Ch. 9.3 - 9.75 through 9.78 Using the parallel-axis theorem,...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the moments of inertia and the product...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the moments of inertia and the product...Ch. 9.3 - Prob. 9.85PCh. 9.3 - 9.86 through 9.88 For the area indicated,...Ch. 9.3 - Prob. 9.87PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 9.88PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 9.89PCh. 9.3 - 9.89 and 9.90 For the angle cross section...Ch. 9.4 - Using Mohrs circle, determine for the quarter...Ch. 9.4 - Using Mohrs circle, determine the moments of...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 9.93PCh. 9.4 - Using Mohrs circle, determine the moments of...Ch. 9.4 - Using Mohrs circle, determine the moments of...Ch. 9.4 - Using Mohrs circle, determine the moments of...Ch. 9.4 - For the quarter ellipse of Prob. 9.67, use Mohrs...Ch. 9.4 - 9.98 though 9.102 Using Mohrs circle, determine...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 9.99PCh. 9.4 - 9.98 though 9.102 Using Mohrs circle, determine...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 9.101PCh. 9.4 - Prob. 9.102PCh. 9.4 - Prob. 9.103PCh. 9.4 - 9.104 and 9.105 Using Mohrs circle, determine the...Ch. 9.4 - 9.104 and 9.105 Using Mohrs circle, determine the...Ch. 9.4 - For a given area, the moments of inertia with...Ch. 9.4 - it is known that for a given area Iy = 48 106 mm4...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 9.108PCh. 9.4 - Prob. 9.109PCh. 9.4 - Prob. 9.110PCh. 9.5 - A thin plate with a mass m is cut in the shape of...Ch. 9.5 - A ring with a mass m is cut from a thin uniform...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 9.113PCh. 9.5 - The parabolic spandrel shown was cut from a thin,...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 9.115PCh. 9.5 - Fig. P9.115 and P9.116 9.116 A piece of thin,...Ch. 9.5 - 9.117 A thin plate with a mass m has the...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 9.118PCh. 9.5 - 9.119 Determine by direct integration the mass...Ch. 9.5 - The area shown is revolved about the x axis to...Ch. 9.5 - 9.121 The area shown is revolved about the x axis...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 9.122PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 9.123PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 9.124PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 9.125PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 9.126PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 9.127PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 9.128PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 9.129PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 9.130PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 9.131PCh. 9.5 - The cups and the arms of an anemometer are...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 9.133PCh. 9.5 - Determine the mass moment of inertia of the 0.9-lb...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 9.135PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 9.136PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 9.137PCh. 9.5 - A section of sheet steel 0.03 in. thick is cut and...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 9.139PCh. 9.5 - A farmer constructs a trough by welding a...Ch. 9.5 - The machine element shown is fabricated from...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the mass moments of inertia and the...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the mass moment of inertia of the steel...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 9.144PCh. 9.5 - Determine the mass moment of inertia of the steel...Ch. 9.5 - Aluminum wire with a weight per unit length of...Ch. 9.5 - The figure shown is formed of 18-in.-diameter...Ch. 9.5 - A homogeneous wire with a mass per unit length of...Ch. 9.6 - Determine the mass products of inertia Ixy, Iyz,...Ch. 9.6 - Determine the mass products of inertia Ixy, Iyz,...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 9.151PCh. 9.6 - Determine the mass products of inertia Ixy, Iyz,...Ch. 9.6 - 9.153 through 9.156 A section of sheet steel 2 mm...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 9.154PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.155PCh. 9.6 - 9.153 through 9.156 A section of sheet steel 2 mm...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 9.157PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.158PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.159PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.160PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.161PCh. 9.6 - For the homogeneous tetrahedron of mass m shown,...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 9.163PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.164PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.165PCh. 9.6 - Determine the mass moment of inertia of the steel...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 9.167PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.168PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.169PCh. 9.6 - 9.170 through 9.172 For the wire figure of the...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 9.171PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.172PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.173PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.174PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.175PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.176PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.177PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.178PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.179PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.180PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.181PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.182PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.183PCh. 9.6 - Prob. 9.184PCh. 9 - Determine by direct integration the moments of...Ch. 9 - Determine the moment of inertia and the radius of...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.187RPCh. 9 - Prob. 9.188RPCh. 9 - Prob. 9.189RPCh. 9 - Two L4 4 12-in. angles are welded to a steel...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.191RPCh. 9 - Prob. 9.192RPCh. 9 - Prob. 9.193RPCh. 9 - Prob. 9.194RPCh. 9 - Prob. 9.195RPCh. 9 - Determine the mass moment of inertia of the steel...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1 Pleasearrow_forwardA spring cylinder system measures the pressure. Determine which spring can measure pressure between 0-1 MPa with a large excursion. The plate has a diameter of 20 mm. Also determine the displacement of each 0.1 MPa step.Spring power F=c x fF=Springpower(N)c=Spring constant (N/mm)f=Suspension (mm) How do I come up with right answer?arrow_forwardA lift with a counterweight is attached to the ceiling. The attachment is with 6 stainless and oiled screws. What screw size is required? What tightening torque? - The lift weighs 500 kg and can carry 800 kg. - Counterweight weight 600 kg - Durability class 12.8 = 960 MPa- Safety factor ns=5+-Sr/Fm= 0.29Gr =0.55arrow_forward
- Knowing that a force P of magnitude 750 N is applied to the pedal shown, determine (a) the diameter of the pin at C for which the average shearing stress in the pin is 40 MPa, (b) the corresponding bearing stress in the pedal at C, (c) the corresponding bearing stress in each support bracket at C. 75 mm 300 mm- mm A B P 125 mm 5 mm C Darrow_forwardAssume the B frame differs from the N frame through a 90 degree rotation about the second N base vector. The corresponding DCM description is: 1 2 3 4 5 6 9 # adjust the return matrix values as needed def result(): dcm = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] return dcmarrow_forwardFind the reaction at A and B The other response I got was not too accurate,I need expert solved answer, don't use Artificial intelligence or screen shot it solvingarrow_forward
- A six cylinder petrol engine has a compression ratio of 5:1. The clearance volume of each cylinder is 110CC. It operates on the four-stroke constant volume cycle and the indicated efficiency ratio referred to air standard efficiency is 0.56. At the speed of 2400 rpm. 44000KJ/kg. Determine the consumes 10kg of fuel per hour. The calorific value of fuel average indicated mean effective pressure.arrow_forwardThe members of a truss are connected to the gusset plate as shown in (Figure 1). The forces are concurrent at point O. Take = 90° and T₁ = 7.5 kN. Part A Determine the magnitude of F for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. F= 7.03 Submit ? kN Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 21 attempts remaining ▾ Part B Determine the magnitude of T2 for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure T₂ = 7.03 C T2 |? KN Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 23 attempts remaining Provide Feedbackarrow_forwardConsider the following acid-base reaction: Fe3+(aq) +3H2O -Fe(OH)3 (s) + 3H* ← A. Using thermodynamics, calculate the equilibrium constant K at 25°C (The AG° of formation of Fe(OH)3(s) is -699 kJ/mol). B. Using the value of K you calculated in part a, if a solution contains 10-4 M Fe3+ and has a pH of 7.5, will Fe(OH)3(s) precipitate? Show all calculations necessary to justify your answer. Note that the reaction as written is for precipitation, not dissolution like Ksp-arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
moment of inertia; Author: NCERT OFFICIAL;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=A4KhJYrt4-s;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY