
Mechanics of Materials
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780133254426
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Prentice Hall
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9.4, Problem 9.50P
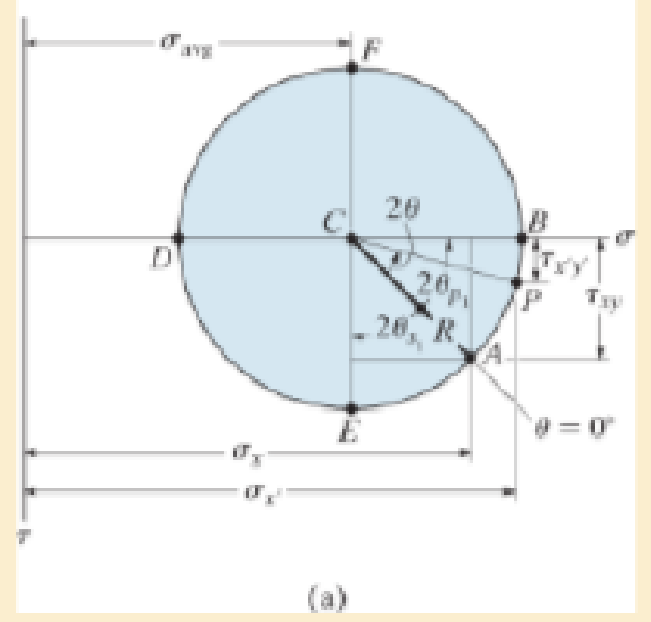
Mohr’s circle for the state of stress is shown in Fig.9–17 a. Show that finding the coordinates of point P (σx′, τx′y′) on the circle gives the same value as the stress transformation Eqs.9–1 and 9–2.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The single degree of freedom (SDOF) system that you studied under free vibration in Assignment #3 - Laboratory Component has been subjected to a strong ground motion. The acceleration at the base (excitation) and the acceleration at the roof (response) of the SDOF system was recorded with sampling rate 50 Hz (50 samples per second, or dt= 0.02 seconds). The file ElCentro.txt includes the two columns of acceleration data. The first column lists the acceleration at the base of the SDOF system. The second column lists the acceleration at the roof of the SDOF system. (a) Plot the time histories of the recorded accelerations at the base and at the roof of the SDOF system. (b) Compute the acceleration, velocity and displacement time histories of the roof of the SDOF system subjected to the recorded base acceleration using the Central Difference method. Plot the accel- eration, velocity and displacement time histories. Plot the restoring force, the damping force, and the inertia force time…
A tensile specimen made of hot-rolled AISI 1020 steel is loaded to point corresponding to a strain of 43%.
60
Su = 66 ksi
Stress σ (ksi)
40 B
20
0
0
0
T
H
Sy = 39 ksi
Se = 36 ksi
Hot-rolled 1020 steel
F
10 20 30 40
50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160
Strain € (%)
T
1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6
Area ratio R
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
Area reduction A,
What value of strain is applicable to this location?
0.6
A tensile specimen made of hot-rolled AISI 1020 steel is loaded to point corresponding to a strain of 40%.
60
Su = 66 ksi
Stress σ (ksi)
S₁ = 39 ksi
40
Se = 36 ksi
Hot-rolled 1020 steel
20
0
10 20 30 40
50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160
Strain € (%)
0
1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5
1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6
Area ratio R
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
Area reduction A,
What value of area ratio is applicable to this location?
0.6
Chapter 9 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials
Ch. 9.3 - In each case, the state of stress x, y, xy...Ch. 9.3 - Given the state of stress shown on the element,...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the normal stress and shear stress...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - Also, find the corresponding orientation of the...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the maximum principal stress at point B.Ch. 9.3 - Determine the principal stress at point C.Ch. 9.3 - Prove that the sum of the normal stresses x + y =...Ch. 9.3 - 9-2. The state of stress at a point in a member is...
Ch. 9.3 - Determine the stress components acting on the...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the normal stress and shear stress...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the normal stress and shear stress...Ch. 9.3 - 9-6. Determine the normal stress and shear stress...Ch. 9.3 - 9-7. Determine the normal stress and shear stress...Ch. 9.3 - *9-8. Determine the equivalent state of stress on...Ch. 9.3 - 9-9. Determine the equivalent state of stress on...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent slate of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - *9-12. Determine the equivalent state of stress on...Ch. 9.3 - 9-13. Determine the equivalent state of stress on...Ch. 9.3 - 9-14. The state of stress at a point is shown on...Ch. 9.3 - The state of stress at a point is shown on the...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - A point on a thin plate is subjected to the two...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - *9-20. Planes AB and BC at a point are subjected...Ch. 9.3 - The stress acting on two planes at a point is...Ch. 9.3 - The grains of wood in the board make an angle of...Ch. 9.3 - The wood beam is subjected to a load of 12 kN. If...Ch. 9.3 - *9-24. The wood beam is subjected to a load of 12...Ch. 9.3 - 9-25. The wooden block will fail if the shear...Ch. 9.3 - 9-26. The bracket is subjected to the force of 3...Ch. 9.3 - 9-27. The bracket is subjected to the force of 3...Ch. 9.3 - 9-28. The 25-mm thick rectangular bar is subjected...Ch. 9.3 - 9-29. The 3-in. diameter shaft is supported by a...Ch. 9.3 - 9-30. The state of stress at a point in a member...Ch. 9.3 - 9-31. Determine the principal stress at point A on...Ch. 9.3 - 9-32. Determine the maximum in-plane shear stress...Ch. 9.3 - 9-33. The clamp bears down on the smooth surface...Ch. 9.3 - 9-34. Determine the principal stress and the...Ch. 9.3 - 9-35. The square steel plate has a thickness of 10...Ch. 9.3 - *9-36. The square steel plate has a thickness of...Ch. 9.3 - The shaft has a diameter d and is subjected to the...Ch. 9.3 - Prob. 9.38PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 9.39PCh. 9.3 - The wide-flange beam is subjected to the 50-kN...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Pro b. 9-40 for point B located on the web...Ch. 9.3 - Prob. 9.42PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 9.43PCh. 9.4 - Use Mohrs circle to determine the normal stress...Ch. 9.4 - Also, find the corresponding orientation of the...Ch. 9.4 - Draw Mohrs circle and determine the principal...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the principal stresses at a point on the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the principal stresses at point A on the...Ch. 9.4 - Point A is just below the flange.Ch. 9.4 - Solve Prob.93 using Mohrs circle. 93. Determine...Ch. 9.4 - 9-45. Solve Prob. 9-6 using Mohr’s circle.
9-6....Ch. 9.4 - 9-46. Solve Prob. 9-14 using Mohr’s circle.
9-14....Ch. 9.4 - Solve Prob.911 using Mohrs circle. 911. Determine...Ch. 9.4 - *9-48. Solve Prob. 9-12 using Mohr’s...Ch. 9.4 - Solve Prob.916 using Mohrs circle. 916. Determine...Ch. 9.4 - Mohrs circle for the state of stress is shown in...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 9.51PCh. 9.4 - Prob. 9.52PCh. 9.4 - 9-53. Determine the equivalent state of stress if...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 9.54PCh. 9.4 - Prob. 9.55PCh. 9.4 - Prob. 9.56PCh. 9.4 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9.4 - 9-58. Determine the equivalent state of stress if...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 9.59PCh. 9.4 - Prob. 9.60PCh. 9.4 - 9-61. Draw Mohr’s circle that describes each of...Ch. 9.4 - The grains of wood in the board make an angle of...Ch. 9.4 - The post is fixed supported at its base and a...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the principal stresses, the maximum...Ch. 9.4 - The thin-walled pipe has an inner diameter of 0.5...Ch. 9.4 - 9-66. Determine the principal stress and maximum...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 9.67PCh. 9.4 - The rotor shaft of the helicopter is subjected to...Ch. 9.4 - The pedal crank for a bicycle has the cross...Ch. 9.4 - A spherical pressure vessel has an inner radius of...Ch. 9.4 - The cylindrical pressure vessel has an inner...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the normal and shear stresses at point D...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the principal stress at point D, Which...Ch. 9.4 - If the box wrench is subjected to the 50 lb force,...Ch. 9.4 - If the box wrench is subjected to the 50-lb force,...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 9.76PCh. 9.5 - Draw the three Mohrs circles that describe each of...Ch. 9.5 - Draw the three Mohrs circles that describe the...Ch. 9.5 - 9-79. The stress at a point is shown on the...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the principal stresses and the absolute...Ch. 9.5 - 9-81. The stress at a point is shown on the...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the principal stresses and the absolute...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the principal stresses and the absolute...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 9.85PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 9.86PCh. 9.5 - 9-87. Determine the principal stresses and...Ch. 9.5 - *9.88. Determine the principal stresses and...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.89RPCh. 9 - Prob. 9.90RPCh. 9 - Prob. 9.91RPCh. 9 - The steel pipe has an inner diameter of 2.75 in....Ch. 9 - Determine the equivalent state of stress If an...Ch. 9 - The crane is used to support the 350-lb load....Ch. 9 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9 - The propeller shaft of the tugboat is subjected to...Ch. 9 - Determine the principal stresses in the box beam...Ch. 9 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9 - Determine the stress components acting on the...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
How does a computers main memory differ from its auxiliary memory?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Write a summary list of the problem-solving steps identified in the chapter, using your own words.
BASIC BIOMECHANICS
This optional Google account security feature sends you a message with a code that you must enter, in addition ...
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
CONCEPT QUESTIONS
15.CQ3 The ball rolls without slipping on the fixed surface as shown. What is the direction ...
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
How is the hydrodynamic entry length defined for flow in a pipe? Is the entry length longer in laminar or turbu...
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A tensile specimen made of hot-rolled AISI 1020 steel is loaded to point corresponding to a strain of 43%. 60 Su = 66 ksi Stress σ (ksi) 20 Sy = 39 ksi Se = 36 ksi Hot-rolled 1020 steel F 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 Strain € (%) 0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Area ratio R 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 Area reduction A, What value of area reduction is applicable to this location? 0.6arrow_forwardTable of Measurements and Results: Reading m/s Ji- a (wh Nu h Re Nu Error% (C) (°C) 2 1 Discussion: 1-Estimate the heat transfer and experimental value of the heat transfer coefficient hex with its unit and Nusselt number Nu expl 2- Find the percentage error for the value of the experimental Nusselt number. 3-Draw the graph showing a relationship between the temperatures difference (T-T) and theoretical and experimental value of Nusselt number. 4-The forced convection heat transfer coefficient of a plate depends on which of the following: a-gravity. b-velocity of fluid. e-conductivity of fluid. d-conductivity of plate material. Experiment: Internal Forced convenction Heat trovate on now through t objectives. Study the convection heat transfer of air flow through stage Calculations. Q & (T-T) Vary Re Q. heup A (TT) (T. Te-T ASPL Nep Re 117 RITT 14 ' 14arrow_forwardIf AE = 1.6 m, ED = CD = 1.9 m and F = 3.1 kN, then find the magnitude of the force acting in EB. B 30° 30° C E D ED m DC m ♥F KNarrow_forward
- Assume multiple single degree of freedom systems with natural periods T ∈ [0.05, 2.00] seconds with in- crement of period dT = 0.05 seconds. Assume three cases of damping ratio: Case (A) ξ = 0%; Case (B) ξ = 2%; Case (C) ξ = 5%. The systems are initially at rest. Thus, the initial conditions are u(t = 0) = 0 and ̇u(t = 0) = 0. The systems are subjected to the base acceleration that was provided in the ElCentro.txt file (i.e., first column). For the systems in Case (A), Case (B), and Case (C) and for each natural period compute the peak acceleration, peak velocity, and peak displacement responses to the given base excitation. Please, use the Newmark method for β = 1/4 (average acceleration) to compute the responses. Create three plots with three lines in each plot. The first plot will have the peak accelerations in y-axis and the natural period of the system in x-axis. The second plot will have the peak velocities in y-axis and the natural period of the system in x-axis. The third plot…arrow_forwardDetermine the resultant stress at points P and Q.arrow_forwardFor the notched specimen with h = 0.13 m and r =11 mm, calculate the nominal stress for F=5 kN. F h F 25 mm Please submit your answer in the units of MPa.arrow_forward
- A tensile specimen made of hot-rolled AISI 1020 steel is loaded to point corresponding to a strain of 49%. 60 Su = 66 ksi Stress σ (ksi) Sy = 39 ksi 400B Se = 36 ksi Hot-rolled 1020 steel 20 F 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 Strain € (%) 0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Area ratio R 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 Area reduction A, What value of Su is applicable to this location? 0.6arrow_forwardA tensile specimen made of hot-rolled AISI 1020 steel is loaded to point corresponding to a strain of 40%. 60 Su = 66 ksi Stress σ (ksi) 40 20 Sy= = 39 ksi Se = 36 ksi Hot-rolled 1020 steel F | G | H 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 0 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 Strain € (%) ☐ T 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Area ratio R 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 Area reduction A, What value of Sy is applicable to this location? 0.6arrow_forwardA vertical .2m by .2m square plate is exposed to saturated water vapor at atmospheric pressure. If the surface temperature is 80 degrees C and the flow is laminar, estimate the loal heat transfer coefficents at the middles and at the bottom of the plate.arrow_forward
- A transformer that is 10 cm long, 6.2 cm wide, and 5 cm high is to be cooled by attaching a 10 cm by 6.2 cm wide polished aluminum heat sink(emissivity=.03) to its top surface. The heat sink has seven fins, which are 5 mm high, 2mm thick, and 10 cm long. A fan blows air at 25 degrees C parallel to the passages between the fins. The heat sink is to dissipate 12W of heat, and the base temp of the ehat sink is not to exceed 60 degrees C. Assuming the fins and the base plate to be nearly isothermal and the radiation heat transfer to be negligible, determine the minimum free-stream velocity the fan needs to supply to avoid overheating. Assume the flow is laminar over the entire finned surface of the transformer.arrow_forwardI need a mechanical engineering expert to solve this question,no Ai pleasearrow_forwardCan you give me the meaning of Combination spanner and Give Examples of Spannersarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Understanding Stress Transformation and Mohr's Circle; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_DH3546mSCM;License: Standard youtube license