
(a)
Interpretation:
The trend of metallic character, atomic size, ionization energy and acidity of oxides is whether increases or decreases from left to right across a period has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
According to physical and chemical properties, the elements can be further divided into metals, non-metals and metalloids.
In a group, the metallic character of an element increases from top to bottom whereas in a period, it decreases from left to right.
The classification elements in the periodic table as metals, nonmetals, or metalloids can be given as
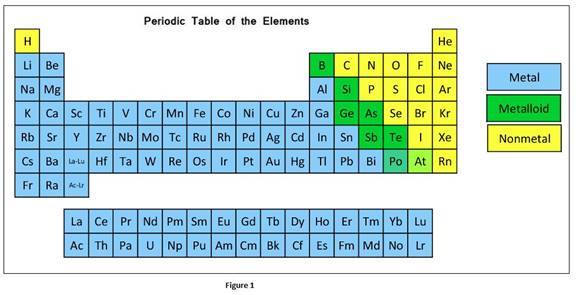
Atomic radius is the distance between the atomic nucleus and outermost shell having electrons of an atom. From the atomic radius, the size of atoms can be visualized
The ionization energy is the minimum energy required to remove the electron from an isolated atom which is in the gaseous state results to give gaseous ion with one positive charge.
Oxide is a compound that is formed when oxygen reacts with another element. Oxides formed with metals are most probably basic. Most of oxides formed with nonmetals are acidic.
(b)
Interpretation:
The trend of metallic character, atomic size, ionization energy and acidity of oxides is whether increases or decreases from top to bottom within a group has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
According to physical and chemical properties, the elements can be further divided into metals, non-metals and metalloids.
In a group, the metallic character of an element increases from top to bottom whereas in a period, it decreases from left to right.
The classification elements in the periodic table as metals, nonmetals, or metalloids can be given as
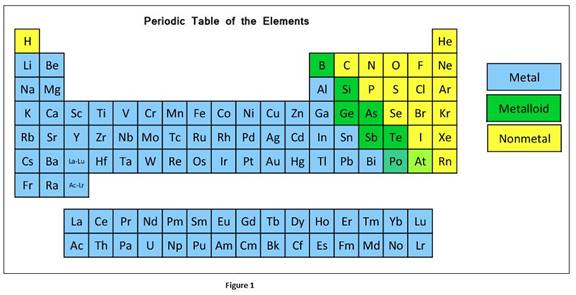
Atomic radius is the distance between the atomic nucleus and outermost shell having electrons of an atom. From the atomic radius, the size of atoms can be visualized
The ionization energy is the minimum energy required to remove the electron from an isolated atom which is in the gaseous state results to give gaseous ion with one positive charge.
Oxide is a compound that is formed when oxygen reacts with another element. Oxides formed with metals are most probably basic. Most of oxides formed with nonmetals are acidic.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK GENERAL CHEMISTRY: THE ESSENTIAL CO
- What is the product of the reaction? F3C. CF3 OMe NaOH / H₂Oarrow_forwardWhat would you expect to be the major product obtained from the following reaction? Please explain what is happening here. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reaction occurs. The correct answer to this question is V.arrow_forwardPlease answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forward
- What is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forwardPlease complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardConsider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forward
- What would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forward
- What would be the reagents and conditions above and below the arrow that will complete the proposed acetoacetic ester synthesis? If it cannot be done efficiently, then I will choose that answer. There could be 2 or 4 reagents involved. Please provide a detailed explanation and drawings showing how it would proceed with the correct reagents.arrow_forwardFor benzene, the ∆H° of vaporization is 30.72 kJ/mol and the ∆S° of vaporization is 86.97 J/mol・K. At 1.00 atm and 228.0 K, what is the ∆G° of vaporization for benzene, in kJ/mol?arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reaction. it is spontaneous only at High T, it is spontaneous at low T it is nonspontaneous at all T it is spontanrous at all T. it is non spontaneous only at low T.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





