
Organic Chemistry
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781118133576
Author: T. W. Graham Solomons, Craig Fryhle
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 7Q
Which reaction sequence converts cyclohexene to cis-1,2-cyclohexanediol? That is,
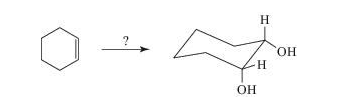
(a) H2O2
(b)
(1) O3
(2) Me2S
(c)
(1) OsO4
(2) NaHSO3/H2O
(d)
(1) 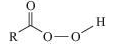
(2) H3O+/H2O
(e) More than one of these
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Draw a curved arrow mechanism for the reaction, adding steps as necessary. Be sure to include all electrons that are necessary to the mechanism and all
nonzero formal charges.
C
Ö-H
H
+
-S-OH
.0.
Add/Remove step
X
टे
Click and drag to start
drawing a structure.
Draw a curved arrow mechanism for its formation. You may need to re-draw structures to show certain bonds. Ensure that HSO is used as the base to
deprotonate the ẞ carbon when necessary.
C
HO
: OH
HO: OH
=s
=
+
1
Add/Remove step
X
Click and drag to start
drawing a structure.
Which of the following could 1,2-ethanediol be directly synthesized from?
OH
HO
О
0
0.
O
?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 8 - Prob. 1PPCh. 8 - PRACTICE PROBLEM Outline mechanisms for the...Ch. 8 - Practice Problem 8.3 Provide mechanistic...Ch. 8 - Prob. 4PPCh. 8 - PRACTICE PROBLEM
8.5 In one industrial synthesis...Ch. 8 - Prob. 6PPCh. 8 - Prob. 7PPCh. 8 - Prob. 8PPCh. 8 - Prob. 9PPCh. 8 - PRACTICE PROBLEM (a) Outline a likely mechanism...
Ch. 8 - Prob. 11PPCh. 8 - Prob. 12PPCh. 8 - Practice Problem 8.13
Specify the appropriate...Ch. 8 - Prob. 14PPCh. 8 - Practice Problem 8.15 Write a mechanism to explain...Ch. 8 - Prob. 16PPCh. 8 - Prob. 17PPCh. 8 - Prob. 18PPCh. 8 - Practice Problem 8.19 Treating cyclohexene with l,...Ch. 8 - Prob. 20PPCh. 8 - Practice Problem 8.21
Predict the products of the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 22PPCh. 8 - Prob. 23PPCh. 8 - Prob. 24PPCh. 8 - Prob. 25PPCh. 8 - Write structural formulas for the products that...Ch. 8 - Prob. 27PCh. 8 - Prob. 28PCh. 8 - 8.29. Give the structure of the products that you...Ch. 8 - Give the structure of the products you would...Ch. 8 - Prob. 31PCh. 8 - Prob. 32PCh. 8 - Prob. 33PCh. 8 - Prob. 34PCh. 8 - Prob. 35PCh. 8 - Prob. 36PCh. 8 - Prob. 37PCh. 8 - When 3, 3-dimethyl-2-butanol is neared with...Ch. 8 - Prob. 39PCh. 8 - Prob. 40PCh. 8 - Prob. 41PCh. 8 - The reaction of bromine with cyclohexene involves...Ch. 8 - Prob. 43PCh. 8 - Internal alkynes can be isomerized to terminal...Ch. 8 - 8.43. Write a mechanism that explains the...Ch. 8 - 8.44. Write a mechanism for the following...Ch. 8 - Write a mechanism that explains formation of the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 48PCh. 8 - 8.49 Farnesene (below) is a compound found in the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 50PCh. 8 - Limonene is a compound found in orange oil and...Ch. 8 - Prob. 52PCh. 8 - Synthesize the following compound starting with...Ch. 8 - Prob. 54PCh. 8 - Predict features of their IR spectra that you...Ch. 8 - Deduce the structures of compounds A, B, and C,...Ch. 8 - Ricinoleic acid, a compound that can be isolated...Ch. 8 - 8.54. There are two dicarboxylic acids with the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 59PCh. 8 - Prob. 60PCh. 8 - Prob. 61PCh. 8 - Prob. 64PCh. 8 - Prob. 66PCh. 8 - Prob. 62PCh. 8 - Prob. 63PCh. 8 - 8.65
(a)Based on the following information, draw...Ch. 8 - Triethylamine, (C2H5)3N, like all amines, has a...Ch. 8 - (a) Synthesize (3S, 4R)-3,...Ch. 8 - Prob. 2LGPCh. 8 - Prob. 3LGPCh. 8 - Prob. 4LGPCh. 8 - 8.1 A hydrocarbon whose molecular formula is...Ch. 8 - Prob. 2QCh. 8 - Give the major product of the reaction of...Ch. 8 - The compound shown here is best prepared by which...Ch. 8 - 8.5 A compound whose formula is C6H10 (Compound A)...Ch. 8 - Prob. 6QCh. 8 - 8.7 Which reaction sequence converts cyclohexene...Ch. 8 - Which of the following sequences leads to the best...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Write a statement or two describing the movement of water through the hydrologic cycle, including several of th...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
8. A human maintaining a vegan diet (containing no animal products) would be a:
a. producer
b. primary consume...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
39. Biologists think that some spiders “tune” strands of their web
to give enhanced response at frequencies co...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Which one of the following is not a fuel produced by microorganisms? a. algal oil b. ethanol c. hydrogen d. met...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Compare each of the mechanisms listed here with the mechanism for each of the two parts of the acid-catalyzed h...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
The following data were obtained from a disk-diffusion test. Antibiotic Zone of Inhibition A 15 mm B 0 mm c 7 m...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Design a synthesis of 1,2-diethoxyethane from an alkene. Select the single best answer for each part. Part: 0/3 Part 1 of 3 Which of the following could 1,2-diethoxyethane be directly synthesized from? O HO 0 HO.... OH HO HO × 5 > ?arrow_forwardDraw the skeletal structure of the major organic product of each step of the reaction sequence. Part: 0/2 Part 1 of 2 Part: 1/2 Part 2 of 2 Continue OH NaH Na Na Br + Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X : X G : Garrow_forwardpleasearrow_forward
- please help me please pleasearrow_forwardUsing reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) = 2NH3 (g) AG⁰ = -34. KJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 8.06 atm of nitrogen (N2) and 2.58 atm of ammonia (NH3) at 106. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: ? rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2 tend to rise or fall? ☐ x10 fall Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding H₂? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding H₂? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N2 will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding H₂? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of H₂ needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. yes no ☐ atm ☑ 5 00. 18 Ararrow_forwardi need help with the followingarrow_forward
- Using reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: 2NO(g) +Cl₂ (g) = 2NOC1 (g) AGº = -41. kJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 8.90 atm of chlorine (C12) and 5.71 atm of nitrosyl chloride (NOC1) at 1075. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of NOCI tend to rise or fall? x10 fall Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding NO? In other words, if you said the pressure of NOCI will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding NO? Similarly, if you said the pressure of NOCI will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding NO? yes no If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of NO needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. atm ☑ 18 Ararrow_forwardIdentifying the major species in weak acid or weak base equilibria The preparations of two aqueous solutions are described in the table below. For each solution, write the chemical formulas of the major species present at equilibrium. You can leave out water itself. Write the chemical formulas of the species that will act as acids in the 'acids' row, the formulas of the species that will act as bases in the 'bases' row, and the formulas of the species that will act as neither acids nor bases in the 'other' row. You will find it useful to keep in mind that HCN is a weak acid. acids: 0.29 mol of NaOH is added to 1.0 L of a 1.2M HCN solution. bases: ☑ other: 0.09 mol of HCl is added to acids: 1.0 L of a solution that is bases: 0.3M in both HCN and KCN. other: 0,0,... ? 00. 18 Ar 日arrow_forwardIdentifying the major species in weak acid or weak base equilibria The preparations of two aqueous solutions are described in the table below. For each solution, write the chemical formulas of the major species present at equilibrium. You can leave out water itself. Write the chemical formulas of the species that will act as acids in the 'acids' row, the formulas of the species that will act as bases in the 'bases' row, and the formulas of the species that will act as neither acids nor bases in the 'other' row. You will find it useful to keep in mind that HF is a weak acid. acids: 0.2 mol of KOH is added to 1.0 L of a 0.5 M HF solution. bases: Х other: ☐ acids: 0.10 mol of HI is added to 1.0 L of a solution that is 1.4M in both HF and NaF. bases: other: ☐ 0,0,... ด ? 18 Ararrow_forward
- Identifying the major species in weak acid or weak base equilibria The preparations of two aqueous solutions are described in the table below. For each solution, write the chemical formulas of the major species present at equilibrium. You can leave out water itself. Write the chemical formulas of the species that will act as acids in the 'acids' row, the formulas of the species that will act as bases in the 'bases' row, and the formulas of the species that will act as neither acids nor bases in the 'other' row. You will find it useful to keep in mind that NH3 is a weak base. acids: ☐ 1.8 mol of HCl is added to 1.0 L of a 1.0M NH3 bases: ☐ solution. other: ☐ 0.18 mol of HNO3 is added to 1.0 L of a solution that is 1.4M in both NH3 and NH₁Br. acids: bases: ☐ other: ☐ 0,0,... ? 000 18 Ar B 1arrow_forwardUsing reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: 2NH3 (g) = N2 (g) +3H₂ —N2 (g) AGº = 34. kJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 4.19 atm of ammonia (NH3) and 9.94 atm of nitrogen (N2) at 378. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of NH 3 tend to rise or fall? ☐ x10 fall Х Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding H₂? In other words, if you said the pressure of NH 3 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding H₂? Similarly, if you said the pressure of NH3 will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding H₂? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of H₂ needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. yes no atm 00. 18 Ar 무ㅎ ?arrow_forwardIdentifying the major species in weak acid or weak base equilibria The preparations of two aqueous solutions are described in the table below. For each solution, write the chemical formulas of the major species present at equilibrium. You can leave out water itself. Write the chemical formulas of the species that will act as acids in the 'acids' row, the formulas of the species that will act as bases in the 'bases' row, and the formulas of the species that will act as neither acids nor bases in the 'other' row. You will find it useful to keep in mind that HF is a weak acid. 2.2 mol of NaOH is added to 1.0 L of a 1.4M HF solution. acids: П bases: Х other: ☐ ப acids: 0.51 mol of KOH is added to 1.0 L of a solution that is bases: 1.3M in both HF and NaF. other: ☐ 00. 18 Ararrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

IR Spectroscopy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_TmevMf-Zgs;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY