
Concept explainers
a.
Stored procedures:
- A procedure is a collection of procedural and SQL statements.
- A procedure may have input parameter, output parameter and both parameters.
- It has a declared with a unique named with a unit of procedural code using the proprietary RDBMS and it is invoked by a host language library routine.
Syntax for stored procedure:
CREATE FUNCTION fun_name(argument IN data-type)RETRUN data-type[IS]
BEGIN
PL/SQL statements;
Return (value or expression);
END;
Explanation of Solution
Query to create stored procedure:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE DISP_CUST_CRED (I_CUSTOMER_NUM IN CUSTOMER.CUSTOMER_NUM%TYPE) AS
I_CUSTOMER_NAME CUSTOMER.CUSTOMER_NAME%TYPE;
I_CREDIT_LIMIT CUSTOMER.CREDIT_LIMIT%TYPE;
BEGIN
SELECT CUSTOMER_NAME, CREDIT_LIMIT
INTO I_CUSTOMER_NAME, I_CREDIT_LIMIT
FROM CUSTOMER
WHERE CUSTOMER_NUM = I_CUSTOMER_NUM;
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE (I_CUSTOMER_NAME);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE (I_CREDIT_LIMIT);
END;
/
Explanation:
- The above query is used to create a procedure named “DISP_CUST_CRED” to select the records in the “CUSTOMER” table.
- Change the “CUSTOMER_NUM” into “I_CUSTOMER_NUM” and place the “CUSTOMER_NAME” and “CREDIT_LIMIT” values into “I_CUSTOMER_NAME” and “I_CREDIT_LIMIT”.
- After placing these values, display the “I_CUSTOMER_NAME” and “I_CREDIT_LIMIT” from the “CUSTOMER” table.
- Once the stored procedure is created, it needs to be executed.
Query to view the customer name and credit limit:
BEGIN
DISP_CUST_CRED (126);
END;
The above query is used to view the customer name and credit limit for the number 126.
Output:
Toys Galore
7500
Explanation of Solution
b.
Query to create stored procedure:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE DISP_ORDERS (I_ORDER_NUM ORDERS.ORDER_NUM%TYPE) AS
I_ORDER_DATE ORDERS.ORDER_DATE%TYPE;
I_CUSTOMER_NUM CUSTOMER.CUSTOMER_NUM%TYPE;
I_CUSTOMER_NAME CUSTOMER.CUSTOMER_NAME%TYPE;
BEGIN
SELECT ORDER_DATE, CUSTOMER.CUSTOMER_NUM, CUSTOMER_NAME
INTO I_ORDER_DATE, I_CUSTOMER_NUM, I_CUSTOMER_NAME
FROM ORDERS, CUSTOMER
WHERE ORDERS.CUSTOMER_NUM = CUSTOMER.CUSTOMER_NUM
AND ORDER_NUM = I_ORDER_NUM;
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(I_ORDER_DATE);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(I_CUSTOMER_NUM);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(I_CUSTOMER_NAME);
END;
/
Explanation:
- The above query is used to create a procedure named “DISP_ORDERS” to select the records in the “CUSTOMER” and “ORDERS” tables.
- Change the “ORDER_NUM” into “I_ORDER_NUM” and place the “ORDER_DATE”, “CUSTOMER_NUM”, and “CUSTOMER_NAME” values into “I_ORDER_DATE”, “I_CUSTOMER_NUM”, and “I_CUSTOMER_NAME”.
- After placing these values, display the “I_ORDER_DATE”, “I_CUSTOMER_NUM”, and “I_CUSTOMER_NAME” from the “CUSTOMER” and “ORDERS” tables.
- Once the stored procedure is created, it needs to be executed.
Query to view the order date, customer name and customer number:
BEGIN
DISP_ORDERS (51608);
END;
The above query is used to view the order date, customer name and customer number for the number 51608.
Output:
10/12/2015
126
Toys Galore
Explanation of Solution
c.
Query to insert the value:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE ADD_ORDER
(I_ORDER_NUM IN ORDERS.ORDER_NUM%TYPE,
I_ORDER_DATE IN ORDERS.ORDER_DATE%TYPE,
I_CUSTOMER_NUM IN ORDERS.CUSTOMER_NUM%TYPE) AS
BEGIN
INSERT INTO ORDERS (ORDER_NUM, ORDER_DATE, CUSTOMER_NUM)
VALUES
(I_ORDER_NUM, I_ORDER_DATE, I_CUSTOMER_NUM);
END;
/
Explanation:
The above query is used to create a stored procedure named “ADD_ORDER” to insert the new record in the “ORDERS” table. Once the stored procedure is created, it needs to be executed.
Query to execute the stored procedure:
BEGIN
ADD_ORDER (51627,'10/16/2015', 334);
END;
After executing the above query, the new record is inserted into the table “ORDERS”.
Output:
Query to view the contents in “ORDERS” table is as follows:
SELECT * FROM ORDERS;
Screenshot of output
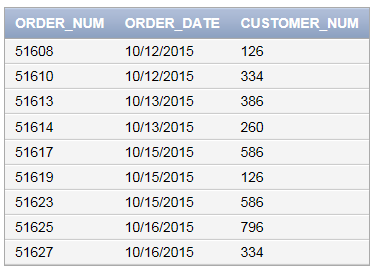
Explanation of Solution
d.
Query to update stored procedure:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE UPDATE_ORDER_DATE
(I_ORDER_NUM IN ORDERS.ORDER_NUM%TYPE,
I_ORDER_DATE IN ORDERS.ORDER_DATE%TYPE) AS
BEGIN
UPDATE ORDERS
SET ORDER_DATE = I_ORDER_DATE
WHERE ORDER_NUM = I_ORDER_NUM;
END;
/
Explanation:
The above query is used to create a stored procedure named “UPDATE_ORDER_DATE” to update the date of the order whose number is stored in “I_ORDER_DATE” to the date presently found in “I_ORDER_DATE”, it needs to be executed.
Executing the stored procedure:
The Content of “ORDERS” table before creating the procedure is given below:
Query to view the contents in “ORDERS” table is as follows:
SELECT*FROM ORDERS;
Screenshot of output

Query to execute the stored procedure:
BEGIN
UPDATE_ORDER_DATE (51614, '02/12/2019');
END;
/
After executing the above query, the date is changed in the table “ORDERS”.
Output:
Query to view the contents in “ORDERS” table is as follows:
SELECT * FROM ORDERS;
Screenshot of output
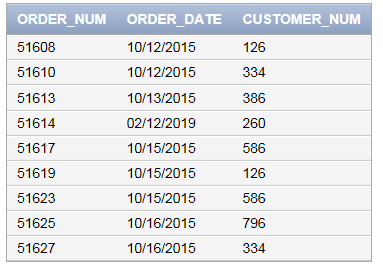
Explanation of Solution
e.
Query to delete the value:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE DELETE_ORDERS
(I_ORDER_NUM ORDERS.ORDER_NUM%TYPE) AS
BEGIN
DELETE
FROM ORDERS
WHERE ORDER_NUM = I_ORDER_NUM;
END;
/
Explanation:
- The above query is used to create a procedure named “DELETE_ORDERS” to delete a record in the “ORDERS” table.
- Once the record is deleted, a procedure should create order number as a parameter.
- Once the stored procedure is created, it needs to be executed.
Executing the stored procedure:
The Content of “ORDERS” table before creating the procedure is given below:
Query to view the contents in “ORDERS” table is as follows:
SELECT * FROM ORDERS;
Screenshot of output

Query to execute the stored procedure:
BEGIN
DELETE_ORDERS (51613);
END;
The above query is used to delete the order number 51613.
Output:
Query to view the contents in “ORDERS” table after deleting the order number 51613 as follows:
SELECT * FROM ORDERS;
Screenshot of output
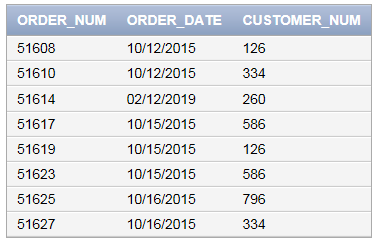
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
A Guide to SQL
- Need help answering this question with a flowchart!arrow_forwardHW: a sewer carry flow = 600 l/s at 34 full at max WWF and 150 l/s at min DWF. Determine the diameter and minimum slope. Then get velocity and depth of sewage flow at max WWF and DWF. Use Vmin = 0.6m/s.arrow_forwardGeneral accountingarrow_forward
- JOB UPDATE Apply on- VinkJobs.com @ OR Search "Vinkjobs.com" on Google COMPANY JOB PROFILE JOB LOCATION INTELLIFLO APPLICATION DEVELOPER MULTIPLE CITIES GLOBAL LOGIC SOFTWARE ENGINEER/SDET DELHI NCR SWIGGY SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT BENGALURU AVALARA SOFTWARE ENGINEER (WFH) MULTIPLE CITIES LENSKART FULL STACK DEVELOPER MULTIPLE CITIES ACCENTURE MEDPACE IT CUST SERVICE SOFTWARE ENGINEER MUMBAI MUMBAI GENPACT BUSINESS ANALYST DELHI NCR WELOCALIZE WORK FROM HOME MULTIPLE CITIES NTT DATA BPO ASSOCIATE DELHI NCRarrow_forward+is+how+many+tree+in+ipl&rlz=1C1GCEA_enIN1122IN1122&oq=1+dot+ball+is+how+many+tree+in Google 1 dot ball is how many tree in ipl All Images News Videos Short videos Shopping Web More 500 trees 4) हिन्दी में In English The step was a part of the Board of Control for Cricket in India's green initiative. The BCCI, having partnered with the Tata Group, has promised to plant as many as 500 trees for every dot ball bowled in the Indian Premier League. 25 Mar 2025 Sportstar https://sportstar.thehindu.com > Cricket IPL IPL News IPL 2025: Why are green tree symbols showing up for every ... A Translate to fo-d About featured snippets . Feedback Toolsarrow_forwardPastner Brands is a calendar-year firm with operations in several countries. As part of its executive compensation plan, at January 1, 2024, the company issued 480,000 executive stock options permitting executives to buy 480,000 shares of Pastner stock for $38 per share. One-fourth of the options vest in each of the next four years beginning at December 31, 2024 (graded vesting). Pastner elects to separate the total award into four groups (or tranches) according to the year in which they vest and measures the compensation cost for each vesting date as a separate award. The fair value of each tranche is estimated at January 1, 2024, as follows: Vesting Date Amount Fair Value Vesting per Option: December 31, 2024 25% $ 3.90 December 31, 2025 25% $ 4.40 25% $ 4.90 25% $ 5.40 December 31, 2026 December 31, 2027 Required: 1. Determine the compensation expense related to the options to be recorded each year 2024-2027, assuming Pastner allocates the compensation cost for each of the four…arrow_forward
- What is one benefit with regards to time complexity of using a Doubly Linked List as opposed to an Array when implementing a Deque?arrow_forwardWhat is one benefit with regards to space complexity of using a Doubly Linked List as opposed to an Array when implementing a Deque?arrow_forwardWhich basic data structure (Doubly Linked List, Singly Linked List, Array) would you use to implement a Stack? Why?arrow_forward
 A Guide to SQLComputer ScienceISBN:9781111527273Author:Philip J. PrattPublisher:Course Technology Ptr
A Guide to SQLComputer ScienceISBN:9781111527273Author:Philip J. PrattPublisher:Course Technology Ptr Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781285196145Author:Steven, Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel, Carlos, Coronel, Carlos; Morris, Carlos Coronel and Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel; Steven Morris, Steven Morris; Carlos CoronelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781285196145Author:Steven, Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel, Carlos, Coronel, Carlos; Morris, Carlos Coronel and Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel; Steven Morris, Steven Morris; Carlos CoronelPublisher:Cengage Learning Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781305627482Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781305627482Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Programming with Microsoft Visual Basic 2017Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102124Author:Diane ZakPublisher:Cengage LearningNp Ms Office 365/Excel 2016 I NtermedComputer ScienceISBN:9781337508841Author:CareyPublisher:Cengage
Programming with Microsoft Visual Basic 2017Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102124Author:Diane ZakPublisher:Cengage LearningNp Ms Office 365/Excel 2016 I NtermedComputer ScienceISBN:9781337508841Author:CareyPublisher:Cengage





