
Concept explainers
To solve the given equation using graphing.
Answer to Problem 29SGR
The roots of x are -0.8 and 3 .
Explanation of Solution
Given information :
The function provided is
Formula used :
The given equation would be graphed as a function and the points of x-intercepts would be the results. For these points, the x-coordinate shall serve the purpose of the results.
If the roots are not on points that are integers, use the approximation method to compute the roots.
Else, put the x-intercept value in the equation. If the left-hand and right-hand sides of the equations match, it is a success and those will be the values of x.
Calculation :
The graph of the given equation is
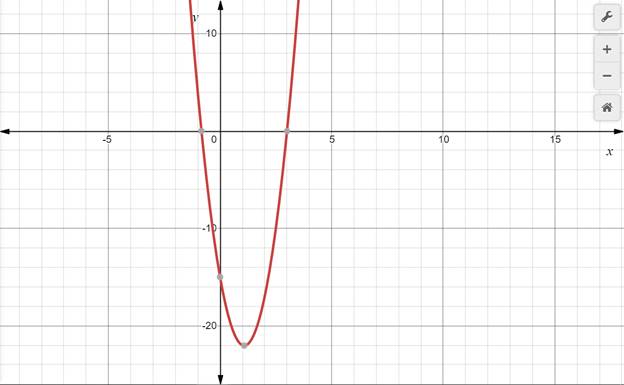
The zeroes in the graph are at
In this, the parabola one x-intercept is between -1 and 0.
To find the root, make a table of values for x in between these points with intervals on 0.1 . The value of x that is result closest to 0 will be the roots of the equation.
Table of values in between -1 and 0
| X | -0.9 | -0.8 | -0.7 | -0.6 | -0.5 | -0.4 | -0.3 | -0.2 | -0.1 |
| Y | 1.56 | -0.76 | -2.96 | -5.04 | -7 | -8.84 | -10.56 | -12.16 | -13.64 |
In the tables, the value of y that is closest to 0 is -0.76. Their corresponding x values would be the roots.
Thus, -0.8 is the first root.
For the second root, check if the value of the x-coordinate matches both sides of the given equation.
Put these values in the given equation to recheck.
Putting
Simplifying
Hence second value of x is a success.
Chapter 9 Solutions
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
- Can someone provide an answer & detailed explanation please? Thank you kindly!arrow_forwardGiven the cubic function f(x) = x^3-6x^2 + 11x- 6, do the following: Plot the graph of the function. Find the critical points and determine whether each is a local minimum, local maximum, or a saddle point. Find the inflection point(s) (if any).Identify the intervals where the function is increasing and decreasing. Determine the end behavior of the graph.arrow_forwardGiven the quadratic function f(x) = x^2-4x+3, plot the graph of the function and find the following: The vertex of the parabola .The x-intercepts (if any). The y-intercept. Create graph also before solve.arrow_forward
- what model best fits this dataarrow_forwardRound as specified A) 257 down to the nearest 10’s place B) 650 to the nearest even hundreds, place C) 593 to the nearest 10’s place D) 4157 to the nearest hundreds, place E) 7126 to the nearest thousand place arrow_forwardEstimate the following products in two different ways and explain each method  A) 52x39 B) 17x74 C) 88x11 D) 26x42arrow_forward
- Find a range estimate for these problems A) 57x1924 B) 1349x45 C) 547x73951arrow_forwardDraw the image of the following figure after a dilation centered at the origin with a scale factor of 14 退 14 12- 10 5- + Z 6 的 A X 10 12 14 16 18 G min 3 5arrow_forwardkofi makes a candle as a gift for his mom. The candle is a cube with a volume of 8/125 ft cubed. Kofi wants to paint each face of the candle exepct for the bottom. what is the area he will paint?arrow_forward
- 10 6 9. 8 -7- 6. 5. 4- 3. 2 1- -1 0 -1 2 3 4 ·10 5 6 7 00 8 6 10arrow_forwardWeek 3: Mortgages and Amortiza X + rses/167748/assignments/5379530?module_item_id=23896312 11:59pm Points 10 Submitting an external tool Gider the following monthly amortization schedule: Payment # Payment Interest Debt Payment Balance 1 1,167.34 540.54 626.80 259,873.20 2 1,167.34 539.24 628.10 259,245.10 3 1,167.34 With the exception of column one, all amounts are in dollars. Calculate the annual interest rate on this loa Round your answer to the nearest hundredth of a percent. Do NOT round until you calculate the final answer. * Previous a Earrow_forwardCafé Michigan's manager, Gary Stark, suspects that demand for mocha latte coffees depends on the price being charged. Based on historical observations, Gary has gathered the following data, which show the numbers of these coffees sold over six different price values: Price Number Sold $2.70 765 $3.50 515 $2.00 990 $4.30 240 $3.10 325 $4.00 475 Using simple linear regression and given that the price per cup is $1.85, the forecasted demand for mocha latte coffees will be cups (enter your response rounded to one decimal place).arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





