
Concept explainers
In the circuit of Fig. 8.95, a 3 mF capacitor is accidentally installed instead of the inductor. Unfortunately, that’s not the end of the problems, as it’s later determined that the real capacitor is not really well modeled by an ideal capacitor, and the dielectric has a resistance of 10 kΩ (which should be viewed as connected in parallel to the ideal capacitor). (a) Compute the circuit time constant with and without taking the dielectric resistance into account. By how much does the dielectric change your answer? (b) Calculate vx at t = 200 ms. Does the dielectric resistance affect your answer significantly? Explain.
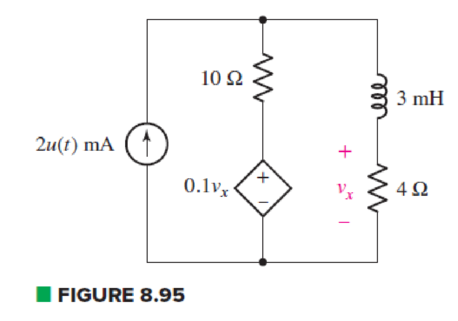
(a)
Find the value of circuit time constant with and without taking dielectric resistance and explain the change in time constant by dielectric resistance.
Answer to Problem 77E
Value of time constant without dielectric is
Explanation of Solution
Given Data:
Value of capacitor by which the
Value of dielectric resistance is
Formula used:
The expression for resistance is as follows:
Here,
The expression for the circuit time constant is as follows:
Here,
Calculation:
To find equivalent resistance of a circuit seen by the capacitor, open circuit the inductor and replace all independent sources by their internal resistances. That is, replace current source by open circuit.
Circuit contains dependent voltage source. So to find equivalent resistance connect an arbitrary voltage source of
The circuit diagram is redrawn as shown in Figure 1.
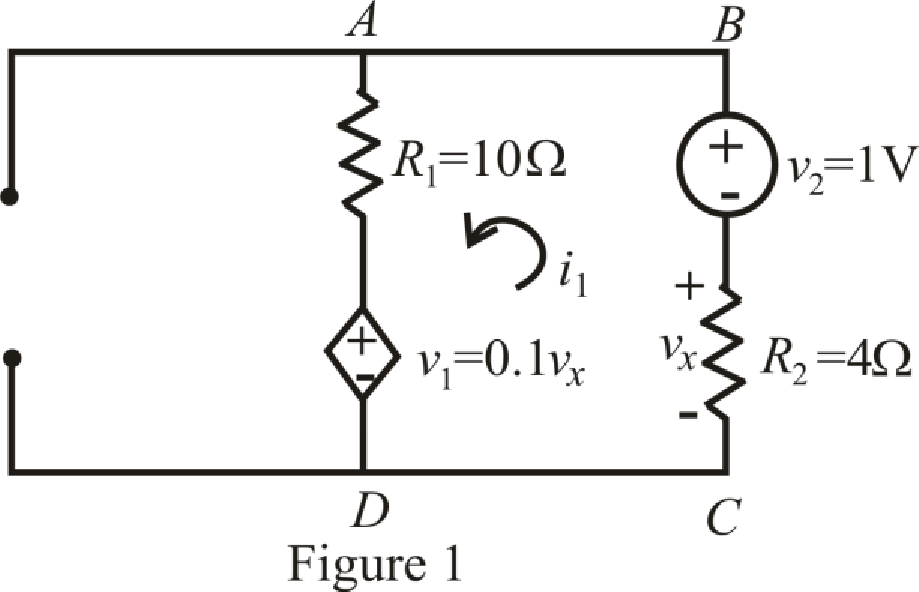
Refer to the redrawn Figure 1.
Circuit is drawn for without dielectric resistor.
The expression for Kirchhoff’s voltage law in mesh
Here,
Substitute
The expression for
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Rearrange equation (6) for
Simplify for
Substitute
Substitute
So, value of time constant without dielectric is
To find equivalent resistance of a circuit, independent sources are replaced by their internal resistances. Therefore, replace current source by open circuit.
Circuit is containing dependent voltage source. So, to find equivalent resistance connect a voltage source of
The circuit diagram is redrawn as shown in Figure 2.
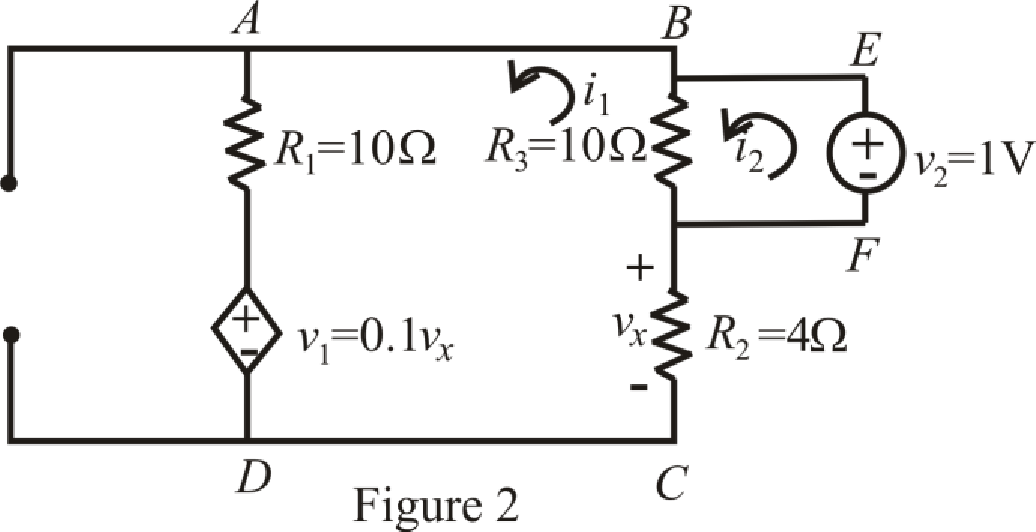
Refer to the redrawn Figure 2:
Circuit is drawn for resistor with dielectric.
The expression for KVL in mesh
Here,
The expression for KVL in mesh
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Rearrange (10) for
Substitute
Rearrange equation (12) for
Substitute
Rearrange equation (13) for
Simplify for
Substitute
Substitute
So value of time constant with dielectric is
The expression for percentage change in time constant with dielectric resistor is as follows;
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, value of time constant without dielectric is
(b)
Calculate
Answer to Problem 77E
Value of voltage
Explanation of Solution
Given Data:
Value of time
Formula used:
The expression for voltage is as follows:
Here,
The expression for the final response is as follows:
Here,
The expression for current flowing through capacitor is as follows:
Here,
Calculation:
The circuit diagram is redrawn as shown in Figure 3 for
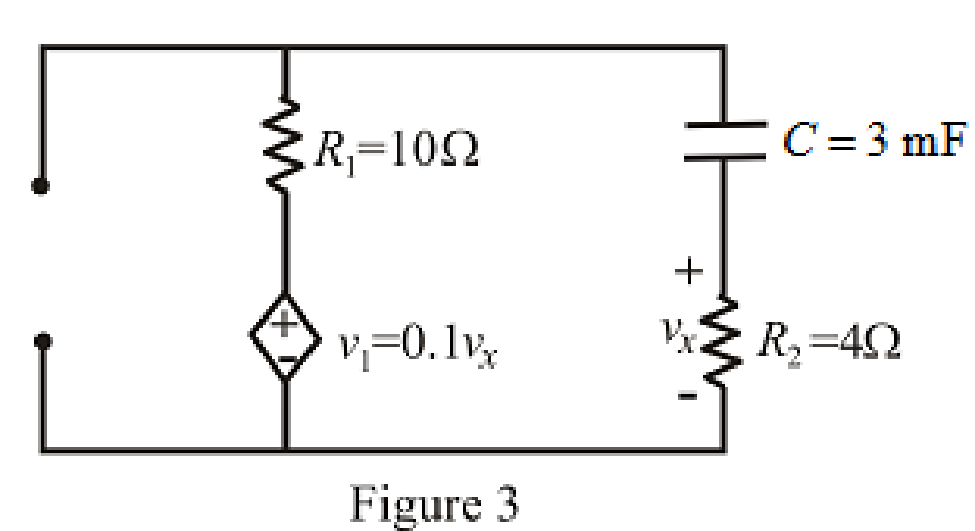
Refer to the redrawn Figure 3:
Circuit is drawn for resistor without dielectric.
As there is no independent source present in the circuit which means voltage across capacitor is also
So, value of
At
Therefore,
So,
The circuit diagram is redrawn as shown in Figure 4 for
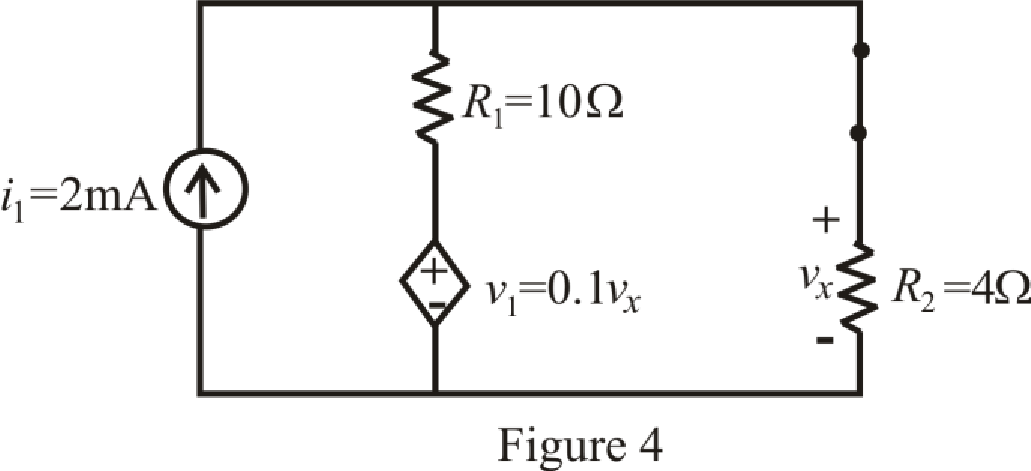
At
So, capacitor behaves as open circuit.
The circuit diagram is redrawn as shown in Figure 5 for
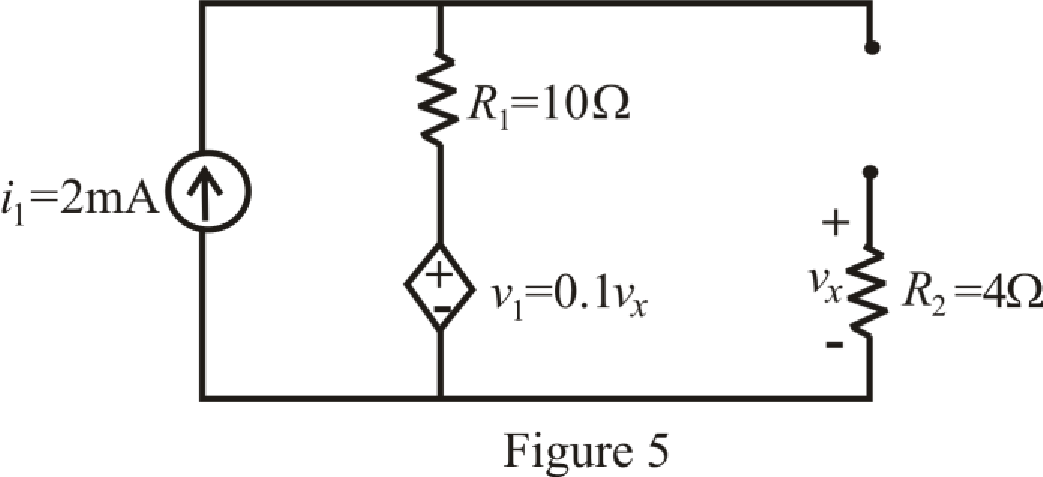
Refer to the redrawn Figure 5:
The expression for voltage
Here,
As capacitor is open circuited, current flowing through resistor
Which means value of voltage
Substitute
The circuit diagram is redrawn as shown in Figure 6 for
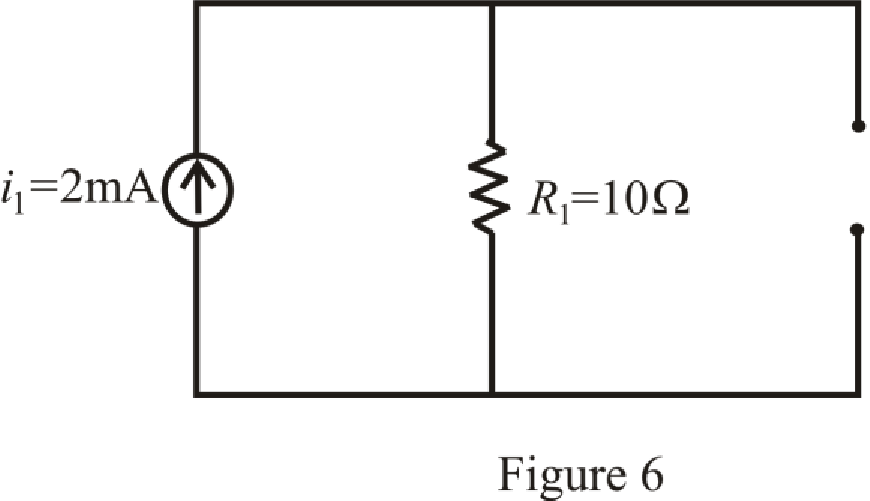
Refer to the redrawn Figure 6:
Substitute
So,
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The expression for voltage
Here,
Substitute
So, value of voltage
Circuit is drawn for resistor with dielectric.
The circuit diagram is redrawn as shown in Figure 7 for
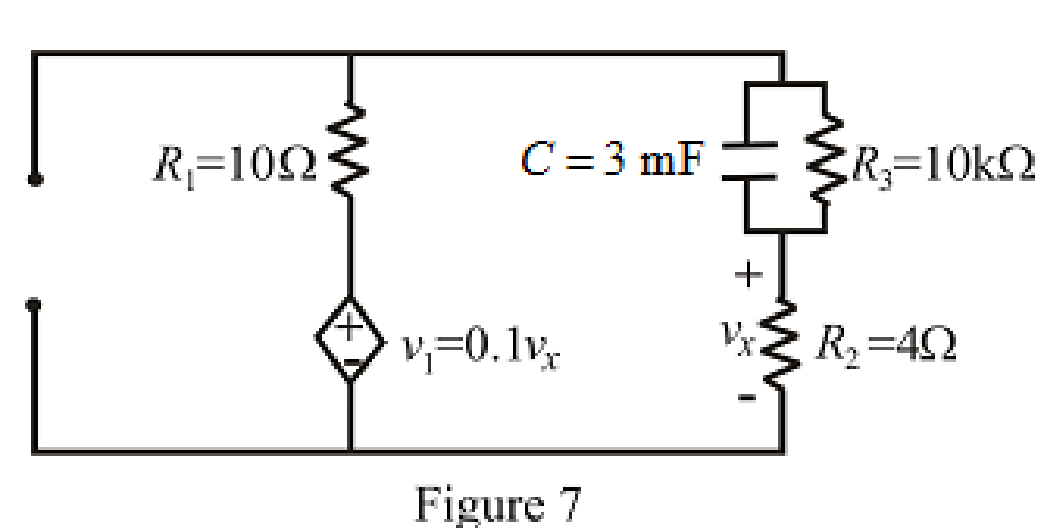
Refer to the redrawn Figure 7:
As there is no independent source present in the circuit which means voltage across capacitor is also
So, value of
At
Therefore,
So,
The circuit diagram is redrawn as shown in Figure 8for
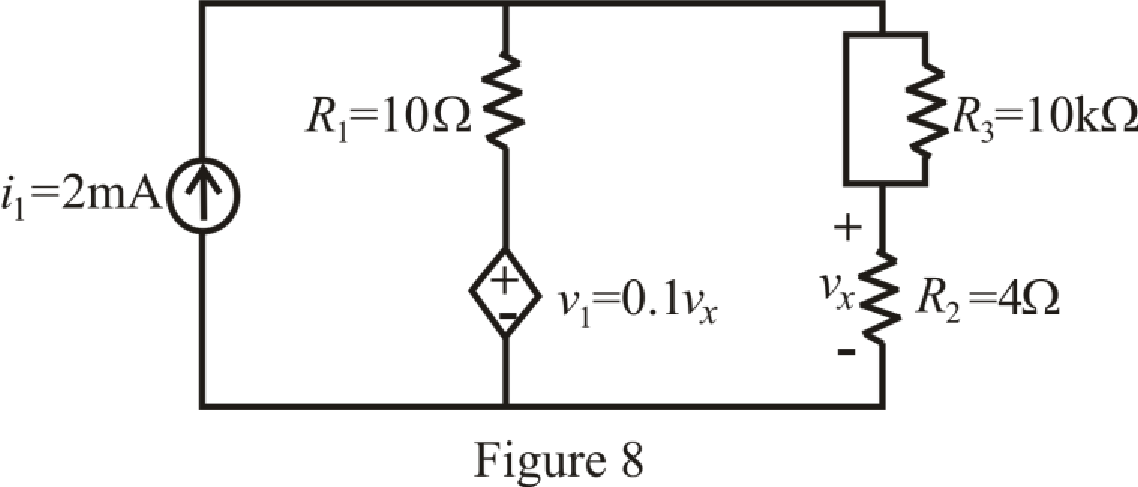
At
So, capacitor behaves as open circuit.
The circuit diagram is redrawn as shown in Figure 9 for
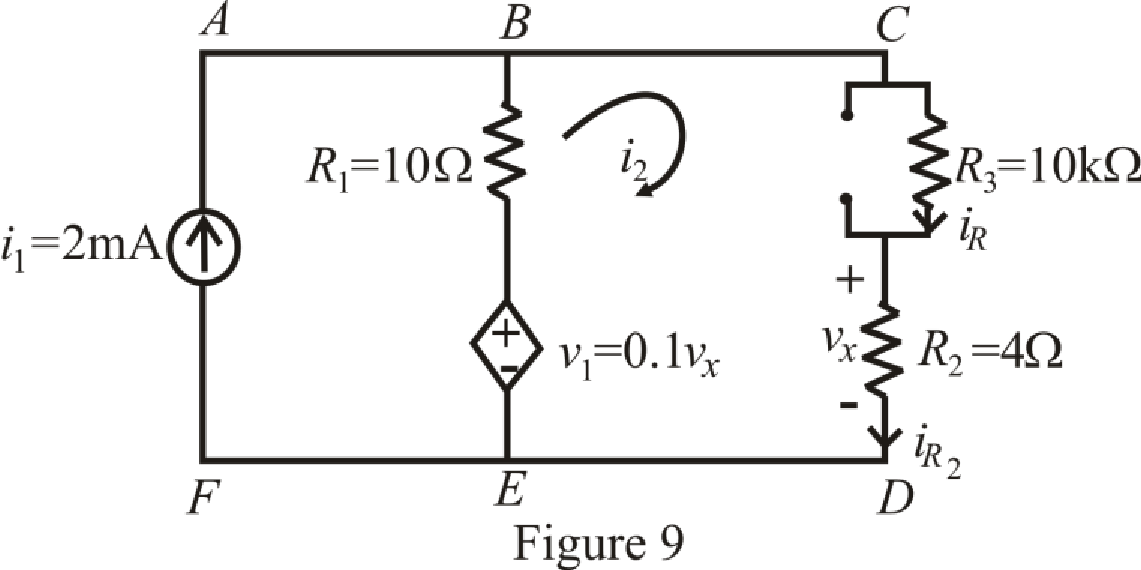
Refer to the redrawn Figure 9:
The expression for KVL in mesh
Here,
Substitute
The expression for voltage
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Rearrange equation (24) for
Simplify for
Substitute
So,
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The expression for current
Here,
Substitute
The expression for current
Here,
Substitute
The expression for voltage
Here,
Substitute
So value of voltage
The expression for percentage change in voltage
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, value of voltage
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
ENGINEERING CIRCUIT...(LL)>CUSTOM PKG.<
- THE SUBJECT IS BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Chapter 11. Capacitorarrow_forward8. a). What are the values of the inductor voltage and current and the capacitor voltage and current assuming the switch has been closed for a very long time. VL= IL = Vc = Ic= 10 v 1H V₁ 000 502 HI 292 Ic↓ 1F Vcarrow_forwardIf two capacitances C, and C, are connected in parallel then the equivalent capacitance is given by: (a) C,C2 (c) C, + C2 (b) CJC, (d) C,/C2arrow_forward
- A capacitor has a capacitance of 0.1 μF with air as the dielectric. If the dielectric material is changed from air to a ceramic material with a dielectric constant of 600, what is the new capacitance? (Note: Neither air nor Ceramic capacitors this large are available.)arrow_forwardA capacitor has been connected in series with a resistor to a DC source at t=0. If the capacitor has an initial voltage R$ Vo=2V with same orientation of the source voltage, then the capacitor voltage v.(t) is A (tRC)arrow_forwardQ8. What is the charge of the second capacitor(C2)? A) 64mc B) 32mc C) 16me D) 48mc E) 24mc C2=8mf] C1=6mf C3-4 mf V=12Varrow_forward
- A circuit having a 120µF capacitor and a 10kN resistance in series is connected across a 230-V dc supply. Determine the final energy (in Joules) stored in the capacitor. Answer:arrow_forwardTRUE or FALSE a. A discontinuous change in the voltage requires an infinite current thus a capacitor resists an abrupt change in the voltage across it. b. The inductor takes power from the circuit when storing energy and delivers power to the circuit when returning previously stored energy.arrow_forward8. A coil of inductance 9 H and resistance 50 2 in series with a capacitor is supplied at constant voltage from a variable frequency source. If the maximum current of 1 A occurs at 75 Hz, find the frequency when the current is 0.5 Aarrow_forward
- A pure capacitance of C =34 µF capacitor is connected to a V = 126 V, 50 Hz supply. The current taken by the capacitor is given by Find the Ceg for the circuit given below: 2 C C Ceq 2C O 20 O 10 O 1.5C O 2.5Carrow_forward4arrow_forwardA 40 μF capacitor is supplied with 100 V, 60 Hz source. Find the resulting current.arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





