
Concept explainers
Preble Company manufactures one product. Its variable manufacturing
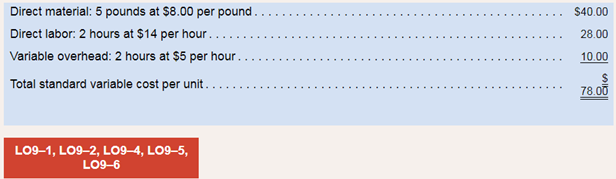
The company also established the following cost formulas for its selling expenses: 
The planning budget for March was based on producing and selling 25.000 units. However, during March the company actually produced and sold 30.000 units and incurred the following costs:
page 42$
- Purchased 160.000 pounds of raw materials at a cost of S7.50 per pound. All of this material was used in production.
- Direct-laborers worked 55.000 hours at a rate of $15.00 per hour. Total variable manufacturing overhead for the month was S280.500.
Total advertising, sales salaries and commissions, and shipping expenses were $210,000, $455,000, and $115.000, respectively.
Required:
12. What amounts of advertising, sales salaries and commissions, and shipping expenses would be included in the company’s flexible budget for March?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
GEN COMBO LOOSELEAF INTRODUCTION TO MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING; CONNECT AC
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning  Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





