
EBK PHYSICS
5th Edition
ISBN: 8220103026918
Author: Walker
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 2PCE
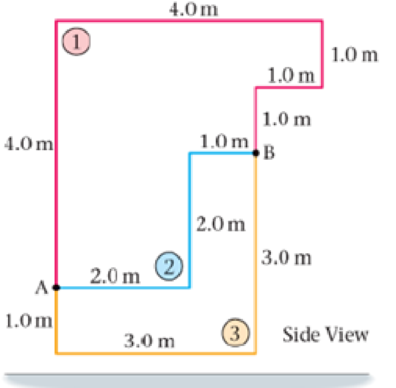
2. • Calculate the work done by gravity as a 3.2-kg object is moved from point A to point B in Figure 8-24 along paths 1, 2, end 3.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS
Ch. 8.1 - 1. In Figure 8-8, the work done by a conservative...Ch. 8.2 - 1. The work done by a conservative force on a...Ch. 8.3 - A system with only conservative forces acting on...Ch. 8.4 - 4. A system is acted on by more than one force,...Ch. 8.5 - A system consists of an object moving along the x...Ch. 8 - Is it possible for the kinetic energy of an object...Ch. 8 - If the stretch of a spring is doubled, the force...Ch. 8 - When a mass is placed on top of a vertical spring,...Ch. 8 - If a spring is stretched so far that it is...Ch. 8 - An object is thrown upward to a person on a roof....
Ch. 8 - It is a law of nature that the total energy of the...Ch. 8 - Discuss the venous energy conversions that occur...Ch. 8 - Discuss the nature of the work done by the...Ch. 8 - It the force on an object is zero, does that mean...Ch. 8 - When a ball is thrown upward, its mechanical...Ch. 8 - When a ball is thrown upward, it spends the same...Ch. 8 - The work done by a conservative force is indicated...Ch. 8 - 2. Calculate the work done by gravity as a 3.2-kg...Ch. 8 - Calculate the work done by friction as a 37-kg box...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate A 2.8-kg block is attached to a...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate (a) Calculate the work done by...Ch. 8 - In the system shown in Figure 8-26, suppose the...Ch. 8 - Predict/Explain Ball 1 is thrown to the ground...Ch. 8 - A mass is attached to the bottom of a vertical...Ch. 8 - Find the gravitational potential energy of an...Ch. 8 - A student lifts a 1.42-kg book from her desk to a...Ch. 8 - At the local ski slope, an 82.0-kg skier rides a...Ch. 8 - BIO The Wing of the Hawkmoth Experiments performed...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate A vertical spring stores 0.962 J...Ch. 8 - Pushing on the pump of a soap dispenser compresses...Ch. 8 - BIO Mantis Shrimp Smasher A peacock mantis shrimp...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate The work required to stretch a...Ch. 8 - A 0.33-kg pendulum bob is attached to a string 1.2...Ch. 8 - Prob. 18PCECh. 8 - Prob. 19PCECh. 8 - For an object moving along the x axis, the...Ch. 8 - At an amusement park, a swimmer uses a water side...Ch. 8 - Prob. 22PCECh. 8 - A skateboarder at a skate park rides along the...Ch. 8 - Three balls are thrown upward with the same...Ch. 8 - A 0.21-kg apple falls from a tree to the ground,...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate A 2.9-kg block slides with a...Ch. 8 - A 0.26-kg rock is thrown vertically upward from...Ch. 8 - A 1 40-kg block sides with a speed of 0.950 m/s on...Ch. 8 - A 5.76-kg rock is dropped and allowed to fall...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate Suppose the pendulum bob m...Ch. 8 - The two masses in the Atwoods machine shown in...Ch. 8 - In the previous problem, suppose the masses have...Ch. 8 - Prob. 33PCECh. 8 - Catching a wave, a 77-kg surfer starts with a...Ch. 8 - At a playground, a 19-kg child plays on a slide...Ch. 8 - Starting at rest at the edge of a swimming pool, a...Ch. 8 - A 22,000-kg airplane lands with a speed of 64 m/s...Ch. 8 - A78-kg skateboarder grinds down a hubba ledge that...Ch. 8 - You ride your bicycle down a hill, maintaining a...Ch. 8 - A 111-kg seal at an amusement park slides from...Ch. 8 - A 1.9-kg rock is released from rest at the surface...Ch. 8 - A 1250-kg car drives up a hill that is 16.2 m...Ch. 8 - The Outlaw Run roller coaster in Branson,...Ch. 8 - A 1.80-kg block slides on a rough horizontal...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-34 shows a potential energy curve as a...Ch. 8 - An object moves along the x axis, subject to the...Ch. 8 - A 1.34-kg object moves along the x axis, subject...Ch. 8 - The potential energy of a particle moving along...Ch. 8 - A block of mass m = 0.88 kg is connected to a...Ch. 8 - A ball of mass m = 0.75 kg is thrown straight...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-35 depicts the potential energy of a...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-35 depicts the potential energy of a...Ch. 8 - CE You and a friend both solve a problem involving...Ch. 8 - CE A particle moves under the influence of a...Ch. 8 - A sled slides without friction down a small,...Ch. 8 - A 74 Kg skier encounters a dip in the snows...Ch. 8 - Running Shoes The soles of a popular make of...Ch. 8 - Nasal Strips The force required to flex a nasal...Ch. 8 - The water slide shown in Figure 8-37 ends at a...Ch. 8 - A skateboarder starts at point A in Figure 8-38...Ch. 8 - The Crash of Skylab NASAs Skylab, the largest...Ch. 8 - BIO Bird Tendons Several studies indicate that the...Ch. 8 - In the Atwoods machine of Problem 31, the mass m2...Ch. 8 - A 6.60-kg block slides with an initial speed of...Ch. 8 - Jeff of the Jungle swings on a 7.6-m vine that...Ch. 8 - A 1.9-kg block slides down a frictionless ramp, as...Ch. 8 - Suppose the ramp in Figure 8-40 is not motionless....Ch. 8 - BIO Compressing the Ground A running track at...Ch. 8 - BIO A Fleas Jump The resilin in the body of a flea...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate Tension at the Bottom A ball of...Ch. 8 - An ice cube is placed on top of an overturned...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate The two blocks shown in Figure...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate Loop-the-Loop (a) A block of...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-45 shows a 1.75-kg block at rest on a...Ch. 8 - In Figure 8-45 a 1.2-kg block is held at rest...Ch. 8 - BIO The Flight of the Dragonflies Of all the...Ch. 8 - BIO The Flight of the Dragonflies Of all the...Ch. 8 - BIO The Flight of the Dragonflies Of all the...Ch. 8 - BIO The Flight of the Dragonflies Of all the...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 8-12...Ch. 8 - Referring to Example 8-12 Suppose the block is...Ch. 8 - Referring to Example 8-17 suppose we would like...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Heat lamps are commonly used to maintain foods at about 50C for as long as 12 hours in cafeteria serving lines....
Microbiology: An Introduction
16. Explain some of the reasons why the human species has been able to expand in number and distribution to a g...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. Based on computer models, when is plan...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
What are the minimum and maximum ages of the island of Kauai? Minimum age: ______million yr Maximum age: ______...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Explain why 92% of 2,4-pemtanedione exists as the enol tautomer in hexane but only 15% of this compound exists ...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
The number of named species is about ________, but the actual number of species on Earth is estimated to be abo...
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A small block of mass m = 200 g is released from rest at point along the horizontal diameter on the inside of a frictionless, hemispherical bowl of radius R = 30.0 cm (Fig. P8.43). Calculate (a) the gravitational potential energy of the block-Earth system when the block is at point relative to point . (b) the kinetic energy of the block at point . (c) its speed at point B, and (d) its kinetic energy and the potential energy when the block is at point . Figure P8.43 Problems 43 and 44.arrow_forwardA hummingbird is able to hover because, as the wings move downward, they exert a downward force on the air. Newtons third law tells us that the air exerts an equal and opposite force (upward) on the wings. The average of this force must be equal to the weight of the bird when it hovers. If the wings move through a distance of 3.5 cm with each stroke, and the wings beat 80 times per second, determine the work performed by the wings on the air in 1 m if the mass of the hummingbird is 3.0 g.arrow_forwardApollo 14 astronaut Alan Shepard famously took two golf shots on the Moon where its been estimated that an expertly hit shot could travel for 70.0 s through the Moons reduced gravity, airless environment to a maximum range of 4.00 km (about 2.5 miles). Assuming such an expert shot has a launch angle of 45.0, determine the golf balls (a) kinetic energy as it leaves the club, and (b) maximum altitude in km above the lunar surface. Take the mass of a golf ball to be 0.045 0 kg and the Moons gravitational acceleration to be gmoon = 1.63 m/s2.arrow_forward
- Give an example of a situation in which there is a force and a displacement, but the force does no work. Explain why it does no work.arrow_forwardA block of mass m = 5.00 kg is released from point and slides on the frictionless track shown in Figure P8.3. Determine (a) the blocks speed at points and and (b) the net work done by the gravitational force on the block as it moves from point to point . Figure P8.3arrow_forwardAs a simple pendulum swings back and forth, the forces acting on the suspended object are the force of gravity, the tension in the supporting cord, and air resistance, (a) Which of these forces, if any, does no work on the pendulum? (b) Which of these forces does negative work at all times during the pendulums motion? (c) Describe the work done by the force of gravity while the pendulum is swinging.arrow_forward
- The swimmer shown in Figure 7.44 exerts an average horizontal backward force of 80.0 N with his arm during each 1.80 m long stroke. (a) What is his work output in each stroke? (b) Calculate the power output of his arms if he does 120 strokes per minute. Figure 7.44arrow_forwardA roller-coaster car of mass 1.50 103 kg is initially at the top of a rise at point . It then moves 35.0 m at an angle of 50.0 below the horizontal to a lower point . (a) Find both the potential energy of the system when the car is at points and and the change in potential energy as the car moves from point to point , assuming y = 0 at point . (b) Repeat part (a), this time choosing y = 0 at point , which is another 15.0 m down the same slope from point .arrow_forwardHow much work is done by the boy pulling his sister 30.0 m in a wagon as shown in Figure 7.36? Assume no friction acts on the wagon. Figure 7.36 The boy does work on the system of the wagon and the child when he pulls them as shown.arrow_forward
- A pile driver drives posts into the ground by repeatedly dropping a heavy object on them. Assume the object is dropped from the same height each time. By what factor does the energy of the pile driverEarth system change when the mass of the object being dropped is doubled? (a) (b) 1; the energy is the same (c) 2 (d) 4arrow_forwardIn Figure 5.5 (a)-(d), a block moves to the right in the positive x-direction through the displacement x while under the influence of a force with the same magnitude F. Which of the following is the correct order of the amount of work done by the force F, from most positive to most negative? (a) d, c, a, b (b) c, a, b, d (c) c, a, d, barrow_forwardAs a mass tied to the end of a string strings from its highest point down to its lowest point, it is acted on by three forces: gravity, tension, and air resistance. Which force does (a) positive work? (b) negative work? (c) zero work?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g7u6pIfUVy4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY