
Concept explainers
For the reaction
(a) Predict the enthalpy of reaction from the average bond enthalpies in Table 8.6. (b) Calculate the enthalpy of reaction from the standard enthalpies of formation (see Appendix 2) of the reactant and product molecules, and compare the result with your answer for part (a).
Interpretation:
The
Concept Introduction:
The enthalpy of the reaction by using the bond enthalpy is calculated by the expression, which is as:
Here,
The enthalpy of the reaction by using the standard enthalpy of formation is calculated by the expression, which is as:
Here,
Rules to write the Lewis structure are as:
The skeletal structure of the compound is drawn in which the less electronegative element is placed as the central atom, which is surrounded by substituent atoms.
The total number of valence electrons for the compound is determined.
Subtract two electrons for each bond in the skeletal structure from the total number of valence electrons to know the number of remaining electrons.
Complete the octet of each terminal atom by placing a pair of electrons from the remaining electrons.
If any of the electrons are remaining after completing the octet of terminal atoms, place the remaining electrons as a pair on the central atom.
Answer to Problem 79QP
Solution:
The
The
Explanation of Solution
a)The enthalpy of reaction from the average bond enthalpies.
The given reaction is
The bond enthalpy value of
The bond enthalpy value of
The bond enthalpy value of
The bond enthalpy value of
The bond enthalpy value of
The Lewis structure of the given reaction is drawn in order to determine which bond is formed and which is broken.
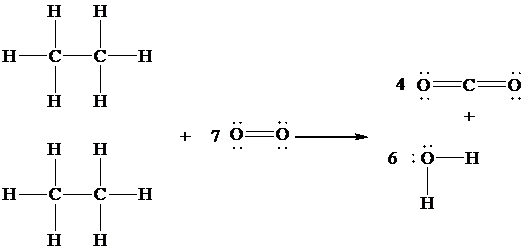
In the given reaction,
The
Substitute the value
b) The enthalpy of reaction from the standard enthalpies of formation
The given reaction is
The value of
The value of
The value of
The value of
Here,
The value of change in the enthalpy for atoms in their standard state is zero. In the reaction,
Substitute
The values of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
CHEMISTRY >CUSTOM<
- Determine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction LiNO3arrow_forwardAn unknown weak acid with a concentration of 0.410 M has a pH of 5.600. What is the Ka of the weak acid?arrow_forward(racemic) 19.84 Using your reaction roadmaps as a guide, show how to convert 2-oxepanone and ethanol into 1-cyclopentenecarbaldehyde. You must use 2-oxepanone as the source of all carbon atoms in the target molecule. Show all reagents and all molecules synthesized along the way. & + EtOH H 2-Oxepanone 1-Cyclopentenecarbaldehydearrow_forward
- R₂ R₁ R₁ a R Rg Nu R₂ Rg R₁ R R₁₂ R3 R R Nu enolate forming R₁ R B-Alkylated carbonyl species or amines Cyclic B-Ketoester R₁₁ HOB R R₁B R R₁₂ B-Hydroxy carbonyl R diester R2 R3 R₁ RB OR R₂ 0 aB-Unsaturated carbonyl NaOR Aldol HOR reaction 1) LDA 2) R-X 3) H₂O/H₂O ketone, aldehyde 1) 2°-amine 2) acid chloride 3) H₂O'/H₂O 0 O R₁ R₁ R R₁ R₁₂ Alkylated a-carbon R₁ H.C R₁ H.C Alkylated methyl ketone acetoacetic ester B-Ketoester ester R₁ HO R₂ R B-Dicarbonyl HO Alkylated carboxylic acid malonic ester Write the reagents required to bring about each reaction next to the arrows shown. Next, record any regiochemistry or stereochemistry considerations relevant to the reaction. You should also record any key aspects of the mechanism, such as forma- tion of an important intermediate, as a helpful reminder. You may want to keep track of all reactions that make carbon-carbon bonds, because these help you build large molecules from smaller fragments. This especially applies to the reactions in…arrow_forwardProvide the reasonable steps to achieve the following synthesis.arrow_forwardIdentify which compound is more acidic. Justify your choice.arrow_forward
- Provide the reasonable steps to achieve the following synthesis.arrow_forwardWhen anisole is treated with excess bromine, the reaction gives a product which shows two singlets in 1H NMR. Draw the product.arrow_forward(ii) Draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction: CI NaOH heat OH (hint: SNAr Reaction) :arrow_forward
 World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





