
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134110684
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus)
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 54EAP
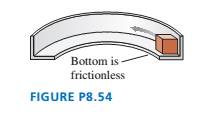
FIGURE P8.54 shows a small block of mass m sliding around the inside of an L-shaped track of radius r. The bottom of the track is frictionless; the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the wall of the track is µk. The block’s speed is v0at t0= 0. Find an expression for the block’s speed at a later time t.
x
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
An m = 69.0-kg person running at an initial speed of v = 4.50 m/s jumps onto an M = 138-kg cart initially at rest (figure below). The person slides on the cart's top surface and finally comes to rest relative to the cart. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the person and the cart is
0.440. Friction between the cart and ground can be ignored. (Let the positive direction be to the right.)
m
M
(a) Find the final velocity of the person and cart relative to the ground. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.)
m/s
(b) Find the friction force acting on the person while he is sliding across the top surface of the cart. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.)
N
(c) How long does the friction force act on the person?
S
(d) Find the change in momentum of the person. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.)
N.S
Find the change in momentum of the cart. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.)
N.S
(e) Determine the displacement of the…
Small ice cubes, each of mass 5.60 g, slide down a frictionless track in a steady stream, as shown in the figure below. Starting from rest, each cube moves down through a net vertical distance of h = 1.50 m and leaves the bottom end of the track at an angle of 40.0° above the horizontal.
At the highest point of its subsequent trajectory, the cube strikes a vertical wall and rebounds with half the speed it had upon impact. If 10 cubes strike the wall per second, what average force is exerted upon the wall?
N ---direction--- ▾
---direction---
to the top
to the bottom
to the left
to the right
1.50 m
40.0°
The magnitude of the net force exerted in the x direction on a 3.00-kg particle varies in time as shown in the figure below.
F(N)
4
3
A
2
t(s)
1
2 3
45
(a) Find the impulse of the force over the 5.00-s time interval.
==
N⚫s
(b) Find the final velocity the particle attains if it is originally at rest.
m/s
(c) Find its final velocity if its original velocity is -3.50 î m/s.
V₁
m/s
(d) Find the average force exerted on the particle for the time interval between 0 and 5.00 s.
=
avg
N
Chapter 8 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Ch. 8 - In uniform circular motion, which of the following...Ch. 8 - A car runs out of gas while driving down a hill....Ch. 8 - FIGURE Q8.3 is a bird's-eye view of particles on...Ch. 8 - Tarzan swings through the jungle on a massless...Ch. 8 - FIGURE Q8.5 shows two balls of equal mass moving...Ch. 8 - Ramon and Sally are observing a toy car speed up...Ch. 8 - A jet plane is flying on a level course at...Ch. 8 - A small projectile is launched parallel to the...Ch. 8 - 9. You can swing a ball on a string in a vertical...Ch. 8 - A golfer starts with the club over her head and...
Ch. 8 - As a science fair project, you want to launch an...Ch. 8 - A 500 g model rocket is on a cart that is rolling...Ch. 8 - A 4.0 × 1010 kg asteroid is heading directly...Ch. 8 - A 55 kg astronaut who weighs 180 N on a distant...Ch. 8 - A 1500 kg car drives around a flat 200-m-diameter...Ch. 8 - A 1500 kg car takes a 50-m-radius unbanked curve...Ch. 8 - A 200 g block on a 50-cm-long string swings in a...Ch. 8 - In the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, an...Ch. 8 - Suppose the moon were held in its orbit not by...Ch. 8 - 10. A highway curve of radius 500 m is designed...Ch. 8 - It is proposed that future space stations create...Ch. 8 - A 5.0 g coin is placed 15 cm from the center of a...Ch. 8 - Mass m1on the frictionless table of FIGURE EX8.13...Ch. 8 - A satellite orbiting the moon very near the...Ch. 8 - What is free-fall acceleration toward the sun at...Ch. 8 - 16. A 9.4 × 1021 kg moon orbits a distant planet...Ch. 8 - Communications satellites are placed in circular...Ch. 8 - A car drives over the top of a hill that has a...Ch. 8 - The weight of passengers on a roller coaster...Ch. 8 - A roller coaster car crosses the top of a circular...Ch. 8 - The normal force equals the magnitude of the...Ch. 8 - A student has 65-cm-long arms. What is the minimum...Ch. 8 - While at the county fair, you decide to ride the...Ch. 8 - A 500 g ball swings in a vertical circle at the...Ch. 8 - A 500 g ball moves in a vertical circle on a...Ch. 8 - A heavy ball with a weight of 100 N (m = 10.2 kg)...Ch. 8 - A toy train rolls around a horizontal...Ch. 8 - 28. A new car is tested on a 200-m-diameter track....Ch. 8 - An 85,000 kg stunt plane performs a loop-the-loop,...Ch. 8 - Three cars are driving at 25 m/s along the road...Ch. 8 - Derive Equations 8.3 for the acceleration of a...Ch. 8 - 32. A 100 g bead slides along a frictionless wire...Ch. 8 - 33. Space scientists have a large test chamber...Ch. 8 - 34. A 5000 kg interceptor rocket is launched at an...Ch. 8 - Prob. 35EAPCh. 8 - 36. A rocket- powered hockey puck has a thrust of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 37EAPCh. 8 - A 2.0 kg projectile with initial velocity m/s...Ch. 8 - A 75 kg man weighs himself at the north pole and...Ch. 8 - A concrete highway curve of radius 70 m banked at...Ch. 8 - a. an object of mass m swings in horizontal circle...Ch. 8 -
42. You’ve taken your neighbor’s young child to...Ch. 8 - A 4.4-cm-diameter, 24 g plastic ball is attached...Ch. 8 - A charged particle of mass m moving with speed v...Ch. 8 - Two wires are tied to the 2.0 kg sphere shown in...Ch. 8 - Two wires are tied to the 300 g sphere shown in...Ch. 8 - A conical pendulum is formed by attaching a ball...Ch. 8 - The 10 mg bead in FIGURE P8.48 is free to slide on...Ch. 8 - In an old-fashioned amusement park ride,...Ch. 8 - The ultracentrifuge is an important tool for...Ch. 8 - In an amusement park ride called The Roundup,...Ch. 8 - 52. Suppose you swing a ball of mass m in a...Ch. 8 - A 30 g ball rolls around a 40-cm-diameter L-shaped...Ch. 8 - FIGURE P8.54 shows a small block of mass m sliding...Ch. 8 - The physics of circular motion sets an upper limit...Ch. 8 - A 100 g ball on a 60-cm-long string is swung in a...Ch. 8 - A 60 g ball is tied to the end of a 50-cm-long...Ch. 8 - Elm Street has a pronounced dip at the bottom of a...Ch. 8 - 59. A 100 g ball on a 60-cm-long string is swung...Ch. 8 - Scientists design a new particle accelerator in...Ch. 8 - 61. A 1500 kg car starts from rest and drives...Ch. 8 - Prob. 62EAPCh. 8 - 63. A 2.0 kg ball swings in a vertical circle on...Ch. 8 - In Problems 64 and 65 you are given the equation...Ch. 8 - In Problems 64 and 65 you are given the equation...Ch. 8 - Sam (75 kg) takes off up a 50-m-high, 10°...Ch. 8 - In the absence of air resistance, a projectile...Ch. 8 - The father of Example 8.2 stands at the summit of...Ch. 8 - A small bead slides around a horizontal circle at...Ch. 8 - A 500 g steel block rotates on a steel table while...Ch. 8 - If a vertical cylinder of water (or any other...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- ••63 SSM www In the circuit of Fig. 27-65, 8 = 1.2 kV, C = 6.5 µF, R₁ S R₂ R3 800 C H R₁ = R₂ = R3 = 0.73 MQ. With C completely uncharged, switch S is suddenly closed (at t = 0). At t = 0, what are (a) current i̟ in resistor 1, (b) current 2 in resistor 2, and (c) current i3 in resistor 3? At t = ∞o (that is, after many time constants), what are (d) i₁, (e) i₂, and (f) iz? What is the potential difference V2 across resistor 2 at (g) t = 0 and (h) t = ∞o? (i) Sketch V2 versus t between these two extreme times. Figure 27-65 Problem 63.arrow_forwardThor flies by spinning his hammer really fast from a leather strap at the end of the handle, letting go, then grabbing it and having it pull him. If Thor wants to reach escape velocity (velocity needed to leave Earth’s atmosphere), he will need the linear velocity of the center of mass of the hammer to be 11,200 m/s. Thor's escape velocity is 33532.9 rad/s, the angular velocity is 8055.5 rad/s^2. While the hammer is spinning at its maximum speed what impossibly large tension does the leather strap, which the hammer is spinning by, exert when the hammer is at its lowest point? the hammer has a total mass of 20.0kg.arrow_forwardIf the room’s radius is 16.2 m, at what minimum linear speed does Quicksilver need to run to stay on the walls without sliding down? Assume the coefficient of friction between Quicksilver and the wall is 0.236.arrow_forward
- In the comics Thor flies by spinning his hammer really fast from a leather strap at the end of the handle, letting go, then grabbing it and having it pull him. If Thor wants to reach escape velocity (velocity needed to leave Earth’s atmosphere), he will need the linear velocity of the center of mass of the hammer to be 11,200 m/s. A) If the distance from the end of the strap to the center of the hammer is 0.334 m, what angular velocity does Thor need to spin his hammer at to reach escape velocity? b) If the hammer starts from rest what angular acceleration does Thor need to reach that angular velocity in 4.16 s? c) While the hammer is spinning at its maximum speed what impossibly large tension does the leather strap, which the hammer is spinning by, exert when the hammer is at its lowest point? The hammer has a total mass of 20.0kg.arrow_forwardThe car goes from driving straight to spinning at 10.6 rev/min in 0.257 s with a radius of 12.2 m. The angular accleration is 4.28 rad/s^2. During this flip Barbie stays firmly seated in the car’s seat. Barbie has a mass of 58.0 kg, what is her normal force at the top of the loop?arrow_forwardConsider a hoop of radius R and mass M rolling without slipping. Which form of kinetic energy is larger, translational or rotational?arrow_forward
- A roller-coaster vehicle has a mass of 571 kg when fully loaded with passengers (see figure). A) If the vehicle has a speed of 22.5 m/s at point A, what is the force of the track on the vehicle at this point? B) What is the maximum speed the vehicle can have at point B, in order for gravity to hold it on the track?arrow_forwardThis one wheeled motorcycle’s wheel maximum angular velocity was about 430 rev/min. Given that it’s radius was 0.920 m, what was the largest linear velocity of the monowheel?The monowheel could not accelerate fast or the rider would start spinning inside (this is called "gerbiling"). The maximum angular acceleration was 10.9 rad/s2. How long, in seconds, would it take it to hit maximum speed from rest?arrow_forwardIf points a and b are connected by a wire with negligible resistance, find the magnitude of the current in the 12.0 V battery.arrow_forward
- Consider the two pucks shown in the figure. As they move towards each other, the momentum of each puck is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Given that v kinetic energy of the system is converted to internal energy? 30.0° 130.0 = green 11.0 m/s, and m blue is 25.0% greater than m 'green' what are the final speeds of each puck (in m/s), if 1½-½ t thearrow_forwardConsider the blocks on the curved ramp as seen in the figure. The blocks have masses m₁ = 2.00 kg and m₂ = 3.60 kg, and are initially at rest. The blocks are allowed to slide down the ramp and they then undergo a head-on, elastic collision on the flat portion. Determine the heights (in m) to which m₁ and m2 rise on the curved portion of the ramp after the collision. Assume the ramp is frictionless, and h 4.40 m. m2 = m₁ m hm1 hm2 m iarrow_forwardA 3.04-kg steel ball strikes a massive wall at 10.0 m/s at an angle of 0 = 60.0° with the plane of the wall. It bounces off the wall with the same speed and angle (see the figure below). If the ball is in contact with the wall for 0.234 s, what is the average force exerted by the wall on the ball? magnitude direction ---Select--- ✓ N xarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Moment of Inertia; Author: Physics with Professor Matt Anderson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZrGhUTeIlWs;License: Standard Youtube License