
Concept explainers
Write Lewis structures that obey the octet rule (duet rule for H) for each of the following molecules. Carbon is the central atom in CH4, nitrogen is the central atom in NH3, and oxygen is the central atom in H2O.
a. F2
b. O2
c. CO
d. CH4
e. NH3
f. H2O
g. HF
(a)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure is to be drawn for the given molecules.
Concept introduction: The Lewis structure is also known as dot structure. This structure depicts the bonding between atoms and the lone pairs of electrons if exists.
The octet rule states that atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons to get the electronic configuration of nearest noble gas.
To determine: The Lewis structure of the molecule
Answer to Problem 81E
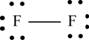
Explanation of Solution
The first step in determining the Lewis structure is to determine the number of valence electrons. The atomic number of fluorine
The valence electron of fluorine is 7
The fluorine molecule
The skeletal structure of
Each fluorine atom requires one electron to complete the octet. Hence, the mutual sharing of two electrons takes place. The 12 valence electrons present are placed as lone pairs in such a way that each atom gets three lone pairs.
The Lewis structure of
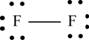
Figure 1
(b)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure is to be drawn for the given molecules.
Concept introduction: The Lewis structure is also known as dot structure. This structure depicts the bonding between atoms and the lone pairs of electrons if exists.
The octet rule states that atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons to get the electronic configuration of nearest noble gas.
To determine: The Lewis structure of the molecule
Answer to Problem 81E
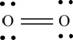
Explanation of Solution
The first step in determining the Lewis structure is to determine the number of valence electrons. The atomic number of oxygen
The valence electron of oxygen is 6
The oxygen molecule
The skeletal structure of
Each oxygen atom requires two electrons to complete the octet. Hence, the mutual sharing of four electrons takes place. The 8 valence electrons present are placed as lone pairs in such a way that each atom gets two lone pairs.
The Lewis structure of
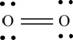
Figure 2
(c)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure is to be drawn for the given molecules.
Concept introduction: The Lewis structure is also known as dot structure. This structure depicts the bonding between atoms and the lone pairs of electrons if exists.
The octet rule states that atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons to get the electronic configuration of nearest noble gas.
To determine: The Lewis structure of the molecule
Answer to Problem 81E

Explanation of Solution
The first step in determining the Lewis structure is to determine the number of valence electrons. The atomic number of oxygen is 8 and its electronic configuration is,
The valence electron of oxygen is 6
The atomic number of carbon
The valence electron of carbon is 4
The molecule
The skeletal structure of
Each oxygen atom requires two electrons to complete the octet whereas carbon requires four electrons to complete the octet. Hence, the mutual sharing of six electrons takes place which is represented by triple bond. The 4 valence electrons left are placed as lone pairs in such a way that each atom gets one lone pair.
The Lewis structure of

Figure 3
(d)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure is to be drawn for the given molecules.
Concept introduction: The Lewis structure is also known as dot structure. This structure depicts the bonding between atoms and the lone pairs of electrons if exists.
The octet rule states that atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons to get the electronic configuration of nearest noble gas.
To determine: The Lewis structure of the molecule
Answer to Problem 81E
Explanation of Solution
The first step in determining the Lewis structure is to determine the number of valence electrons. The atomic number of carbon is 6 and its electronic configuration is,
The valence electron of carbon is 4
The atomic number of hydrogen
The valence electron of hydrogen is 1
The molecule
The skeletal structure of
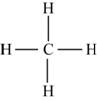
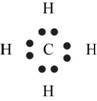
Figure 4
Each hydrogen atom requires one electron to complete the octet whereas carbon requires four electrons to complete the octet. In the molecule
The Lewis structure of

Figure 5
(e)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure is to be drawn for the given molecules.
Concept introduction: The Lewis structure is also known as dot structure. This structure depicts the bonding between atoms and the lone pairs of electrons if exists.
The octet rule states that atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons to get the electronic configuration of nearest noble gas.
To determine: The Lewis structure of the molecule
Answer to Problem 81E
Explanation of Solution
The first step in determining the Lewis structure is to determine the number of valence electrons. The atomic number of nitrogen
The valence electron of nitrogen is 5
The atomic number of hydrogen is 1 and its electronic configuration is,
The valence electron of hydrogen is 1
The molecule
The skeletal structure of
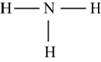
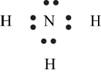
Figure 6
Each hydrogen atom requires one electron to complete the octet whereas nitrogen requires three electrons to complete the octet. In the molecule
The Lewis structure of

Figure 7
(f)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure is to be drawn for the given molecules.
Concept introduction: The Lewis structure is also known as dot structure. This structure depicts the bonding between atoms and the lone pairs of electrons if exists.
The octet rule states that atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons to get the electronic configuration of nearest noble gas.
To determine: The Lewis structure of the molecule
Answer to Problem 81E
Explanation of Solution
The first step in determining the Lewis structure is to determine the number of valence electrons. The atomic number of oxygen is 8 and its electronic configuration is,
The valence electron of oxygen is 6
The atomic number of hydrogen is 1 and its electronic configuration is,
The valence electron of hydrogen is 1
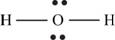
The molecule
The skeletal structure of
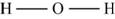
Figure 8
Each hydrogen atom requires one electron to complete the octet whereas oxygen requires two electrons to complete the octet. In the molecule
The Lewis structure of

Figure 9
(g)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure is to be drawn for the given molecules.
Concept introduction: The Lewis structure is also known as dot structure. This structure depicts the bonding between atoms and the lone pairs of electrons if exists.
The octet rule states that atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons to get the electronic configuration of nearest noble gas.
To determine: The Lewis structure of the molecule
Answer to Problem 81E
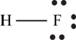
Explanation of Solution
The first step in determining the Lewis structure is to determine the number of valence electrons. The atomic number of fluorine is 9 and its electronic configuration is,
The valence electron of fluorine is 7
The atomic number of hydrogen is 1 and its electronic configuration is,
The valence electron of hydrogen is 1
The molecule
The skeletal structure of
Each hydrogen atom requires one electron to complete the octet whereas fluorine requires one electron to complete the octet. Hence, the mutual sharing of eight electrons takes place.
The Lewis structure of
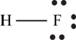
Figure 10
The Lewis dot structure is drawn to satisfy the octets of atoms. The octet rule states that elements gain or lose electrons to get the nearest noble gas configuration.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemistry
- What is the preparation of 500 mL of 100mM MOPS buffer (pH=7.5) starting with 1 M MOPS and 1 M NaOH? How would I calculate the math?arrow_forwardIndicate the correct option.a) Isopolianions are formed around metallic atoms in a low oxidation state.b) Non-metals such as N, S, C, Cl, ... give rise to polyacids (oxygenated).c) Both are incorrect.arrow_forward14. Which one of the compounds below is the major organic product obtained from the following series of reactions? Br OH OH CH3O™ Na+ H*, H₂O SN2 HO OH A B C D 0 Earrow_forward
- Wavelength (nm) I'm not sure what equation I can come up with other than the one generated with my graph. Can you please show me the calculations that were used to find this equation? Give an equation that relates energy to wavelength. Explain how you arrived at your equation. Wavelength Energy (kJ/mol) (nm) 350 341.8 420 284.8 470 254.5 530 225.7 580 206.3 620 192.9 700 170.9 750 159.5 Energy vs. Wavelength (Graph 1) 400 350 y=-0.4367x+470.82 300 250 200 150 100 50 O 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 Energy (kJ/mol)arrow_forward5. Draw molecular orbital diagrams for superoxide (O2¯), and peroxide (O2²-). A good starting point would be MO diagram for O2 given in your textbook. Then: a) calculate bond orders in superoxide and in peroxide; indicate which species would have a stronger oxygen-oxygen bond; b) indicate which species would be a radical. (4 points)arrow_forward16. Which one of the compunds below is the final product of the reaction sequence shown here? عملاء .OH Br. (CH3)2CH-C=C H+,H,O 2 mol H2, Pt A OH B OH D OH E OH C OHarrow_forward
- Indicate whether any of the two options is correct.a) The most common coordination structure for isopolianions is the prismb) Heteropolianions incorporate alkaline cations into their structuresarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't use hand ratingarrow_forwardWavelength (nm) I'm not sure what equation I can come up with other than the one generated with my graph. Can you please show me the calculations that were used to find this equation? Give an equation that relates energy to wavelength. Explain how you arrived at your equation. Wavelength Energy (kJ/mol) (nm) 350 341.8 420 284.8 470 254.5 530 225.7 580 206.3 620 192.9 700 170.9 750 159.5 Energy vs. Wavelength (Graph 1) 400 350 y=-0.4367x+470.82 300 250 200 150 100 50 O 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 Energy (kJ/mol)arrow_forward
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
 Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





