
(a)
Interpretation:
Two
Concept Introduction:
Functional group: They are certain substitutes in the organic molecules which determine the characteristic reactions taking place in it.
There are different types of functional groups and it includes
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts, namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix- Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an
Root word - Represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo, if it is two cyclic structure combined then prefixed with bicyclo.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Using chapter 10 the two functional groups that are not discussed in this chapter are ethers and
The organic compound that contains aryl/alkyl groups bonded to an
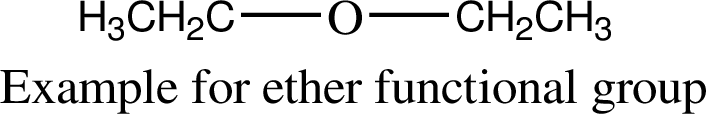
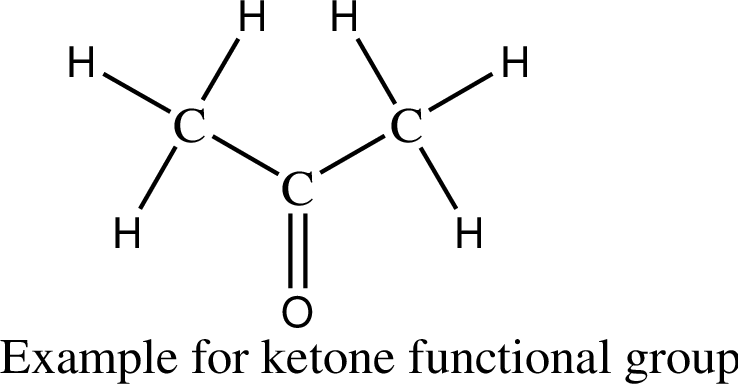
The ketone is an organic functional group that contains a
(b)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for acetone molecule in question 45 has to identified also the functional group present in it has to be indicated.
Concept Introduction:
Functional group: They are certain substitutes in the organic molecules which determine the characteristic reactions taking place in it.
There are different types of functional groups and it includes alkane, alcohol, aldehyde, amine, ether, carboxylic acid etc.
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts, namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix- Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc...
Root word - Represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
When a molecule consists of cyclic structure, the root word of the molecule is prefixed with cyclo, if it is two cyclic structure combined then prefixed with bicyclo.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
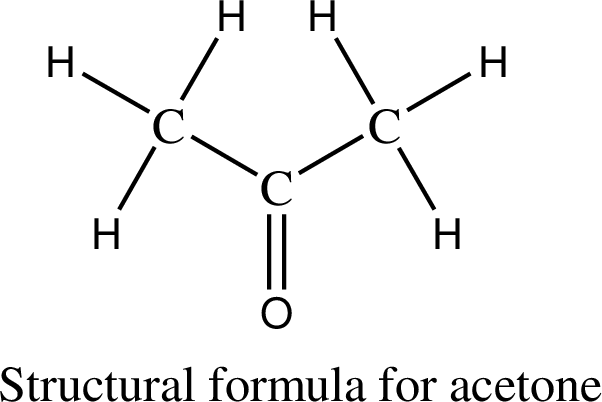
Following the IUPAC rules the structure for acetone is drawn as follows,
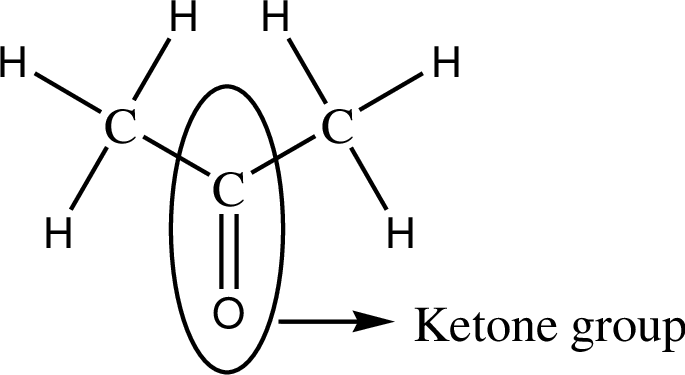
Observing the structure clearly shows that it contains ketone group with it since it consists of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Laboratory Manual Chemistry in Context
- please provide the structure for this problem, thank you!arrow_forwardDraw the Fischer projection from the skeletal structure shown below. HO OH OH OH OH H Q Drawing Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges I ☐ T HO H H OH HO I CH2OH H OH Drag H OH -CH2OH CHO -COOH Undo Reset Remove Donearrow_forwardplease provide the structure for this problem, thank youarrow_forward
- presented by Morallen Lig Intermine the hand product for the given mution by adding atoms, bonds, nonhonding diarion panda скуль Step 3: Comp the draw the product Step 2: Agama workup Compithe 429 ملولةarrow_forwardReaction A 0,0arrow_forwardpresented by Morillon Leaning Predict the organic product for the min кусур HSC Adithane carved arnown to come than that to the condon slchroruis in acid in in aquishri with ноюarrow_forward
- 6.15PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Include any relevant stereochemistry. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Problem 1 of O H [PhзPCH2CH3]*C|¯ NaH Drawing > Q Atoms, Bonds and Draw or tap a nearrow_forward8:17 PM Sun Mar 30 Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HSCH2CH2CH2SH, BF3 Probler Drawing Ato Bonds Clarrow_forwardpresented by Mr L How the coprion. (Il Done in no wraction, dew the starting redential) доarrow_forward
- 8:16 PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Proble 1. CH3MgBr 2. H3O+ F Drawingarrow_forwardо но оarrow_forwardName the major organic product of the following action of 4-chloro-4-methyl-1-pentanol in neutral pollution 10+ Now the product. The product has a molecular formula f b. In a singly hain, the starting, material again converts into a secule with the molecular kormula CIO. but with comply Draw the major organic structure inhalationarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





