
Concept explainers
For each of the following molecules or ions that contain sulfur, write the Lewis structure(s), predict the molecular structure (including bond angles), and give the expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur.
a. SO2
b. SO3
c. 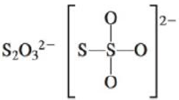
d. 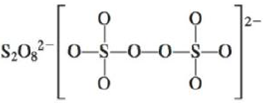
e. SO32−
f. SO42−
g. SF2
h. SF4
i. SF6
j. F3S—SF
k. SF5+
(a)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on each sulfur and oxygen atom. Two oxygen atoms are bonded to sulfur atom. Therefore, the total valence electrons are
Therefore the geometry is bent. The bond angle is less than
The Lewis structure of
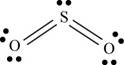
Figure 1
(b)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and each oxygen atom. Two oxygen atoms are attached to sulfur, therefore, the total number of valence electrons is
The molecule has trigonal planar geometry with bond angle
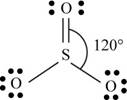
Figure 2
(c)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and each oxygen atom. Three oxygen atoms and one sulfur atom is attached to central sulfur atom and charge on the molecule is
By bonding in this way, they complete their octet. The molecular structure is tetrahedral with bond angle approximately equal to
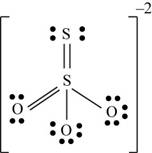
Figure 3
(d)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and each oxygen atom. There are eight oxygen atoms and two sulfur atoms are present in the molecule and charge on the molecule is
The two oxygen atoms in the centre are bonded by single bond. By bonding in this way, they complete their octet. The molecular structure is tetrahedral with bond angle approximately equal to
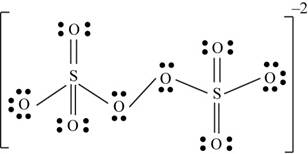
Figure 4
(e)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and each oxygen atom. Three oxygen atoms and one sulfur atom present in the molecule and charge on the molecule is
One oxygen atom is single bonded with sulfur and one is joined by pi bond. By bonding in this way, they complete their octet. The molecular structure is trigonal pyramidal with bond angle approximately equal to
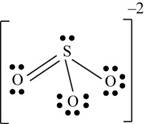
Figure 5
(f)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and each oxygen atom. Four oxygen atoms and one sulfur atom is present in the molecule and charge on the molecule is
Two oxygen atoms are single bonded with sulfur and two joined by pi bond. By bonding in this way, they complete their octet. The molecular structure is tetrahedral with bond angle approximately equal to
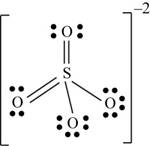
Figure 6
(g)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and seven valence electrons on each fluorine atom. Two fluorine atoms and one sulfur atom is present in the molecule, therefore, the total number of valence electrons is
The sulfur is bonded to two fluorine atoms by sigma bond. By bonding in this way, they complete their octet. The molecular structure is bent due to presence of lone pairs of electrons on sulfur. The bond angle is less than
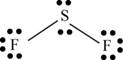
Figure 7
(h)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and seven valence electrons on each fluorine atom. Four fluorine atoms and one sulfur atom is present in the molecule, therefore, the total number of valence electrons is
The molecular structure is see-saw due to presence of lone pair of electrons on sulfur. The equatorial bond angles are
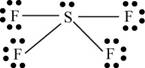
Figure 8
(i)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and seven valence electrons on each fluorine atom. Six fluorine atoms and one sulfur atom is present in the molecule, therefore, the total number of valence electrons is
The molecular structure is octahedral with bond angle
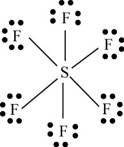
Figure 9
(j)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and seven valence electrons on each fluorine atom. Four fluorine atoms and two sulfur atoms are present in the molecule, therefore, the total number of valence electrons is
The molecular structure is see-saw due to presence of lone pair of electrons on sulfur. The equatorial bond angles are
The Lewis structure of
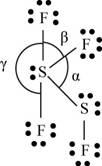
Figure 10
(k)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and seven valence electrons on each fluorine atom. Five fluorine atoms and one sulfur atom is present in the molecule and charge on the molecule is
The molecular structure is trigonal bipyramidal with equatorial bond angles
The Lewis structure of
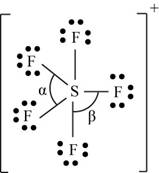
Figure 11
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry with Access Code, Hybrid Edition
- I need help with the following questionarrow_forwardFor CARS, which statement is not true regarding its advantages? a) Contrast signal based on vibrational characteristics, no need for fluorescent tagging. b) Stronger signals than spontaneous Raman. c) Suffers from fluorescence interference, because CARS signal is at high frequency. d) Faster, more efficient imaging for real-time analysis. e) Higher resolution than spontaneous Raman microscopy.arrow_forwardDraw the major product of the Claisen condensation reaction between two molecules of this ester. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 5 attempts remaining 1. NaOCH3/CH3OH 2. Acidic workup Select to Draw O Incorrect, 5 attempts remaining The total number of carbons in the parent chain is incorrect. Review the reaction conditions including starting materials and/or intermediate structures and recount the number of carbon atoms in the parent chain of your structure. OKarrow_forward
- Using a cell of known pathlength b = 1.25115 x 10-3 cm, a water absorption spectrum was measured. The band at 1645 cm-1, assigned to the O-H bending, showed an absorbance, A, of 1.40. a) Assuming that water density is 1.00 g/mL, calculate the water molar concentration c (hint: M= mole/L) b) Calculate the molar absorptivity, a, of the 1645 cm-1 band c) The transmitted light, I, can be written as I= Ioexp(-xb), where x is the absorption coefficient (sometimes designated as alpha), Io is the input light, and b is the cell pathlength. Prove that x= (ln10)*x*c d) Calculate x for the 1645 cm-1 bandarrow_forwardConvert 1.38 eV into wavelength (nm) and wavenumber (cm-1) (c = 2.998 x 108 m/s; h = 6.626 x 10-34 J*s).arrow_forwardCan you help me understand the CBC method on metal bridging by looking at this problem?arrow_forward
- A partir de Aluminio y Co(NO3)2ꞏ6H2O, indicar las reacciones a realizar para obtener Azul de Thenard (Al2CoO4).arrow_forwardTo obtain Thenard Blue (Al2CoO4), the following reaction is correct (performed in an oven):Al(OH)3 + Co(OH)2 → Al2CoO4 + 4 H2Oarrow_forwardProblem 38 can u explain and solve thanks april 24arrow_forward

 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





