
Concept explainers
Petrillo Company produces engine parts for large motors. The company uses a
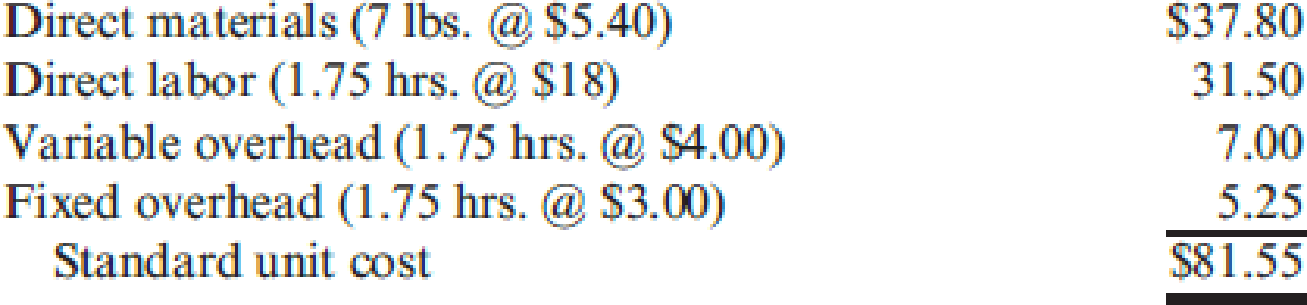
During the year, Petrillo had the following activity related to valve production:
- a. Production of valves totaled 20,600 units.
- b. A total of 135,400 pounds of direct materials was purchased at $5.36 per pound.
- c. There were 10,000 pounds of direct materials in beginning inventory (carried at $5.40 per pound). There was no ending inventory.
- d. The company used 36,500 direct labor hours at a total cost of $656,270.
- e. Actual fixed
overhead totaled $110,000. - f. Actual variable overhead totaled $168,000.
Petrillo produces all of its valves in a single plant. Normal activity is 20,000 units per year. Standard overhead rates are computed based on normal activity measured in standard direct labor hours.
Required:
- 1. Compute the direct materials price and usage variances.
- 2. Compute the direct labor rate and efficiency variances.
- 3. Compute overhead variances using a two-
variance analysis . - 4. Compute overhead variances using a four-variance analysis.
- 5. Assume that the purchasing agent for the valve plant purchased a lower-quality direct material from a new supplier. Would you recommend that the company continue to use this cheaper direct material? If so, what standards would likely need revision to reflect this decision? Assume that the end product’s quality is not significantly affected.
- 6. Prepare all possible
journal entries (assuming a four-variance analysis of overhead variances).
1.
Compute the direct materials price variance and the direct materials usage variance.
Explanation of Solution
Direct material price variance: The variation in between actual price and estimated price paid for materials multiplied by the actual quantity is called material price variance. It is used to determine difference in price paid for material the price that was supposed to be paid for material.
The following formula is used to calculate direct material price variance:
Direct material usage (efficiency) variance: It is a measure that determines the variation in between actual and standard quantity of input multiplied by the standard unit price is called material usage variance.
The following formula is used to calculate direct material usage variance:
Compute the direct materials price variance:
Compute the direct materials usage variance:
Working note 1: Calculate the standard quantity:
Working note 2: Calculate the actual quantity:
Therefore, the direct materials price variance and the usage variance is $5,416 F and $6,480 U respectively.
2.
Calculate the direct labor rate variance and labor efficiency variance.
Explanation of Solution
Direct Labor Rate Variance: The direct labor rate variance is a measure to determine the variation in the estimated cost of the direct labor and the actual cost of the direct labor and is multiplied by the actual hours is called direct labor rate variance.
The following formula is used to calculate the direct labor rate variance:
Direct labor efficiency variance is a measure that determines the difference between the estimated labor hours and the actual labor hours used and is multiplied by the standard rate per hour is called material usage variance.
The following formula is used to calculate direct labor efficiency variance:
Calculate the direct labor rate variance:
Calculate the labor efficiency variance:
Working note 3: Calculate the standard hours:
Therefore, the direct labor rat variance and the efficiency variance are $730 F and $8,100 U respectively.
3.
Calculate the overhead variances using two variance analysis.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the overhead variances using two variance analysis:
Budget variance:
Working note 4: Calculate the actual overhead:
Working note 5: Calculate the budgeted overhead:
Step 1: Calculate the budgeted fixed overhead.
Step 2: Calculate the budgeted variable overhead.
Step 3: Calculate the total budgeted overhead.
Volume variance:
Step 1: Compute the applied fixed overhead.
Step 2: Compute the volume variance.
Working note 5: Calculate the standard hours:
Therefore, the budgeted and volume variance are $28,800 U and $3,150 F respectively.
4.
Calculate the overhead variances using a four-variance analysis.
Explanation of Solution
Overhead Variance: The overhead variance is the difference arising between the real overhead consumed in the production of a product, and the estimated overhead determined in the production of that product.
Calculate the overhead variances using a four-variance analysis:
Step 1: Compute the budgeted variable overhead cost.
Step 2: Compute the variable overhead spending variance.
Compute the variable overhead efficiency variance:
Step 1: Compute the applied variable overhead.
Step 2: Compute the variable overhead efficiency variance.
Working note 6: Calculate the direct labor hour per unit:
Working note 7: Calculate the actual direct labor hours:
Therefore, the variable overhead spending and efficiency variance are $22,000 U and $1,800 U respectively.
5.
Explain whether the company continues to purchases cheaper direct materials if so indicate the standard need revision to reflect this decision.
Explanation of Solution
The company would not continue to purchase low –quality materials because it affects the company. The budgeted cost of direct materials at the 20,600 units’ production level is $778,680
6.
Prepare journal entries (four-variance analysis of overhead variances).
Explanation of Solution
Journalizing: It is the process of recording the transactions of an organization in a chronological order. Based on these journal entries recorded, the amounts are posted to the relevant ledger accounts.
Accounting rules for journal entries:
- To increase balance of the account: Debit assets, expenses, losses and credit all liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
- To decrease balance of the account: Credit assets, expenses, losses and debit all liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
Prepare journal entries (four-variance analysis of overhead variances):
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Direct Materials | 731,160 | ||
| Direct Materials Price variance | 5,416 | ||
| Accounts Payable | 725,744 | ||
| (To record the purchase of direct materials) | |||
| Work in Process | 778,680 | ||
| Direct Materials Usage Variance | 6,480 | ||
| Direct Materials | 785,160 | ||
| (To record the usage of direct materials) | |||
| Work in Process | 648,900 | ||
| Direct Labor Efficiency Variance | 8,100 | ||
| Direct Labor Rate Variance | 730 | ||
| Wages Payable | 656,270 | ||
| (To record the use of direct labor) | |||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 13,850 | ||
| Direct Labor Rate Variance | 730 | ||
| Direct Materials Usage Variance | 6,480 | ||
| Direct Labor Efficiency Variance | 8,100 | ||
| (To record the use of direct material and labor variances) | |||
| Direct Materials Price variance | 5,416 | ||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 5,416 | ||
| (To close the direct materials price variance) | |||
| Variable Overhead Control | 168,000 | ||
| Miscellaneous Accounts | 168,000 | ||
| (To record incurrence of actual overhead) | |||
| Fixed Overhead Control | 110,000 | ||
| Miscellaneous Accounts | 110,000 | ||
| (To record incurrence of actual overhead) | |||
| Work in Process | 144,200 | ||
| Variable Overhead Control | 144,200 | ||
| (To close the overhead variances) | |||
| Work in Process | 108,150 | ||
| Fixed Overhead Control | 108,150 | ||
| (To close the overhead variances) | |||
| Variable Overhead Spending Variance | 22,000 | ||
| Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance | 1,800 | ||
| Fixed Overhead Spending Variance | 5,000 | ||
| Fixed Overhead Volume Variance | 3,150 | ||
| Fixed Overhead Control | 1,850 | ||
| Variable Overhead Control | 23,800 | ||
| (To close the overhead variances) | |||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 28,800 | ||
| Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance | 1,800 | ||
| Fixed Overhead Spending Variance | 5,000 | ||
| Variable Overhead Spending Variance | 22,000 | ||
| (To close the overhead variances) | |||
| Fixed Overhead Volume Variance | 3,150 | ||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 3,150 | ||
| (To close the cost of goods sold) |
Table (1)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
- What is the value of this investment of this financial accounting question?arrow_forwardFinancial Accounting Question please provide solution this questionarrow_forwardDuring its first month of operation, Peter's Auto Supply Corporation, which specializes the sale of auto equipment and supplies, completed the following transactions. July Transactions July 1 Issued Common Stock in exchange for $100,000 cash. July 1 Paid $4,000 rent for the months of July and August July 2 Paid the insurance company $2,400 for a one year insurance policy, beginning July 1. July 5 Purchased inventory on account for $35,000 (Assume that the perpetual inventory system is used.) July 6 Borrowed $36,500 from a local bank and signed a note. The interest rate is 10%, and principal and interest is due to be repaid in six months. July 8 Sold inventory on account for $17,000. The cost of the inventory is $7,000. July 15 Paid employees $6,000 salaries for the first half of the month. July 18 Sold inventory for $15,000 cash. The cost of the inventory was $6,000. July 20 Paid $15,000 to suppliers for the inventory purchased on January 5. July 26…arrow_forward
- Please solve these general accounting question without use Aiarrow_forwardDuring its first month of operation, Peter's Auto Supply Corporation, which specializes the sale of auto equipment and supplies, completed the following transactions. July Transactions July 1 Issued Common Stock in exchange for $100,000 cash. July 1 Paid $4,000 rent for the months of July and August July 2 Paid the insurance company $2,400 for a one year insurance policy, beginning July 1. July 5 Purchased inventory on account for $35,000 (Assume that the perpetual inventory system is used.) July 6 Borrowed $36,500 from a local bank and signed a note. The interest rate is 10%, and principal and interest is due to be repaid in six months. July 8 Sold inventory on account for $17,000. The cost of the inventory is $7,000. July 15 Paid employees $6,000 salaries for the first half of the month. July 18 Sold inventory for $15,000 cash. The cost of the inventory was $6,000. July 20 Paid $15,000 to suppliers for the inventory purchased on January 5. July 26…arrow_forwardOceanic Boat works manufactures boat hulls at a cost of... Please solve this general accounting questionarrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,




