
Concept explainers
Ingles Company manufactures external hard drives. At the beginning of the period, the following plans for production and costs were revealed:

During the year, 24,800 units were produced and sold. The following actual costs were incurred:

There were no beginning or ending inventories of direct materials. The direct materials price variance was $10,168 unfavorable. In producing the 24,800 units, a total of 12,772 hours were worked, 3 percent more hours than the standard allowed for the actual output.
Required:
- 1. Prepare a performance report comparing expected costs to actual costs.
- 2. Determine the following:
- a. Direct materials usage variance
- b. Direct labor rate variance
- c. Direct labor usage variance
- d. Fixed overhead spending and volume variances
- e. Variable overhead spending and efficiency variances
- 3. Use T-accounts to show the flow of costs through the system. In showing the flow, you do not need to show detailed overhead variances. Show only the over- and underapplied variances for fixed and variable overhead.
1.
Prepare a performance report by comparing the expected costs to actual costs.
Explanation of Solution
Flexible budget performance report: This report associates actual performance and budgeted performance on par with actual sales volume. Flexible budget performance report gains the management attention to the cost or revenues that differ from budgeted amount.
A flexible budget performance report is used for analyzing the difference between actual performance and budgeted performance. It is also called as variance analysis. Its usefulness comes from the budgeted and actual results that are based on similar level of activity.
Prepare a performance report by comparing the expected costs to actual costs:
| Particulars | Actual Cost | Flexible Budget Cost | Variance |
| Direct materials | 264,368 | 248,000 | 16,368 U |
| Direct labor | 204,352 | 198,400 | 5,952 U |
| Variable overhead | 107,310 | 99,200 | 8,110 U |
| Fixed overhead | 73,904 | 75,000 | 1,096 F |
| Total cost | $649,934 | $620,600 | $29,334 U |
Table (1)
Working note 1: Calculate the budgeted cost for direct materials:
Working note 2: Calculate the budgeted cost for direct labor:
Working note 3: Calculate the budgeted cost for variable overhead:
Working note 4: Calculate the budgeted cost for fixed overhead:
Note: Fixed overhead unit is based on 25,000.
2.
Calculate the followings:
- a. Direct materials usage variance.
- b. Direct labor rate variance.
- c. Direct labor usage variance.
- d. Fixed overhead spending and volume variances.
- e. Variable overhead spending and efficiency variances.
Explanation of Solution
a.
Direct material usage (efficiency) variance: It is a measure that determines the variation in between actual and standard quantity of input multiplied by the standard unit price is called material usage variance.
The following formula is used to calculate direct material usage variance:
Calculate direct materials usage variance by using total variance formula:
b.
Direct Labor Rate Variance: The direct labor rate variance is a measure to determine the variation in the estimated cost of the direct labor and the actual cost of the direct labor and is multiplied by the actual hours is called direct labor rate variance.
The following formula is used to calculate the direct labor rate variance:
Calculate direct labor rate variance:
Step 1: Calculate standard hour.
Step 2: Calculate standard rate.
Step 3: Calculate direct labor rate variance.
c.
Direct labor efficiency variance is a measure that determines the difference between the estimated labor hours and the actual labor hours used and is multiplied by the standard rate per hour is called material usage variance.
The following formula is used to calculate direct labor efficiency variance:
Calculate the direct labor usage or efficiency variance:
d.
Fixed overhead spending variance: It is the difference between actual fixed overhead and the budgeted fixed overhead.
The following formula is used to calculate fixed overhead spending variance:
Calculate the fixed overhead spending variance:
Fixed overhead volume variance: It is the difference between budgeted fixed overhead and the applied fixed overhead.
The following formula is used to calculate fixed overhead volume variance:
Calculate the volume variance:
Working note 5: Calculate the applied fixed overhead:
Working note 6: Calculate the standard fixed overhead rate:
e.
Spending variances: It arises when management pays an amount which is different from the standard price for purchasing an item. The variable overhead spending variance measures the total effect of differences in the actual variable overhead rate (AVOR) and the standard variable overhead rate (SVOR).
Efficiency variances: It arises when standard direct labor hours expected for actual production different from labor the actual direct labor hours used.
Variable overhead efficiency variance tells managers how much of the total variable manufacturing overhead variance is due to using more or fewer machine hours than anticipated for the actual volume of output.
Calculate variable overhead spending variance:
Calculate variable overhead efficiency variance:
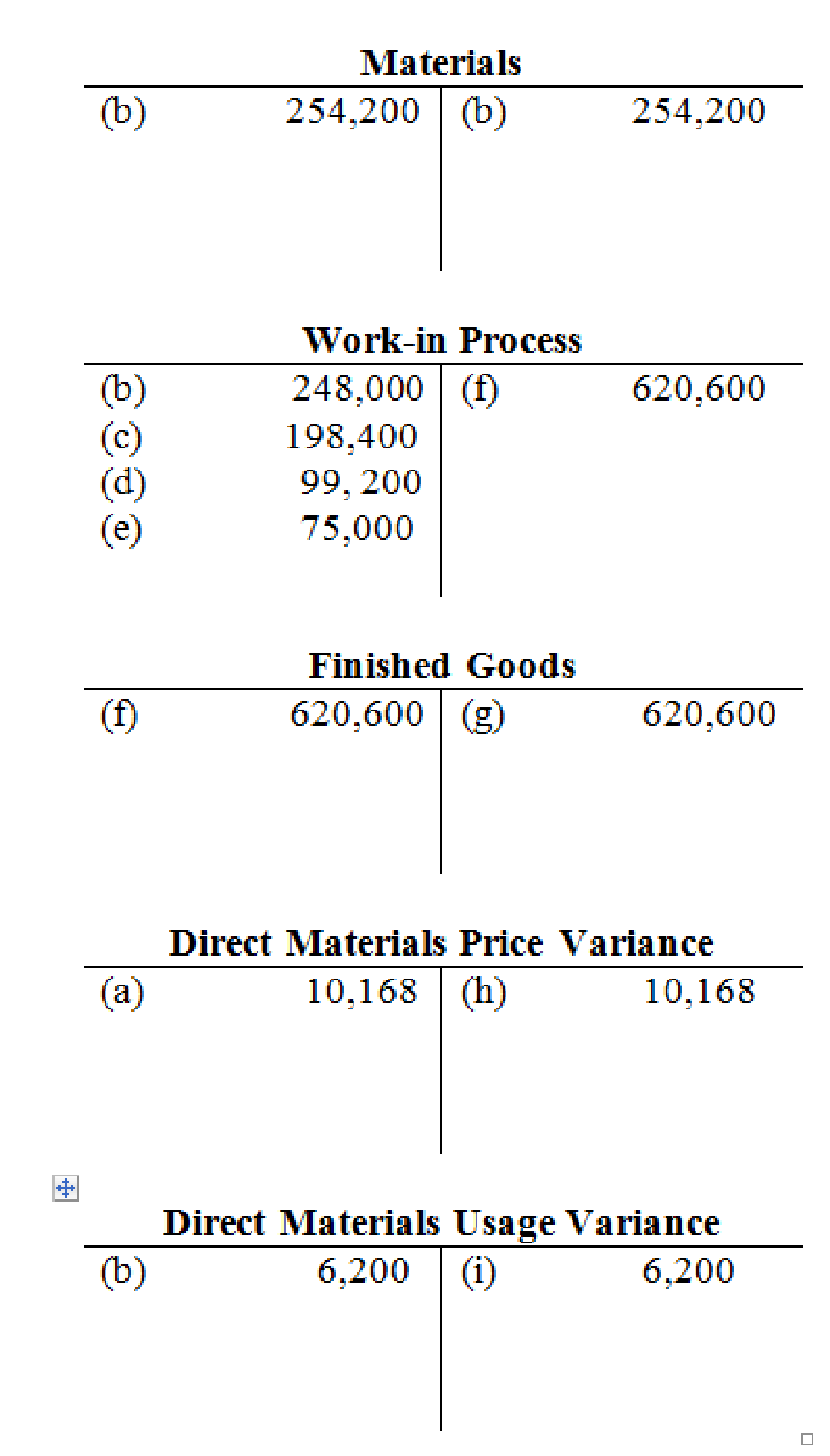
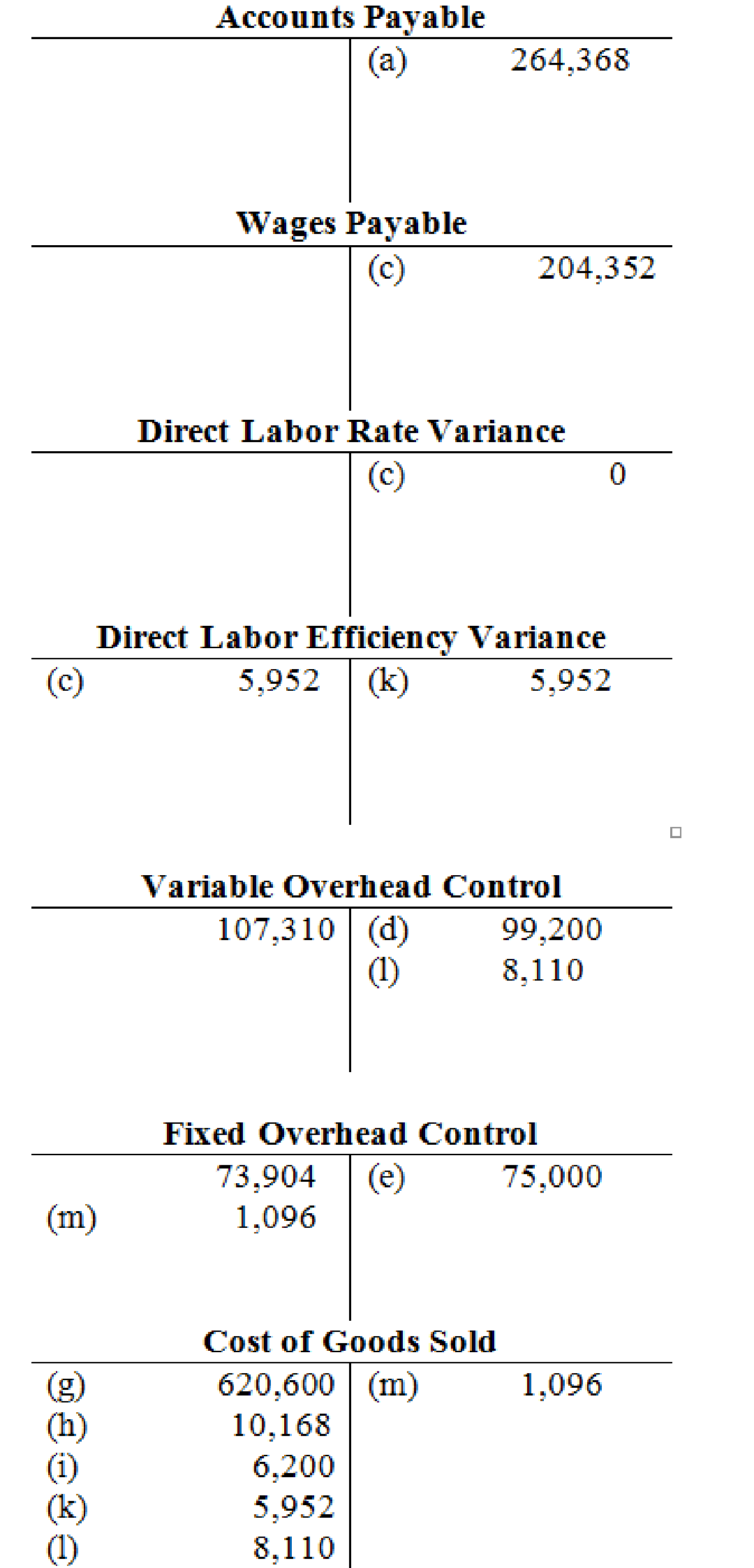
3.
Prepare T-accounts to show the flow of costs through the system.
Explanation of Solution
T-account: The condensed form of a ledger is referred to as T-account. The left-hand side of this account is known as debit, and the right hand side is known as credit.
Prepare T-accounts to show the flow of costs through the system:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning

