
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:Compound
Concept introduction:In accordance with Bronsted definition an acid can act as a proton donor and a base can act as a proton acceptor. Thus in a typical acid-base reaction, the fundamental principle is a lone pair of base reaches out for an acidic proton. Similar curved arrows are used to show the movement of electrons. After deprotonation, the species left with a negative charge is referred as the conjugate base of acid while the other with a positive charge is termed conjugate acid of given base. For example;
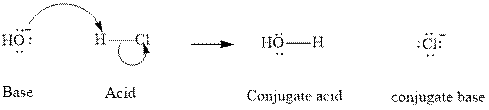
The strength of various conjugate acid-base pairs varies inversely to one another; the strong acid has a weak conjugate base and the strong base has weak conjugate acid and vice-versa.
The order of acidic strength of various alcohols is as follows:
For tertiary alcohols, the steric bulk is maximum that leads to inhibition in solvation of
(b)
Interpretation:Compounds
Concept introduction: In accordance with Bronsted definition an acid can act as a proton donor and a base can act as a proton acceptor. Thus in a typical acid-base reaction, the fundamental principle is a lone pair of base reaches out for an acidic proton. Similar curved arrows are used to show the movement of electrons. After deprotonation, the species left with a negative charge is referred as the conjugate base of acid while the other with a positive charge is termed conjugate acid of given base. For example;
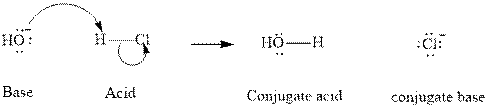
The strength of various conjugate acid-base pairs varies inversely to one another; the strong acid has a weak conjugate base and the strong base has weak conjugate acid and vice-versa.
The order of acidic strength of various alcohols is as follows:
For tertiary alcohols, the steric bulk is maximum that leads to inhibition in solvation of
(c)
Interpretation:Compounds
Concept introduction: In accordance with Bronsted definition an acid can act as a proton donor and a base can act as a proton acceptor. Thus in a typical acid-base reaction, the fundamental principle is a lone pair of base reaches out for an acidic proton. Similar curved arrows are used to show the movement of electrons. After deprotonation, the species left with a negative charge is referred as the conjugate base of acid while the other with a positive charge is termed conjugate acid of given base. For example;
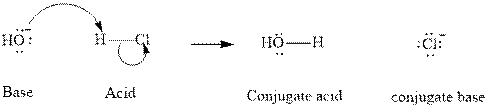
The strength of various conjugate acid-base pairs varies inversely to one another; the strong acid has a weak conjugate base and the strong base has weak conjugate acid and vice-versa.
The order of acidic strength of various alcohols is as follows:
For tertiary alcohols, the steric bulk is maximum that leads to inhibition in solvation of
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK STUDY GUIDE/SOLUTIONS MANUAL FOR OR
- Provide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardFirst image: Why can't the molecule C be formed in those conditions Second image: Synthesis for lactone C its not an examarrow_forwardFirst image: I have to show the mecanism for the reaction on the left, where the alcohol A is added fast in one portion Second image: I have to show the mecanism of the reaction at the bottom. Also I have to show by mecanism why the reaction wouldn't work if the alcohol was primaryarrow_forward
- First image: I have to explain why the molecule C is never formed in those conditions. Second image: I have to propose a synthesis for the lactone Aarrow_forwardFirst image: I have to explain why the molecule C is never formed in these conditions Second image: I have to propose a synthesis for the lactone Aarrow_forwardHelp fix my arrows pleasearrow_forward
- Provide the drawing of the unknown structure that corresponds with this data.arrow_forward20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forwardGiven the attached data, provide the drawing for the corresponding structure.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning


