
Mechanics of Materials
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780133254426
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Prentice Hall
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9.3, Problem 9.22P
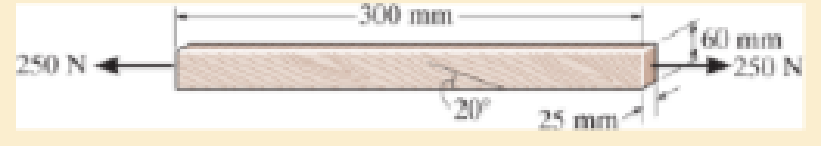
The grains of wood in the board make an angle of 20° with the horizontal as shown. Determine the normal and shear stress that act perpendicular and parallel to the grains if the board is subjected to an axial load of 250 N.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Water enters the rigid, covered tank shown in Figure P3.2 with a volumetric flow rate of 0.32L/s. The water line has an inside diameter of 6.3 cm. The air vent on the tank has an inside diameterof 4.5 cm. The water is at a temperature of 30°C and the air in the tank is at atmospheric pressure(1 atm) and 30°C. Determine the air velocity leaving the vent at the instant shown in the figure
Using method of sections, determine the force in member
BC, HC, and HG. State if these members are in tension or
compression.
2 kN
A
5 kN
4 kN
4 kN
3 kN
H
B
C
D
E
3 m
F
2 m
-5 m 5 m-
G
5 m 5 m-
Determine the normal stresses σn and σt and the shear stress τnt at this point if they act on the rotated stress element shown
Chapter 9 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials
Ch. 9.3 - In each case, the state of stress x, y, xy...Ch. 9.3 - Given the state of stress shown on the element,...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the normal stress and shear stress...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - Also, find the corresponding orientation of the...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the maximum principal stress at point B.Ch. 9.3 - Determine the principal stress at point C.Ch. 9.3 - Prove that the sum of the normal stresses x + y =...Ch. 9.3 - 9-2. The state of stress at a point in a member is...
Ch. 9.3 - Determine the stress components acting on the...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the normal stress and shear stress...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the normal stress and shear stress...Ch. 9.3 - 9-6. Determine the normal stress and shear stress...Ch. 9.3 - 9-7. Determine the normal stress and shear stress...Ch. 9.3 - *9-8. Determine the equivalent state of stress on...Ch. 9.3 - 9-9. Determine the equivalent state of stress on...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent slate of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - *9-12. Determine the equivalent state of stress on...Ch. 9.3 - 9-13. Determine the equivalent state of stress on...Ch. 9.3 - 9-14. The state of stress at a point is shown on...Ch. 9.3 - The state of stress at a point is shown on the...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - A point on a thin plate is subjected to the two...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - *9-20. Planes AB and BC at a point are subjected...Ch. 9.3 - The stress acting on two planes at a point is...Ch. 9.3 - The grains of wood in the board make an angle of...Ch. 9.3 - The wood beam is subjected to a load of 12 kN. If...Ch. 9.3 - *9-24. The wood beam is subjected to a load of 12...Ch. 9.3 - 9-25. The wooden block will fail if the shear...Ch. 9.3 - 9-26. The bracket is subjected to the force of 3...Ch. 9.3 - 9-27. The bracket is subjected to the force of 3...Ch. 9.3 - 9-28. The 25-mm thick rectangular bar is subjected...Ch. 9.3 - 9-29. The 3-in. diameter shaft is supported by a...Ch. 9.3 - 9-30. The state of stress at a point in a member...Ch. 9.3 - 9-31. Determine the principal stress at point A on...Ch. 9.3 - 9-32. Determine the maximum in-plane shear stress...Ch. 9.3 - 9-33. The clamp bears down on the smooth surface...Ch. 9.3 - 9-34. Determine the principal stress and the...Ch. 9.3 - 9-35. The square steel plate has a thickness of 10...Ch. 9.3 - *9-36. The square steel plate has a thickness of...Ch. 9.3 - The shaft has a diameter d and is subjected to the...Ch. 9.3 - Prob. 9.38PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 9.39PCh. 9.3 - The wide-flange beam is subjected to the 50-kN...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Pro b. 9-40 for point B located on the web...Ch. 9.3 - Prob. 9.42PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 9.43PCh. 9.4 - Use Mohrs circle to determine the normal stress...Ch. 9.4 - Also, find the corresponding orientation of the...Ch. 9.4 - Draw Mohrs circle and determine the principal...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the principal stresses at a point on the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the principal stresses at point A on the...Ch. 9.4 - Point A is just below the flange.Ch. 9.4 - Solve Prob.93 using Mohrs circle. 93. Determine...Ch. 9.4 - 9-45. Solve Prob. 9-6 using Mohr’s circle.
9-6....Ch. 9.4 - 9-46. Solve Prob. 9-14 using Mohr’s circle.
9-14....Ch. 9.4 - Solve Prob.911 using Mohrs circle. 911. Determine...Ch. 9.4 - *9-48. Solve Prob. 9-12 using Mohr’s...Ch. 9.4 - Solve Prob.916 using Mohrs circle. 916. Determine...Ch. 9.4 - Mohrs circle for the state of stress is shown in...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 9.51PCh. 9.4 - Prob. 9.52PCh. 9.4 - 9-53. Determine the equivalent state of stress if...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 9.54PCh. 9.4 - Prob. 9.55PCh. 9.4 - Prob. 9.56PCh. 9.4 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9.4 - 9-58. Determine the equivalent state of stress if...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 9.59PCh. 9.4 - Prob. 9.60PCh. 9.4 - 9-61. Draw Mohr’s circle that describes each of...Ch. 9.4 - The grains of wood in the board make an angle of...Ch. 9.4 - The post is fixed supported at its base and a...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the principal stresses, the maximum...Ch. 9.4 - The thin-walled pipe has an inner diameter of 0.5...Ch. 9.4 - 9-66. Determine the principal stress and maximum...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 9.67PCh. 9.4 - The rotor shaft of the helicopter is subjected to...Ch. 9.4 - The pedal crank for a bicycle has the cross...Ch. 9.4 - A spherical pressure vessel has an inner radius of...Ch. 9.4 - The cylindrical pressure vessel has an inner...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the normal and shear stresses at point D...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the principal stress at point D, Which...Ch. 9.4 - If the box wrench is subjected to the 50 lb force,...Ch. 9.4 - If the box wrench is subjected to the 50-lb force,...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 9.76PCh. 9.5 - Draw the three Mohrs circles that describe each of...Ch. 9.5 - Draw the three Mohrs circles that describe the...Ch. 9.5 - 9-79. The stress at a point is shown on the...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the principal stresses and the absolute...Ch. 9.5 - 9-81. The stress at a point is shown on the...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the principal stresses and the absolute...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the principal stresses and the absolute...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 9.85PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 9.86PCh. 9.5 - 9-87. Determine the principal stresses and...Ch. 9.5 - *9.88. Determine the principal stresses and...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.89RPCh. 9 - Prob. 9.90RPCh. 9 - Prob. 9.91RPCh. 9 - The steel pipe has an inner diameter of 2.75 in....Ch. 9 - Determine the equivalent state of stress If an...Ch. 9 - The crane is used to support the 350-lb load....Ch. 9 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9 - The propeller shaft of the tugboat is subjected to...Ch. 9 - Determine the principal stresses in the box beam...Ch. 9 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9 - Determine the stress components acting on the...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Why is the study of database technology important?
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
What types of coolant are used in vehicles?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
A byte is made up of eight a. CPUs b. addresses c. variables d. bits
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
How does a computers main memory differ from its auxiliary memory?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
1.2 Explain the difference between geodetic and plane
surveys,
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Using method of joints, determine the force in each member of the truss and state if the members are in tension or compression. A E 6 m D 600 N 4 m B 4 m 900 Narrow_forwardQuestion 5. The diagram below shows a mass suspended from a tie supported by two horizontal braces of equal length. The tie forms an angle "a" of 60° to the horizontal plane, the braces form an angle 0 of 50° to the vertical plane. If the mass suspended is 10 tonnes, and the braces are 10m long, find: a) the force in the tie; & b) the force in the braces Horizontal Braces, Tie Massarrow_forward= MMB 241 Tutorial 2.pdf 1 / 3 75% + + Tutorial z Topic: Kinematics of Particles:-. QUESTIONS 1. Use the chain-rule and find y and ŷ in terms of x, x and x if a) y=4x² b) y=3e c) y = 6 sin x 2. The particle travels from A to B. Identify the three unknowns, and write the three equations needed to solve for them. 8 m 10 m/s 30° B x 3. The particle travels from A to B. Identify the three unknowns, and write the three equations needed to solve for them. A 40 m/s 20 m B 1arrow_forward
- 3 m³/s- 1 md 45° V 1.8 mr 2mrarrow_forward= MMB 241 Tutorial 2.pdf 3/3 75% + + 6. A particle is traveling along the parabolic path y = 0.25 x². If x = 8 m, vx=8 m/s, and ax= 4 m/s² when t = 2 s, determine the magnitude of the particle's velocity and acceleration at this instant. y = 0.25x² -x 7. Determine the speed at which the basketball at A must be thrown at the angle of 30° so that it makes it to the basket at B. 30° -x 1.5 m B 3 m -10 m- 8. The basketball passed through the hoop even though it barely cleared the hands of the player B who attempted to block it. Neglecting the size of the ball, determine the 2arrow_forwardAdhesives distribute loads across the interface, whereas fasteners create areas of localized stresses. True or Falsearrow_forward
- A continuous column flash system is separating 100 kmol/h of a saturated liquid feed that is 45 mol% methanol and 55 mol% water at 1.0 atm. Operate with L/V = 1.5 and the outlet bottoms at xN = 0.28. Find the values of FL, FV, y1, and the number of equilibrium stages required. Find the value of Q used to vaporize FV. For a normal flash with the same feed and the same V/F, find the values of x and y.arrow_forwardA beer still is being used to separate ethanol from water at 1.0 atm. The saturated liquid feed flow rate is F = 840.0 kmol/h. The feed is 44.0 mol% ethanol. The saturated vapor steam is pure water with ratio of steam flow rate S to feed rate, S/F = 2/3. We desire a bottoms product that is 4.0 mol% ethanol. CMO is valid. Find the mole fraction of ethanol in the distillate vapor, yD,E. Find the number of equilibrium stages required. If the feed is unchanged and the S/F ratio is unchanged, but the number of stages is increased to a very large number, what is the lowest bottoms mole fraction of ethanol that can be obtained?arrow_forward3.1 Convert the following base-2 numbers to base-10: (a) 1011001, (b) 110.0101, and (c) 0.01011.arrow_forward
- Consider the forces acting on the handle of the wrench in (Figure 1). a) Determine the moment of force F1={−F1={−2i+i+ 4 jj −−8k}lbk}lb about the zz axis. Express your answer in pound-inches to three significant figures. b) Determine the moment of force F2={F2={3i+i+ 7 jj −−6k}lbk}lb about the zz axis. Express your answer in pound-inches to three significant figures.arrow_forwardI need you to explain each and every step (Use paper)arrow_forwardCalculate the Moment About the Point A -20"- 5 lb 40 N D 1.5 m 40 N 4.5 m A 15 lb. 150 mm 52 N 5 12 100 mm 15 lb. 26 lb. 12 5 34 lb. 13 8 15 77777 36 lb.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
EVERYTHING on Axial Loading Normal Stress in 10 MINUTES - Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jQ-fNqZWrNg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY