
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:The major product of indicated reaction should be identified.
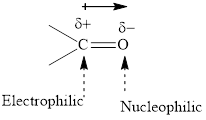
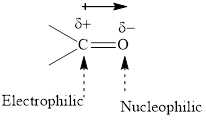
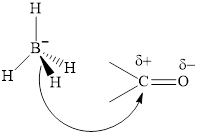
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with partial postive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
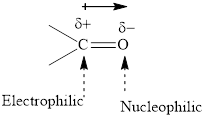
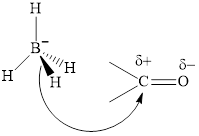
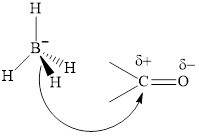
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include sodium borohydride, lithium aluminum hydride. The boron and lithium in these reagents tend to push the electron of
Any organic compound must have no plane of symmetry in order to be chiral or optically active. The compounds with any plane of symmetry are achiral and optically inactive.
(b)
Interpretation:The major product of indicated reaction should be identified.
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with partial postive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
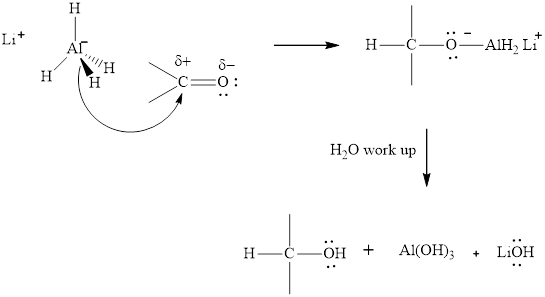
The aluminum and lithium in these reagents such as
(c)
Interpretation: The major product of indicated reaction should be identified.
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with partial postive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include sodium borohydride, lithium aluminum hydride. The boron and lithium in these reagents tend to push the electron of
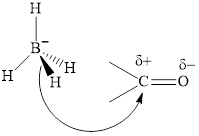
(d)
Interpretation: The major product of indicated reaction should be identified.

Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with partial postive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
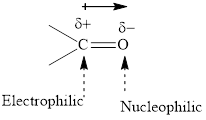
The aluminum and lithium in these reagents such as
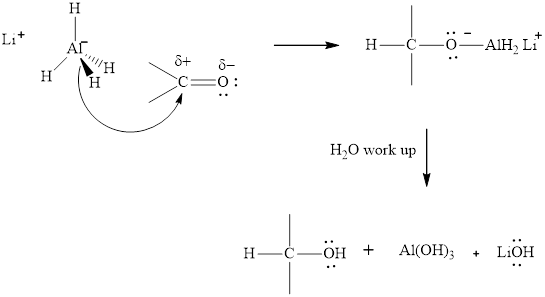
(e)
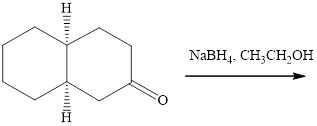
Interpretation: The major product of indicated reaction should be identified.
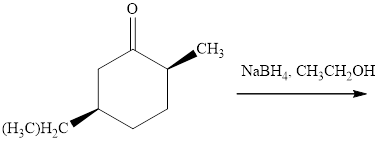
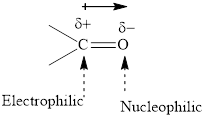
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with partial postive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include sodium borohydride, lithium aluminum hydride. The boron and lithium in these reagents tend to push the electron of
(f)
Interpretation: The major product of indicated reaction should be identified.
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with partial postive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
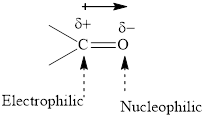
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include sodium borohydride, lithium aluminum hydride. The boron and lithium in these reagents tend to push the electron of
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK STUDY GUIDE/SOLUTIONS MANUAL FOR OR
- Provide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardFirst image: Why can't the molecule C be formed in those conditions Second image: Synthesis for lactone C its not an examarrow_forwardFirst image: I have to show the mecanism for the reaction on the left, where the alcohol A is added fast in one portion Second image: I have to show the mecanism of the reaction at the bottom. Also I have to show by mecanism why the reaction wouldn't work if the alcohol was primaryarrow_forward
- First image: I have to explain why the molecule C is never formed in those conditions. Second image: I have to propose a synthesis for the lactone Aarrow_forwardFirst image: I have to explain why the molecule C is never formed in these conditions Second image: I have to propose a synthesis for the lactone Aarrow_forwardHelp fix my arrows pleasearrow_forward
- Provide the drawing of the unknown structure that corresponds with this data.arrow_forward20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forwardGiven the attached data, provide the drawing for the corresponding structure.arrow_forward
