
(a)
Interpretation: The structure of product with ethyl magnesium bromide with indicated carbonyl compound should be written.
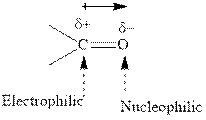
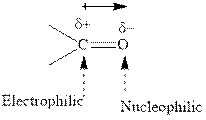
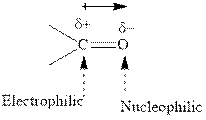
Concept introduction:The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
Grignard reagents are
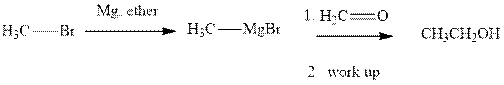
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol.
Chiral carbon is any stereocenter attached to four different alkyl substituents. It is also known as stereocenter. If any two of the substituent happen to be similar the center is regarded as achiral.
(b)
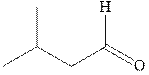
Interpretation: The structure of product with ethyl magnesium bromide with indicated carbonyl compound should be written and any stereoisomers formed and whether they are formed in equal or unequal numbers should be identified.
Concept introduction:The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
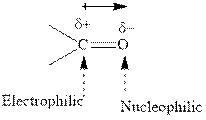
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. This reagent is useful precursor for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
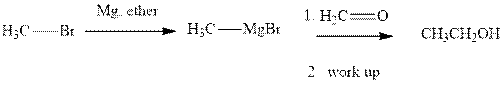
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol.
The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral. Together enantiomers and diastereomers constitute the total stereoisomers of any chiral compound.
(c)
Interpretation: The structure of product with ethyl magnesium bromide with indicated carbonyl compound should be written and any stereoisomers formed and whether they are formed in equal or unequal numbers should be identified.
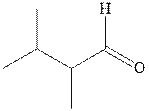
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is a polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
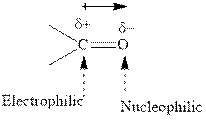
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. This reagent is useful precursor for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
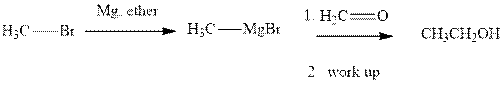
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol.
The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral. Together enantiomers and diastereomers constitute the total stereoisomers of any chiral compound.
(d)
Interpretation: The structure of product with ethyl magnesium bromide with indicated carbonyl compound should be written and any stereoisomers formed and whether they are formed in equal or unequal numbers should be identified.
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
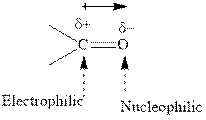
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. This reagent is useful precursor for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
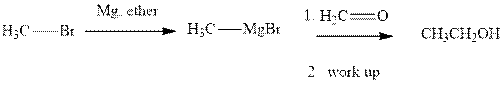
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol.
The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral. Together enantiomers and diastereomers constitute the total stereoisomers of any chiral compound.
(e)
Interpretation: The structure of product with ethyl magnesium bromide with indicated carbonyl compound should be written and any stereoisomers formed and whether they are formed in equal or unequal numbers should be identified.
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
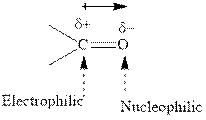
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. This reagent is useful precursor for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
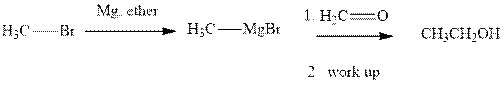
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol.
The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral. Together enantiomers and diastereomers constitute the total stereoisomers of any chiral compound.
(f)
Interpretation: The structure of product with ethyl magnesium bromide with indicated carbonyl compound should be written.
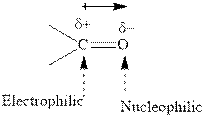
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. This reagent is useful precursor for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
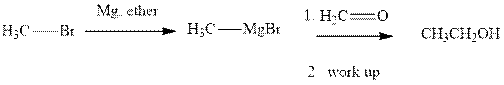
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol.
Chiral carbon is any stereocenter attached to four different alkyl substituents. It is also known as stereocenter. If any two of the substituent happen to be similar the center is regarded as achiral.
(g)
Interpretation: The structure of product with ethyl magnesium bromide with indicated carbonyl compound should be written and any stereoisomers formed and whether they are formed in equal or unequal numbers should be identified.
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. This reagent is useful precursor for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
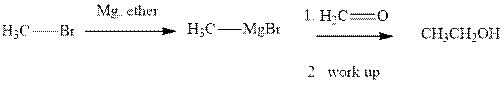
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol.
The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral. Together enantiomers and diastereomers constitute the total stereoisomers of any chiral compound.
(h)
Interpretation: The structure of product with ethyl magnesium bromide with indicated carbonyl compound should be written and any stereoisomers formed and whether they are formed in equal or unequal numbers should be identified.
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
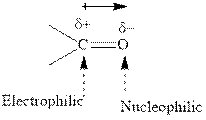
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. This reagent is useful precursor for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohols as illustrated below.
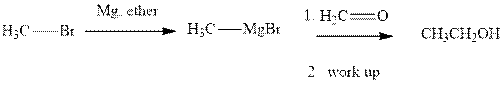
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol.
Chiral carbon is any stereocenter attached to four different alkyl substituents. It is also known as stereocenter. If any two of the substituent happen to be similar the center is regarded as achiral. However the most essential criteria that help to distinguish a chiral or non-chiral system is Presence of any symmetry element.
The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral. Together enantiomers and diastereomers constitute the total stereoisomers of any chiral compound.
(i)
Interpretation: The structure of product with ethyl magnesium bromide with indicated carbonyl compound should be written and any stereoisomers formed and whether they are formed in equal or unequal numbers should be identified.
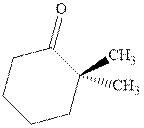
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
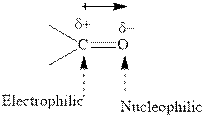
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. This reagent is useful precursor for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
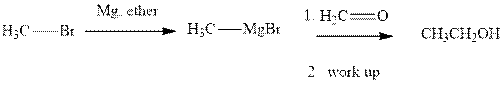
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol.
Chiral carbon is any stereocenter attached to four different alkyl substituents. The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral. Together enantiomers and diastereomers constitute the total stereoisomers of any chiral compound.
(j)
Interpretation: The structure of product with ethyl magnesium bromide with indicated carbonyl compound should be written and any stereoisomers formed and whether they are formed in equal or unequal numbers should be identified.
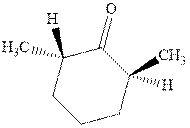
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. This reagent is useful precursor for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
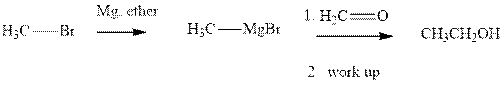
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol.
Chiral carbon is any stereocenter attached to four different alkyl substituents. The enantiomers are identical chemical compounds that have a mirror-image relationship to each other while diastereomers do not hold mirror image relationships. The former are chiral and optically active while the latter can be chiral or achiral. Together enantiomers and diastereomers constitute the total stereoisomers of any chiral compound.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK STUDY GUIDE/SOLUTIONS MANUAL FOR OR
- Provide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardFirst image: Why can't the molecule C be formed in those conditions Second image: Synthesis for lactone C its not an examarrow_forwardFirst image: I have to show the mecanism for the reaction on the left, where the alcohol A is added fast in one portion Second image: I have to show the mecanism of the reaction at the bottom. Also I have to show by mecanism why the reaction wouldn't work if the alcohol was primaryarrow_forward
- First image: I have to explain why the molecule C is never formed in those conditions. Second image: I have to propose a synthesis for the lactone Aarrow_forwardFirst image: I have to explain why the molecule C is never formed in these conditions Second image: I have to propose a synthesis for the lactone Aarrow_forwardHelp fix my arrows pleasearrow_forward
- Provide the drawing of the unknown structure that corresponds with this data.arrow_forward20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forwardGiven the attached data, provide the drawing for the corresponding structure.arrow_forward

 Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole

