
Chemistry with Access Code, Hybrid Edition
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781285188492
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl
Publisher: CENGAGE L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 82CWP
Pelargondin is the molecule responsible for the red color of the geranium flower. It also contributes to the color of ripe strawberries and raspberries. The structure of pelargondin is:
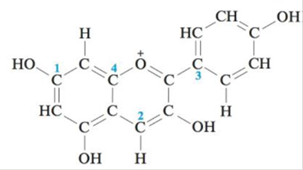
How many σ and π bonds exist in pelargondin? What is the hybridization of the carbon atoms marked 1–4?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Circle the compound in each pair where the indicated bond vibrates at higher frequency. WHY IS THIS? Provide thorough explanation to tie topic.
How can you distinguish between each pair of compounds below using IR? Cite a bond and frequency that can be used to distinguish. Provide thorough steps and explanation.
Propagation of uncertainty. Find the absolute and percent relative uncertainty assuming the ±-values are random error.
65±0.04 + 5.28±0.02 – 1.12±0.01
6±0.9 × 50.2±0.7 ÷ 13.8±0.5
[4.88±0.07 + 3.22±0.05] / 1.53±0.02
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry with Access Code, Hybrid Edition
Ch. 9 - Why do we hybtidize atomic orbitals to explain the...Ch. 9 - What hybridization is required for central atoms...Ch. 9 - Describe the bonding in H2S, CH4, H2CO and HCN...Ch. 9 - What hybridization is required for central atoms...Ch. 9 - Electrons in bonding molecular orbitals are most...Ch. 9 - What are molecular orbitals? How do they compare...Ch. 9 - Explain the difference between the and MOs for...Ch. 9 - Compare Figs. 4-47 and 4-49. Why are they...Ch. 9 - Which of the following would you expect to be more...Ch. 9 - Draw the Lewis structure for HCN. Indicate the...
Ch. 9 - Which is the more correct statement: The methane...Ch. 9 - Compare and contrast the MO model with the local...Ch. 9 - What are the relationships among bond order, bond...Ch. 9 - In the hybrid orbital model, compare and contrast ...Ch. 9 - In the molecular orbital mode l, compare and...Ch. 9 - Why are d orbitals sometimes used to form hybrid...Ch. 9 - The atoms in a single bond can rotate about the...Ch. 9 - Compare and contrast bonding molecular orbitals...Ch. 9 - What modification to the molecular orbital model...Ch. 9 - Why does the molecular orbital model do a better...Ch. 9 - The three NO bonds in NO3 are all equivalent in...Ch. 9 - Use the localized electron model to describe the...Ch. 9 - Use the localized electron model to describe the...Ch. 9 - Use the localized electron model to describe the...Ch. 9 - Use the localized electron model to describe the...Ch. 9 - The space-filling models of ethane and ethanol are...Ch. 9 - The space-filling models of hydrogen cyanide and...Ch. 9 - Give the expected hybridization of the central...Ch. 9 - Give the expected hybridization of the central...Ch. 9 - Give the expected hybridization of the central...Ch. 9 - Give the expected hybridization of the central...Ch. 9 - For each of the following molecules, write the...Ch. 9 - For each of the following molecules or ions that...Ch. 9 - Prob. 31ECh. 9 - The allene molecule has the following Lewis...Ch. 9 - Indigo is the dye used in coloring blue jeans. The...Ch. 9 - Urea, a compound formed in the liver, is one of...Ch. 9 - Biacetyl and acetoin are added to margarine to...Ch. 9 - Many important compounds in the chemical industry...Ch. 9 - Two molecules used in the polymer industry are...Ch. 9 - Hot and spicy foods contain molecules that...Ch. 9 - One of the first drugs to be approved for use in...Ch. 9 - The antibiotic thiarubin-A was discovered by...Ch. 9 - Consider the following molecular orbitals formed...Ch. 9 - Sketch the molecular orbital and label its type (...Ch. 9 - Which of the following are predicted by the...Ch. 9 - Which of the following are predicted by the...Ch. 9 - Using the molecular orbital model, write electron...Ch. 9 - Consider the following electron configuration:...Ch. 9 - Using molecular orbital theory, explain why the...Ch. 9 - Using the molecular orbital model to describe the...Ch. 9 - The transport of O2 in the blood is carried out by...Ch. 9 - A Lewis structure obeying the octet rule can be...Ch. 9 - Using the molecular orbital model, write electron...Ch. 9 - Using the molecular orbital model, write electron...Ch. 9 - In which of the following diatomic molecules would...Ch. 9 - In terms of the molecular orbital model, which...Ch. 9 - Show how two 2p atomic orbitals can combine to...Ch. 9 - Show how a hydrogen 1s atomic orbital and a...Ch. 9 - Use Figs. 4-54 and 4-55 to answer the following...Ch. 9 - Acetylene (C2H2) can be produced from the reaction...Ch. 9 - Describe the bonding in NO+, NO, and NO, using...Ch. 9 - Describe the bonding in the O3 molecule and the...Ch. 9 - Describe the bonding in the CO32 ion using the...Ch. 9 - Draw the Lewis structures, predict the molecular...Ch. 9 - FClO2 and F3ClO can both gain a fluoride ion to...Ch. 9 - Two structures can be drawn for cyanuric acid: a....Ch. 9 - Give the expected hybridization for the molecular...Ch. 9 - Vitamin B6 is an organic compound whose deficiency...Ch. 9 - Aspartame is an artificial sweetener marketed...Ch. 9 - Prob. 69AECh. 9 - The three most stable oxides of carbon are carbon...Ch. 9 - Complete the following resonance structures for...Ch. 9 - Prob. 73AECh. 9 - Describe the bonding in the first excited state of...Ch. 9 - Using an MO energy-level diagram, would you expect...Ch. 9 - Show how a dxz. atomic orbital and a pz, atomic...Ch. 9 - What type of molecular orbital would result from...Ch. 9 - Consider three molecules: A, B, and C. Molecule A...Ch. 9 - Draw the Lewis structures for TeCl4, ICl5, PCl5,...Ch. 9 - A variety of chlorine oxide fluorides and related...Ch. 9 - Pelargondin is the molecule responsible for the...Ch. 9 - Complete a Lewis structure for the compound shown...Ch. 9 - Which of the following statements concerning SO2...Ch. 9 - Consider the molecular orbital electron...Ch. 9 - Place the species B2+ , B2, and B2 in order of...Ch. 9 - Consider the following computer-generated model of...Ch. 9 - Cholesterol (C27liu;O) has the following...Ch. 9 - Cyanamide (H2NCN), an important industrial...Ch. 9 - A flask containing gaseous N2 is irradiated with...Ch. 9 - Prob. 92CPCh. 9 - Values of measured bond energies may vary greatly...Ch. 9 - Use the MO model to explain the bonding in BeH2....Ch. 9 - Prob. 95CPCh. 9 - Arrange the following from lowest to highest...Ch. 9 - Use the MO model to determine which of the...Ch. 9 - Given that the ionization energy of F2 is 290...Ch. 9 - Carbon monoxide (CO) forms bonds to a variety of...Ch. 9 - Prob. 100CPCh. 9 - As the bead engineer of your starship in charge of...Ch. 9 - Determine the molecular structure and...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Match to correct spectrum and explain the bonds and frequencies used to tell what spectrum connected to the given option. Thanks.arrow_forwardDraw the virtual orbitals for the planar and pyramidal forms of CH3 and for the linear and bent forms of CH2arrow_forwardQ2: Draw the molecules based on the provided nomenclatures below: (2R,3S)-2-chloro-3-methylpentane: (2S, 2R)-2-hydroxyl-3,6-dimethylheptane:arrow_forward
- Q3: Describes the relationship (identical, constitutional isomers, enantiomers or diastereomers) of each pair of compounds below. ག H CH3 OH OH CH3 H3C OH OH OH ////////// C CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 H3C CH 3 C/III..... Physics & Astronomy www.physics.northweste COOH H нош..... H 2 OH HO CH3 HOOC H CH3 CH3 CH3 Br. H H Br and H H H Harrow_forwardQ1: For each molecule, assign each stereocenter as R or S. Circle the meso compounds. Label each compound as chiral or achiral. OH HO CI Br H CI CI Br CI CI Xf x f g Br D OH Br Br H₂N R. IN Ill I -N S OMe D II H CO₂H 1/111 DuckDuckGarrow_forwardThese are synthesis questions. You need to show how the starting material can be converted into the product(s) shown. You may use any reactions we have learned. Show all the reagents you need. Show each molecule synthesized along the way and be sure to pay attention to the regiochemistry and stereochemistry preferences for each reaction. If a racemic molecule is made along the way, you need to draw both enantiomers and label the mixture as "racemic". All of the carbon atoms of the products must come from the starting material! ? H Harrow_forward
- Q5: Draw every stereoisomer for 1-bromo-2-chloro-1,2-difluorocyclopentane. Clearly show stereochemistry by drawing the wedge-and-dashed bonds. Describe the relationship between each pair of the stereoisomers you have drawn.arrow_forwardClassify each pair of molecules according to whether or not they can participate in hydrogen bonding with one another. Participate in hydrogen bonding CH3COCH3 and CH3COCH2CH3 H2O and (CH3CH2)2CO CH3COCH3 and CH₂ CHO Answer Bank Do not participate in hydrogen bonding CH3CH2OH and HCHO CH3COCH2CH3 and CH3OHarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:OpenStax
Stoichiometry - Chemistry for Massive Creatures: Crash Course Chemistry #6; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UL1jmJaUkaQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Bonding (Ionic, Covalent & Metallic) - GCSE Chemistry; Author: Science Shorts;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p9MA6Od-zBA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
General Chemistry 1A. Lecture 12. Two Theories of Bonding.; Author: UCI Open;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dLTlL9Z1bh0;License: CC-BY