
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780134641621
Author: Dean R. Appling, Spencer J. Anthony-Cahill, Christopher K. Mathews
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 9P
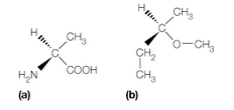
Indicate whether the structures shown are R and S in the absolute system.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Insert Format Tools Extensions Help
Normal text ▾ Arial
C
2
10
3
+ BIUA
Student Guide (continued)
Record data and conclusions about the mystery food sample either below or in a lab notebook.
Step 2: Protein Test (Biuret Solution)
Gelatin
Water
[Mystery Food
(Positive Control)
(Negative Control)
Sample
pink purple
no change
no change
They mystery food sample does not contain protein because the color of the
test tube wasn't pink or purple
Color
Conclusion They mystery food sample does not contain protein because the color of the test tube
wasn't pink or purple
Step 3: Lipid Test (Sudan Red Solution)
Vegetable Oil
Water
(Positive Control)
(Negative Control)
Mystery Food
Sample
floating red
no change
floating red
the mystery food dosnt contain lipids because the test tube has floating red
75
%
87
8
9
7
ChromeOS C
Device will pow
26.battery lea
power
The rate data from an enzyme catalyzed reaction with and without an inhibitor present is found in the image.
Question: what is the KM and Vm and the nature of inhibition
1. Estimate the concentration of an enzyme within a living cell. Assume that:
(a): fresh tissue is 80% water and all of it is intracellular
(b): the total soluble protein represents 15% of the weight
(c): all the soluble proteins are enzymes
(d): the average molecular weight of the proteins is 150,000
(E): about 100 different enzymes are present
please help I am lost
Chapter 9 Solutions
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
Ch. 9 - Prob. 1PCh. 9 - -D-Galactopyranose rotates the plane of polarized...Ch. 9 - Provide an explanation for the fact that a-...Ch. 9 - Why is a type O individual considered a universal...Ch. 9 - The disaccharide , -trehalose differs from the ,...Ch. 9 - A reducing sugar will undergo the Fehling...Ch. 9 - Prob. 7PCh. 9 - Prob. 8PCh. 9 - Indicate whether the structures shown are R and S...Ch. 9 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 9 - Draw (using Haworth projections) the fragments of...Ch. 9 - One or more of the compounds shown below will...Ch. 9 - Why do you suppose that the influenza virus...Ch. 9 - Prob. 14PCh. 9 - Are mannose and galactose epimers? Allose and...Ch. 9 - Prob. 16PCh. 9 - Explain in about one sentence why it is important...Ch. 9 - Prob. 18PCh. 9 - Prob. 19PCh. 9 - Prob. 20PCh. 9 - Prob. 21PCh. 9 - Prob. 22PCh. 9 - Prob. 23P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following data were recorded for the enzyme catalyzed conversion of S -> P Question: what would the rate be at 5.0 x 10-5 M [S] and the enzyme concentration was doubled? Also, the rate given in the table is from product accumulation after 10 minuets of reaction time. Verify these rates represent a true initial rate (less than 5% turnover). Please helparrow_forwardThe following data was obtained on isocitrate lyase from an algal species. Identify the reaction catalyzed by this enzyme, deduce the KM and Vmax , and determine the nature of the inhibition by oxaloacetate. Please helparrow_forwardIn the table below, there are sketches of four crystals made of positively-charged cations and negatively-charged anions. Rank these crystals in decreasing order of stability (or equivalently increasing order of energy). That is, select "1" below the most stable (lowest energy) crystal. Select "2" below the next most stable (next lowest energy) crystal, and so forth. A B 鹽 (Choose one) +2 C +2 +2 (Choose one) D 鹽雞 (Choose one) (Choose one)arrow_forward
- 1. Draw the structures for the fats A. 16:2: w-3 and B. 18:3:49,12,15 2. Name each of the molecules below (image attached)arrow_forwarddraw the structures for the fats A. 16:2:w-3 B 18:3:9,12,15arrow_forward1. Below is a template strand of DNA. Show the mRNA and protein that would result. label the ends of the molecules ( refer to attached image)arrow_forward
- Attach the followina labels to the diagram below: helicase, single stranded binding proteins, lagging strand, leading strand, DNA polymerase, primase, 5' ends (3), 3' ends (3) (image attached)arrow_forward1. How much energy in terms of ATP can be obtained from tristearin (stearate is 18:0) Show steps pleasearrow_forwardMultiple choice urgent!!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning


Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781337711067
Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna Balac
Publisher:Cengage Learning




Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning
The Sensorimotor System and Human Reflexes; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M0PEXquyhA4;License: Standard youtube license