
(a)
Interpretation:The product formed in indicated reaction should be formulated and whether it is chiral and shows any optical activity or not should be determined.
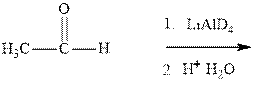
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include
Optical activity refers to ability to rotate the plane polarized light. For example, if the light is passed through a substance and the light that emerges has radiations are confined to one plane only the substance is said to be optically active.
The earliest criteria for optical activity were presence of a chiral center. The chiral refer to species attached to four different substituents. Chiral center leads to existence of organic compounds as two enantiomeric forms. However chiral center alone is not sufficient condition for determination of optical activity.
The criteria to identify the optical activity are to look for absence of any symmetry element. The symmetry elements make any molecule optically inactive.
(b)
Interpretation: The product formed in indicated reaction should be formulated and whether it is chiral and shows any optical activity or not should be determined.

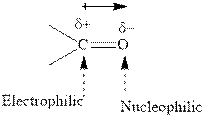
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
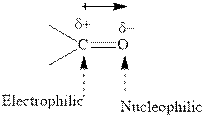
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include
Optical activity refers to ability to rotate the plane polarized light. For example, if the light is passed through a substance and the light that emerges has radiations are confined to one plane only the substance is said to be optically active.
The earliest criteria for optical activity were presence of a chiral center. The chiral refer to species attached to four different substituents. Chiral center leads to exists of organic compounds as two enantiomeric forms. However chiral center alone is not sufficient condition for determination of optical activity.
The criteria to identify the optical activity are to look for absence of any symmetry element. The symmetry elements make any molecule optically inactive.
(c)
Interpretation: The product formed in indicated reaction should be formulated and whether it is chiral and shows any optical activity or not should be determined.
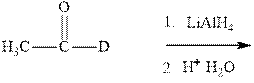
Concept introduction:The carbonyl bond is polar with partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
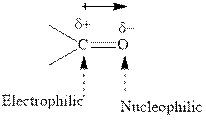
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include
Optical activity refers to ability to rotate the plane polarized light. For example, if the light is passed through a substance and the light that emerges has radiations are confined to one plane only the substance is said to be optically active.
The earliest criteria for optical activity were presence of a chiral center. The chiral refer to species attached to four different substituents. Chiral center leads to exists of organic compounds as two enantiomeric forms. However chiral center alone is not sufficient condition for determination of optical activity.
The criteria to identify the optical activity are to look for absence of any symmetry element. The symmetry elements make any molecule optically inactive.
(d)
Interpretation: The product formed in indicated reaction should be formulated and whether it is chiral and shows any optical activity or not should be determined.

Concept introduction:The carbonyl bond is polar with partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
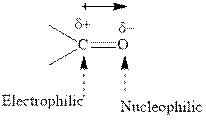
Thus it can undergo hydride addition at carbon and proton addition at oxygen. Certain reagents that are useful for such hydride addition at carbonyl carbon include
Optical activity refers to ability to rotate the plane polarized light. For example, if the light is passed through a substance and the light that emerges has radiations are confined to one plane only the substance is said to be optically active.
The earliest criteria for optical activity were presence of a chiral center. The chiral refer to species attached to four different substituents. Chiral center leads to exists of organic compounds as two enantiomeric forms. However chiral center alone is not sufficient condition for determination of optical activity.
The criteria to identify the optical activity are to look for absence of any symmetry element. The symmetry elements make any molecule optically inactive.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK STUDY GUIDE/SOLUTIONS MANUAL FOR OR
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning




