
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337093347
Author: Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 9.5.15P
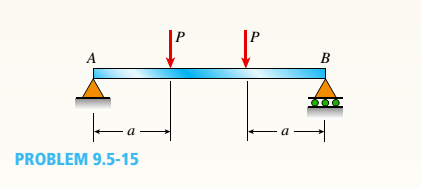
Use the method of superposition to find the angles of rotation 9Aand SBat the supports, and the maximum deflection for a simply supported beam subjected to symmetric loads P at distance a from each support. Assume that EI is constant, total beam length is L and a = U3. Hint: Use the formulas of Example 9-3.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
3-141
(3-113)
I just want to know the units of C_dot. Would it be rad/sec?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 9 - The equation of the deflection curve for a...Ch. 9 - The equation of the deflection curve for a simply...Ch. 9 - -3 The deflection curve for a simple beam AB (see...Ch. 9 - The deflection curve for a simple beam AB (sec...Ch. 9 - The deflection curve for a cantilever beam AB (sec...Ch. 9 - The deflection curve for a cantilever beam AB (see...Ch. 9 - A simply supported beam is loaded with a point...Ch. 9 - A I-meter-long, simply supported copper beam (E =...Ch. 9 - A wide-flange beam (W 12 x 35) supports a uniform...Ch. 9 - A uniformly loaded, steel wide-flange beam with...
Ch. 9 - What is the span length L of a uniformly loaded,...Ch. 9 - -6 Calculate the maximum deflection of a uniformly...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam with a uniform load (see figure)...Ch. 9 - A gold-alloy microbeam attached to a silicon wafer...Ch. 9 - Obtain a formula for the ratio c/maxof the...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam model is often used to represent...Ch. 9 - B cams AB and CDE are connected using rigid link...Ch. 9 - -12 Derive the equation of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -13 Derive the equation of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -14 A cantilever beam AB supporting a triangularly...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam has a length L = 12 ft and a...Ch. 9 - A simple beam with an overhang is subjected to d...Ch. 9 - -17 A cantilever beam AB is acted upon by a...Ch. 9 - -18 The beam shown in the figure has a sliding...Ch. 9 - -19 Derive the equations of the deflect ion curve...Ch. 9 - -20 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -21 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -22 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -23 The beam shown in the figure has a sliding...Ch. 9 - -1 Derive the equation of the deflection curve for...Ch. 9 - -2 A simple beam AB is subjected to a distrib uted...Ch. 9 - -3 The simple beam AB shown in the figure has...Ch. 9 - -4 A beam with a uniform load has a sliding...Ch. 9 - -5 The distributed load acting on a cantilever...Ch. 9 - -6 A cantilever beam .4B is subjected to a...Ch. 9 - -7 A beam on simple supports is subjected to a...Ch. 9 - Derive the equation of the deflection curve for...Ch. 9 - -9 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -10 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - A simply supported beam (E = 1600 ksi) is loaded...Ch. 9 - A simply supported beam (E = 12 GPa) carries a...Ch. 9 - Copper beam AB has circular cross section with a...Ch. 9 - Beam ABC is loaded by a uniform load q and point...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam of a length L = 2.5 ft has a...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam carries a trapezoidal...Ch. 9 - -5-7 A cantilever beam AB carries three equalaly...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB supports five equally spaced...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam AB shown in the figure has an...Ch. 9 - Beam ACE hangs from two springs, as shown in the...Ch. 9 - What must be the equation y =f(x) of the axis of...Ch. 9 - -12 Determine the angle of rotation Band...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam ACE shown in the figure has...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam is subjected to load P at...Ch. 9 - Use the method of superposition to find the angles...Ch. 9 - Repeat Problem 9,5-15 for the anti-symmetric...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam is subjected to a quadratic...Ch. 9 - A beam ABCD consisting of a simple span BD and an...Ch. 9 - A horizontal load P acts at end C of the bracket...Ch. 9 - A beam ABC having flexural rigidity EI = 75 kN irT...Ch. 9 - Determine the angle of rotation 0Band deflectionCh. 9 - -22 A simple beam AB supports a uniform load of...Ch. 9 - The overhanging beam A BCD supports two...Ch. 9 - A thin metal strip of total weight W and length L...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC with flexural rigidity EI...Ch. 9 - A beam A BCD rests on simple supports at B and C...Ch. 9 - The compound beam ABC shown in the figure has a...Ch. 9 - A compound beam ABC DE (see figure) consists of...Ch. 9 - A steel beam ABC is simply supported at A and held...Ch. 9 - -30. Calculate the deflection at point C of a beam...Ch. 9 - Compound beam ABC is loaded by point load P = 1.5...Ch. 9 - The compound beam shown in the figure consists of...Ch. 9 - -33 Find the horizontal deflection hand verti cal...Ch. 9 - The fr a me A BCD shown in the heure is squeezed...Ch. 9 - A framework A BCD is acted on by counterclockwise...Ch. 9 - A framework A BCD is acted on by force P at 2L/3...Ch. 9 - A beam ABCDE has simple supports at B and D and...Ch. 9 - A frame ABC is loaded at point C by a force P...Ch. 9 - The wing of a large commercial jet is represented...Ch. 9 - The wing of a small plane is represented by a...Ch. 9 - Find an expression for required moment MA(in terms...Ch. 9 - Find an expression for required moment MA(in terms...Ch. 9 - Find required distance d (in terms of L) so that...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam has two triangular loads as...Ch. 9 - -1 A cantilever beam AB is subjected to a uniform...Ch. 9 - The load on a cantilever beam AB has a triangular...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam AB is subjected to a...Ch. 9 - Determine the angle of rotation BBand the...Ch. 9 - -5 Calen1ate the deflections S 3a ndCh. 9 - A cantileverbeam^Cßsupportstwo concentrated loads...Ch. 9 - Obtain formulas for the angle of rotation 0Aat...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB supports two concentrated loads P...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB is subjected to a load in the...Ch. 9 - -10 The simple beam AB shown in the figure...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB is subjected to couples M0and 2A0...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam ACB shown in the figure has...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam ACB shown in the figure...Ch. 9 - Beam ACB hangs from two springs, as shown in the...Ch. 9 - -4 A simple beam ABCD has moment of inertia I near...Ch. 9 - A beam ABC has a rigid segment from A to B and a...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ABC has a moment of inertia 1,5 from...Ch. 9 - The tapered cantilever beam AB shown in the figure...Ch. 9 - The tapered cantilever beam AB shown in the figure...Ch. 9 - A tapered cantilever beam A B supports a...Ch. 9 - A tapered cantilever beam AB supports a...Ch. 9 - Repeat Problem 97-10, but now use the tapered...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ACE is constructed with square cross...Ch. 9 - A uniformly loaded simple beam AB (see figure) of...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L supports a...Ch. 9 - A propped cantilever beam AB of length L and with...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L is subjected to loads...Ch. 9 - A beam ABC with simple supports at A and B and an...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ACB supporting a uniform load q over...Ch. 9 - The frame shown in the figure consists of a beam...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L is loaded at the...Ch. 9 - The simple beam shown in the figure supports a...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC supports a concentrated...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam shown in the figure supports a...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ACB supports a uniform load of...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam ACB supports two concentrated...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam A CB shown in the hgure is...Ch. 9 - The frame A BC support s a concentrated load P at...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ABC DE supports a uniform load of...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC is subjected to a couple...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC rests on a simple support...Ch. 9 - A symmetric beam A BCD with overhangs at both ends...Ch. 9 - A heavy object of weight W is dropped onto the...Ch. 9 - An object of weight Wis dropped onto the midpoint...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam AB of length L = 6 It is...Ch. 9 - A weight W = 20 kN falls through a height h = 1,0...Ch. 9 - A weight W = 4000 lb falls through a height h =...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC with a rectangular cross...Ch. 9 - A heavy flywheel rotates at an angular speed m...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L and height /;...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam JA of length Land height/; (see...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC of height h has a sliding...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L and height h (see...Ch. 9 - Beam AB has an elastic support kR at A, pin...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (read image)arrow_forwardQu 2 Schematically plot attractive, repulsive, and net energies versus interatomic separation for two atoms or ions. Note on this plot the equilibrium separation (distance) ro and the bonding energy Eo. Qu 3 How many atoms (or molecules) are in one mole of the substance? Qu 4 Mole, in the context of this book, is taken in units of gram-mole. On this basis, how many atoms are there in a pound-mole of a substance? Qu 5 The atomic radii of Mg* and F ions are 0.072 and 0.133 nm, respectively. Calculate the force of attraction between these two ions at their equilibrium interionic separation (i.e., when the ions just touch one another). What is the force of repulsion at this same separation distance?show all work step by step problems formulaarrow_forwardQu 4 Silver has FCC crystal structure at room temperature, and a lattice constant, a, of 0.407 nm. Draw a reduced sphere silver unit cell in the grids provided below, clearly label the lattice dimensions. Within the unit cell you drew, shade the (1 0 0) plane. How many atoms are contained within the (1 0 0) plane? Calculate the area of (1 0 0) plane in [nm?]. Express your answer in [nm?] to three significant figures. Calculate the planar density of the (1 0 0) plane in [atoms/nm?]. Express the answer in atoms/nm to three significant figures. show all work step by steparrow_forward
- Can I get help on this question?arrow_forwardDuring some actual expansion and compression processes in piston–cylinder devices, the gases have been observed to satisfy the relationship PVn = C, where n and C are constants. Calculate the work done when a gas expands from 350 kPa and 0.03 m3 to a final volume of 0.2 m3 for the case of n = 1.5. The work done in this case is kJ.arrow_forwardCarbon dioxide contained in a piston–cylinder device is compressed from 0.3 to 0.1 m3. During the process, the pressure and volume are related by P = aV–2, where a = 6 kPa·m6. Calculate the work done on carbon dioxide during this process. The work done on carbon dioxide during this process is kJ.arrow_forward
- The volume of 1 kg of helium in a piston–cylinder device is initially 5 m3. Now helium is compressed to 3 m3 while its pressure is maintained constant at 130 kPa. Determine the initial and final temperatures of helium as well as the work required to compress it, in kJ. The gas constant of helium is R = 2.0769 kJ/kg·K. The initial temperature of helium is K. The final temperature of helium is K. The work required to compress helium is kJ.arrow_forwardA piston-cylinder device initially contains 0.4 kg of nitrogen gas at 160 kPa and 140°C. Nitrogen is now expanded isothermally to a pressure of 80 kPa. Determine the boundary work done during this process. The properties of nitrogen are R= 0.2968 kJ/kg-K and k= 1.4. N₂ 160 kPa 140°C The boundary work done during this process is KJ.arrow_forward! Required information An abrasive cutoff wheel has a diameter of 5 in, is 1/16 in thick, and has a 3/4-in bore. The wheel weighs 4.80 oz and runs at 11,700 rev/min. The wheel material is isotropic, with a Poisson's ratio of 0.20, and has an ultimate strength of 12 kpsi. Choose the correct equation from the following options: Multiple Choice о σmax= (314) (4r2 — r²) - о σmax = p² (3+) (4r² + r²) 16 σmax = (314) (4r² + r²) σmax = (314) (4² - r²)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Solids: Lesson 53 - Slope and Deflection of Beams Intro; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I7lTq68JRmY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY