
EBK PHYSICS
5th Edition
ISBN: 8220103026918
Author: Walker
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 31PCE
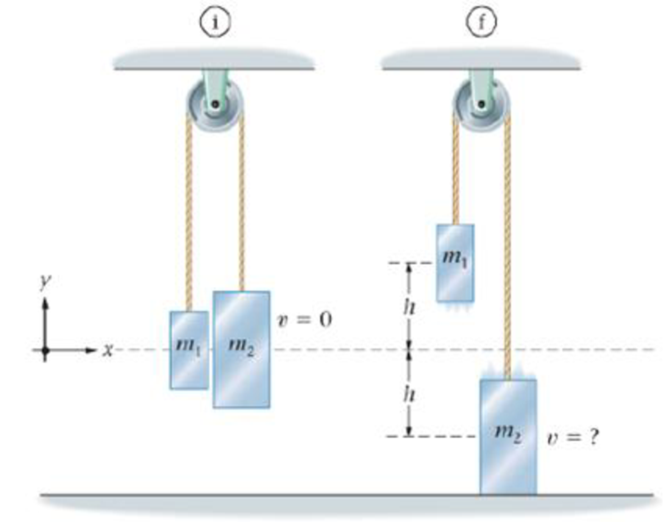
The two masses in the Atwood’s machine shown in Figure 8-33 are initially at rest at the same height. After they are released, the large mass, m2, falls through a height h and hits the floor, and the small mass, m1, rises through a height h. (a) Find the speed of the masses just before m2 lands, giving your answer in terms of m1, m2 g, and h. Assume the ropes and pulley have negligible mass and that friction can be ignored. (b) Evaluate your answer to part (a) for the case h = 1.2m, m1 = 3.7 kg, and m3 = 4.1kg.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
In the Donkey Kong Country video games you often get around by shooting yourself out of barrel cannons. Donkey Kong wants to launch out of one barrel and land in a different one that is a distance in x of 9.28 m away. To do so he launches himself at a velocity of 22.6 m/s at an angle of 30.0°. At what height does the 2nd barrel need to be for Donkey Kong to land in it? (measure from the height of barrel 1, aka y0=0)
For which value of θ is the range of a projectile fired from ground level a maximum?
90° above the horizontal
45° above the horizontal
55° above the horizontal
30° above the horizontal
60° above the horizontal
A map from The Legend of Zelda: The Breath of the Wild shows that Zora's Domain is 7.55 km in a direction 25.0° north of east from Gerudo Town. The same map shows that the Korok Forest is 3.13 km in a direction 55.0° west of north from Zora's Domain. The figure below shows the location of these three places. Modeling Hyrule as flat, use this information to find the displacement from Gerudo Town to Korok Forest. What is the magnitude of the displacement? Find the angle of the displacement. Measure the angle in degrees north of east of Gerudo Town.
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS
Ch. 8.1 - 1. In Figure 8-8, the work done by a conservative...Ch. 8.2 - 1. The work done by a conservative force on a...Ch. 8.3 - A system with only conservative forces acting on...Ch. 8.4 - 4. A system is acted on by more than one force,...Ch. 8.5 - A system consists of an object moving along the x...Ch. 8 - Is it possible for the kinetic energy of an object...Ch. 8 - If the stretch of a spring is doubled, the force...Ch. 8 - When a mass is placed on top of a vertical spring,...Ch. 8 - If a spring is stretched so far that it is...Ch. 8 - An object is thrown upward to a person on a roof....
Ch. 8 - It is a law of nature that the total energy of the...Ch. 8 - Discuss the venous energy conversions that occur...Ch. 8 - Discuss the nature of the work done by the...Ch. 8 - It the force on an object is zero, does that mean...Ch. 8 - When a ball is thrown upward, its mechanical...Ch. 8 - When a ball is thrown upward, it spends the same...Ch. 8 - The work done by a conservative force is indicated...Ch. 8 - 2. Calculate the work done by gravity as a 3.2-kg...Ch. 8 - Calculate the work done by friction as a 37-kg box...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate A 2.8-kg block is attached to a...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate (a) Calculate the work done by...Ch. 8 - In the system shown in Figure 8-26, suppose the...Ch. 8 - Predict/Explain Ball 1 is thrown to the ground...Ch. 8 - A mass is attached to the bottom of a vertical...Ch. 8 - Find the gravitational potential energy of an...Ch. 8 - A student lifts a 1.42-kg book from her desk to a...Ch. 8 - At the local ski slope, an 82.0-kg skier rides a...Ch. 8 - BIO The Wing of the Hawkmoth Experiments performed...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate A vertical spring stores 0.962 J...Ch. 8 - Pushing on the pump of a soap dispenser compresses...Ch. 8 - BIO Mantis Shrimp Smasher A peacock mantis shrimp...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate The work required to stretch a...Ch. 8 - A 0.33-kg pendulum bob is attached to a string 1.2...Ch. 8 - Prob. 18PCECh. 8 - Prob. 19PCECh. 8 - For an object moving along the x axis, the...Ch. 8 - At an amusement park, a swimmer uses a water side...Ch. 8 - Prob. 22PCECh. 8 - A skateboarder at a skate park rides along the...Ch. 8 - Three balls are thrown upward with the same...Ch. 8 - A 0.21-kg apple falls from a tree to the ground,...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate A 2.9-kg block slides with a...Ch. 8 - A 0.26-kg rock is thrown vertically upward from...Ch. 8 - A 1 40-kg block sides with a speed of 0.950 m/s on...Ch. 8 - A 5.76-kg rock is dropped and allowed to fall...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate Suppose the pendulum bob m...Ch. 8 - The two masses in the Atwoods machine shown in...Ch. 8 - In the previous problem, suppose the masses have...Ch. 8 - Prob. 33PCECh. 8 - Catching a wave, a 77-kg surfer starts with a...Ch. 8 - At a playground, a 19-kg child plays on a slide...Ch. 8 - Starting at rest at the edge of a swimming pool, a...Ch. 8 - A 22,000-kg airplane lands with a speed of 64 m/s...Ch. 8 - A78-kg skateboarder grinds down a hubba ledge that...Ch. 8 - You ride your bicycle down a hill, maintaining a...Ch. 8 - A 111-kg seal at an amusement park slides from...Ch. 8 - A 1.9-kg rock is released from rest at the surface...Ch. 8 - A 1250-kg car drives up a hill that is 16.2 m...Ch. 8 - The Outlaw Run roller coaster in Branson,...Ch. 8 - A 1.80-kg block slides on a rough horizontal...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-34 shows a potential energy curve as a...Ch. 8 - An object moves along the x axis, subject to the...Ch. 8 - A 1.34-kg object moves along the x axis, subject...Ch. 8 - The potential energy of a particle moving along...Ch. 8 - A block of mass m = 0.88 kg is connected to a...Ch. 8 - A ball of mass m = 0.75 kg is thrown straight...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-35 depicts the potential energy of a...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-35 depicts the potential energy of a...Ch. 8 - CE You and a friend both solve a problem involving...Ch. 8 - CE A particle moves under the influence of a...Ch. 8 - A sled slides without friction down a small,...Ch. 8 - A 74 Kg skier encounters a dip in the snows...Ch. 8 - Running Shoes The soles of a popular make of...Ch. 8 - Nasal Strips The force required to flex a nasal...Ch. 8 - The water slide shown in Figure 8-37 ends at a...Ch. 8 - A skateboarder starts at point A in Figure 8-38...Ch. 8 - The Crash of Skylab NASAs Skylab, the largest...Ch. 8 - BIO Bird Tendons Several studies indicate that the...Ch. 8 - In the Atwoods machine of Problem 31, the mass m2...Ch. 8 - A 6.60-kg block slides with an initial speed of...Ch. 8 - Jeff of the Jungle swings on a 7.6-m vine that...Ch. 8 - A 1.9-kg block slides down a frictionless ramp, as...Ch. 8 - Suppose the ramp in Figure 8-40 is not motionless....Ch. 8 - BIO Compressing the Ground A running track at...Ch. 8 - BIO A Fleas Jump The resilin in the body of a flea...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate Tension at the Bottom A ball of...Ch. 8 - An ice cube is placed on top of an overturned...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate The two blocks shown in Figure...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate Loop-the-Loop (a) A block of...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-45 shows a 1.75-kg block at rest on a...Ch. 8 - In Figure 8-45 a 1.2-kg block is held at rest...Ch. 8 - BIO The Flight of the Dragonflies Of all the...Ch. 8 - BIO The Flight of the Dragonflies Of all the...Ch. 8 - BIO The Flight of the Dragonflies Of all the...Ch. 8 - BIO The Flight of the Dragonflies Of all the...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 8-12...Ch. 8 - Referring to Example 8-12 Suppose the block is...Ch. 8 - Referring to Example 8-17 suppose we would like...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
12. Which of the following experiments could test the hypothesis that bacteria cause ulcers in humans? (Assume ...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
1. Which is a function of the skeletal system? (a) support, (b) hematopoietic site, (c) storage, (d) providing ...
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
2. Define equilibrium population. Outline the conditions that must be met for a population to stay in genetic e...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Match the following examples of mutagens. Column A Column B ___a. A mutagen that is incorporated into DNA in pl...
Microbiology: An Introduction
If someone at the other end of a room smokes a cigarette, you may breathe in some smoke. The movement of smoke ...
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Race car driver is cruising down the street at a constant speed of 28.9 m/s (~65 mph; he has a “lead” foot) when the traffic light in front of him turns red. a) If the driver’s reaction time is 160 ms, how far does he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he begins to slow down? b) If the driver’s combined reaction and movement time is 750 ms, how far do he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he slams on her brakes and car begins to slow down? c) If the driver’s average rate of acceleration is -9.5 m/s2 as he slows down, how long does it take him to come to a stop (use information about his speed of 28.9 m/s but do NOT use his reaction and movement time in this computation)? Please answer parts a-c. Show all work. For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.arrow_forwardBelow you will find 100 m split times for the American and France men’s 4x100 meter free style relay race during the 2008 Beijing Summer Olympics). Answer questions a-d. a) What was the total race time for each team, in seconds? b) Which team won the race? What was the difference in the teams’ times? c) What was the average speed for each team for the whole race? (provide answer to 3 decimal places). d) Calculate the average speed for each swimmer and report the results in a table like the one above. Remember to show the calculation steps. (provide answer to 3 decimal places). PLEASE SHOW ALL WORK AND STEPS.arrow_forwardNeed complete solution Pleasearrow_forward
- Below you will find 100 m split times for the American and France men’s 4x100 meter free style relay race during the 2008 Beijing Summer Olympics). Fill out the chart below. Calculate average speed per split (m/s). Show all work.arrow_forwardThe magnitude of vector →A i s 261. m and points in the direction 349.° counterclockwise from the positive x-axis. Calculate the x-component of this vector . Calculate the y-component of this vector.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 4.4 A man is dragging a trunk up the loading ramp of a mover's truck. The ramp has a slope angle of 20.0°, and the man pulls upward with a force F whose direction makes an angle of 30.0° 75.0° with the ramp (Fig. E4.4). (a) How large a force F is necessary for the component Fx parallel to the ramp to be 90.0 N? (b) How large will the component Fy perpendicular to the ramp be then? Figure E4.4 30.0 20.0°arrow_forward1. * A projectile is shot from a launcher at an angle e, with an initial velocity magnitude v., from a point even with a tabletop. The projectile lands on the tabletop a horizontal distance R (the "range") away from where it left the launcher. Set this up as a formal problem, and solve for vo (i.e., determine an expression for Vo in terms of only R, 0., and g). Your final equation will be called Equation 1.arrow_forward2. A projectile is shot from a launcher at an angle 0,, with an initial velocity magnitude vo, from a point even with a tabletop. The projectile hits an apple atop a child's noggin (see Figure 1). The apple is a height y above the tabletop, and a horizontal distance x from the launcher. Set this up as a formal problem, and solve for x. That is, determine an expression for x in terms of only v₁, o,y and g. Actually, this is quite a long expression. So, if you want, you can determine an expression for x in terms of v., 0., and time t, and determine another expression for timet (in terms of v., 0., y and g) that you will solve and then substitute the value of t into the expression for x. Your final equation(s) will be called Equation 3 (and Equation 4).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Conservative and Non Conservative Forces; Author: AK LECTURES;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vFVCluvSrFc;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY