
FUND.OF GEN CHEM CHAP 1-13 W/ACCESS
16th Edition
ISBN: 9781323406038
Author: McMurry
Publisher: PEARSON C
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 8.27UKC
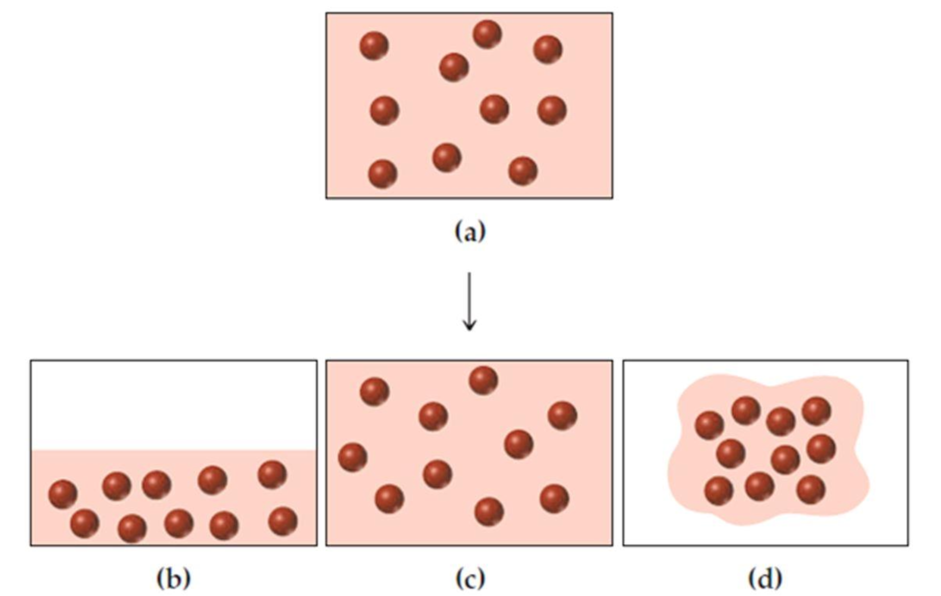
Assume that you have a sample of gas at 350 K in a sealed container, as represented in part (a). Which of the drawings (b)–(d) represents the gas after the temperature is lowered from 350 K to 150 K and if the gas has a boiling point of 200 K? Which drawing represents the gas at 150 K if the gas has a boiling point of 100 K?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Draw the product of this reaction.
Ignore inorganic byproducts.
H
H ⚫OH
HO-
-H
H-
-OH
H-
-OH
CH2OH
Ag*, NH4OH, H2O
Draw Fischer Projection
Draw the product of this reaction.
Ignore inorganic byproducts.
H₂O
-OH
H
⚫OH
HO
H
HO-
CH2OH
Cu2+
Draw Fischer Projection
Draw the product of this reaction.
Ignore inorganic byproducts.
H、
H
-OH
H
⚫OH
H
-OH
CH2OH
Fehlings' solution
⑤
Draw Fischer Projection
Chapter 8 Solutions
FUND.OF GEN CHEM CHAP 1-13 W/ACCESS
Ch. 8.2 - Would you expect the boiling points to increase or...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 8.3PCh. 8.2 - Identify the intermolecular forces (dipoledipole,...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 8.5PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 8.6PCh. 8.4 - What evidence is there that global warming is...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 8.2CIAPCh. 8.4 - Prob. 8.7PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 8.8KCPCh. 8.5 - Prob. 8.3CIAP
Ch. 8.5 - Prob. 8.4CIAPCh. 8.5 - Prob. 8.5CIAPCh. 8.5 - Prob. 8.9PCh. 8.5 - Prob. 8.10PCh. 8.6 - Prob. 8.11PCh. 8.7 - Prob. 8.12PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 8.13PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 8.14KCPCh. 8.9 - Prob. 8.15PCh. 8.10 - Prob. 8.16PCh. 8.10 - Prob. 8.17PCh. 8.10 - Prob. 8.18KCPCh. 8.11 - Prob. 8.19PCh. 8.11 - Prob. 8.20PCh. 8.11 - Prob. 8.21PCh. 8.11 - Prob. 8.22KCPCh. 8.14 - How much heat in kilocalories is required to (a)...Ch. 8.14 - Prob. 8.24PCh. 8.14 - Compare the Hvap values for water, isopropyl...Ch. 8.14 - What is a supercritical fluid?Ch. 8.14 - What are the environmental advantages of using...Ch. 8.14 - Prob. 8.8CIAPCh. 8 - Prob. 8.26UKCCh. 8 - Assume that you have a sample of gas at 350 K in a...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.28UKCCh. 8 - Three bulbs, two of which contain different gases...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.30UKCCh. 8 - The following graph represents the heating curve...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.32UKCCh. 8 - Prob. 8.33UKCCh. 8 - Prob. 8.34APCh. 8 - Identify the predominant intermolecular force in...Ch. 8 - Dimethyl ether (CH3OCH3) and ethanol (C2H5OH) have...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.37APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.38APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.39APCh. 8 - What are the four assumptions of the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.41APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.42APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.43APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.44APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.45APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.46APCh. 8 - Which assumptions of the kinetic-molecular theory...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.48APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.49APCh. 8 - The use of CFCs as refrigerants and propellants in...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.51APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.52APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.53APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.54APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.55APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.56APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.57APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.58APCh. 8 - Which assumptions of the kinetic-molecular theory...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.60APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.61APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.62APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.63APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.64APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.65APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.66APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.67APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.68APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.69APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.70APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.71APCh. 8 - What is the mass of CH4 in a sample that occupies...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.73APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.74APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.75APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.76APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.77APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.78APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.79APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.80APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.81APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.82APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.83APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.84APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.85APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.86APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.87APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.88APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.89APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.90APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.91APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.92APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.93APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.94APCh. 8 - Patients with a high body temperature are often...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.96APCh. 8 - List three kinds of crystalline solids, and give...Ch. 8 - The heat of fusion of acetic acid, the principal...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.99APCh. 8 - Prob. 8.100CPCh. 8 - Prob. 8.101CPCh. 8 - Prob. 8.102CPCh. 8 - Prob. 8.103CPCh. 8 - Prob. 8.104CPCh. 8 - Prob. 8.105CPCh. 8 - Prob. 8.106CPCh. 8 - Prob. 8.107CPCh. 8 - Prob. 8.108CPCh. 8 - Ethylene glycol, C2H6O2, has one OH bonded to each...Ch. 8 - Prob. 8.110CPCh. 8 - Prob. 8.111GPCh. 8 - Prob. 8.112GPCh. 8 - Prob. 8.113GPCh. 8 - Prob. 8.114GPCh. 8 - Prob. 8.115GP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO C=0 H ⚫OH H ⚫OH HO- H HO H CH2OH Tollens' solution Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H-C=O HO H HO H H- ⚫OH HO H CH2OH HNO3, H2O Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO HO- HO H HO ∙H HO CH2OH NaBH4, CH3OH Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forward
- Draw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Но сво HO H HO H H OH H -OH CH2OH H2 Pd Draw Fischer Projectionarrow_forwardDraw the Haworth projection for Gulose-ẞ-1,6-sorbose and answer the following questions. (Gulose will be in the pyranose form and Sorbose will be in the furanose form) a. Label the reducing and nonreducing ends of the disaccharide b. Label the glycosidic bond c. Circle the anomeric carbons and label them as hemiacetals or acetals. d. Can this disaccharide undergo mutarotation?arrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H OH HO HO HO ·H H OH H OH excess CH3CH2I KOHarrow_forward
- Draw the Haworth structures for the following: a. α-D-Gulopyranose b. ẞ-D-Sorbofuranose c. The two possible isomers of a-D-altrose (furanose and pyranose forms)arrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO H ⚫OH HO- ∙H H- -OH H ⚫OH CH2OH HNO3, H2Oarrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HO CH2OH OH OH OH excess CHзI Ag2Oarrow_forward
- Draw the product of the reaction below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HOH HO H -OAC H OH OH H excess CHзI Ag2Oarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H- H ⚫OH HO H H- OH H ⚫OH CH2OH NaBH4, CH3OHarrow_forwardDraw B-D-galactopyranose and ẞ-D-mannopyranose in their chair conformations. Label the axial and equatorial positions.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage LearningBasic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:Cengage
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage LearningBasic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...NursingISBN:9781285244662Author:WhitePublisher:Cengage




Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781337711067
Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna Balac
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Basic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C...
Nursing
ISBN:9781285244662
Author:White
Publisher:Cengage
GCSE Chemistry - Acids and Bases #34; Author: Cognito;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vt8fB3MFzLk;License: Standard youtube license