
EBK PHYSICS
5th Edition
ISBN: 8220103026918
Author: Walker
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 73GP
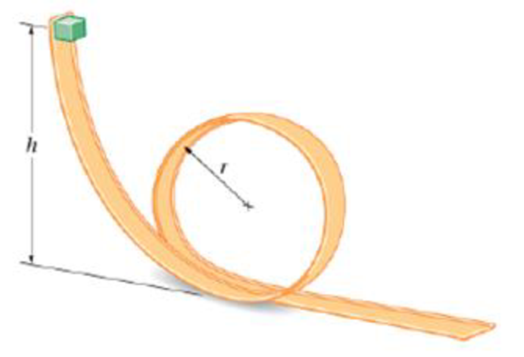
Predict/Calculate Loop-the-Loop (a) A block of mass m slides from rest on a frictionless top-the-loop track, as shown in Figure 8-44. What is the minimum release height, h, required for the block to maintain contact with the track at all times? Give your answer in terms of the radius of the loop, r. (b) Explain why the release height obtained in part (a) is independent of the block’s mass.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
You are standing a distance x = 1.75 m away from this mirror. The object you are looking at is y = 0.29 m from the mirror. The angle of incidence is θ = 30°. What is the exact distance from you to the image?
For each of the actions depicted below, a magnet and/or metal loop moves with velocity v→ (v→ is constant and has the same magnitude in all parts). Determine whether a current is induced in the metal loop. If so, indicate the direction of the current in the loop, either clockwise or counterclockwise when seen from the right of the loop. The axis of the magnet is lined up with the center of the loop. For the action depicted in (Figure 5), indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). I know that the current is clockwise, I just dont understand why. Please fully explain why it's clockwise, Thank you
A planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS
Ch. 8.1 - 1. In Figure 8-8, the work done by a conservative...Ch. 8.2 - 1. The work done by a conservative force on a...Ch. 8.3 - A system with only conservative forces acting on...Ch. 8.4 - 4. A system is acted on by more than one force,...Ch. 8.5 - A system consists of an object moving along the x...Ch. 8 - Is it possible for the kinetic energy of an object...Ch. 8 - If the stretch of a spring is doubled, the force...Ch. 8 - When a mass is placed on top of a vertical spring,...Ch. 8 - If a spring is stretched so far that it is...Ch. 8 - An object is thrown upward to a person on a roof....
Ch. 8 - It is a law of nature that the total energy of the...Ch. 8 - Discuss the venous energy conversions that occur...Ch. 8 - Discuss the nature of the work done by the...Ch. 8 - It the force on an object is zero, does that mean...Ch. 8 - When a ball is thrown upward, its mechanical...Ch. 8 - When a ball is thrown upward, it spends the same...Ch. 8 - The work done by a conservative force is indicated...Ch. 8 - 2. Calculate the work done by gravity as a 3.2-kg...Ch. 8 - Calculate the work done by friction as a 37-kg box...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate A 2.8-kg block is attached to a...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate (a) Calculate the work done by...Ch. 8 - In the system shown in Figure 8-26, suppose the...Ch. 8 - Predict/Explain Ball 1 is thrown to the ground...Ch. 8 - A mass is attached to the bottom of a vertical...Ch. 8 - Find the gravitational potential energy of an...Ch. 8 - A student lifts a 1.42-kg book from her desk to a...Ch. 8 - At the local ski slope, an 82.0-kg skier rides a...Ch. 8 - BIO The Wing of the Hawkmoth Experiments performed...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate A vertical spring stores 0.962 J...Ch. 8 - Pushing on the pump of a soap dispenser compresses...Ch. 8 - BIO Mantis Shrimp Smasher A peacock mantis shrimp...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate The work required to stretch a...Ch. 8 - A 0.33-kg pendulum bob is attached to a string 1.2...Ch. 8 - Prob. 18PCECh. 8 - Prob. 19PCECh. 8 - For an object moving along the x axis, the...Ch. 8 - At an amusement park, a swimmer uses a water side...Ch. 8 - Prob. 22PCECh. 8 - A skateboarder at a skate park rides along the...Ch. 8 - Three balls are thrown upward with the same...Ch. 8 - A 0.21-kg apple falls from a tree to the ground,...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate A 2.9-kg block slides with a...Ch. 8 - A 0.26-kg rock is thrown vertically upward from...Ch. 8 - A 1 40-kg block sides with a speed of 0.950 m/s on...Ch. 8 - A 5.76-kg rock is dropped and allowed to fall...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate Suppose the pendulum bob m...Ch. 8 - The two masses in the Atwoods machine shown in...Ch. 8 - In the previous problem, suppose the masses have...Ch. 8 - Prob. 33PCECh. 8 - Catching a wave, a 77-kg surfer starts with a...Ch. 8 - At a playground, a 19-kg child plays on a slide...Ch. 8 - Starting at rest at the edge of a swimming pool, a...Ch. 8 - A 22,000-kg airplane lands with a speed of 64 m/s...Ch. 8 - A78-kg skateboarder grinds down a hubba ledge that...Ch. 8 - You ride your bicycle down a hill, maintaining a...Ch. 8 - A 111-kg seal at an amusement park slides from...Ch. 8 - A 1.9-kg rock is released from rest at the surface...Ch. 8 - A 1250-kg car drives up a hill that is 16.2 m...Ch. 8 - The Outlaw Run roller coaster in Branson,...Ch. 8 - A 1.80-kg block slides on a rough horizontal...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-34 shows a potential energy curve as a...Ch. 8 - An object moves along the x axis, subject to the...Ch. 8 - A 1.34-kg object moves along the x axis, subject...Ch. 8 - The potential energy of a particle moving along...Ch. 8 - A block of mass m = 0.88 kg is connected to a...Ch. 8 - A ball of mass m = 0.75 kg is thrown straight...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-35 depicts the potential energy of a...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-35 depicts the potential energy of a...Ch. 8 - CE You and a friend both solve a problem involving...Ch. 8 - CE A particle moves under the influence of a...Ch. 8 - A sled slides without friction down a small,...Ch. 8 - A 74 Kg skier encounters a dip in the snows...Ch. 8 - Running Shoes The soles of a popular make of...Ch. 8 - Nasal Strips The force required to flex a nasal...Ch. 8 - The water slide shown in Figure 8-37 ends at a...Ch. 8 - A skateboarder starts at point A in Figure 8-38...Ch. 8 - The Crash of Skylab NASAs Skylab, the largest...Ch. 8 - BIO Bird Tendons Several studies indicate that the...Ch. 8 - In the Atwoods machine of Problem 31, the mass m2...Ch. 8 - A 6.60-kg block slides with an initial speed of...Ch. 8 - Jeff of the Jungle swings on a 7.6-m vine that...Ch. 8 - A 1.9-kg block slides down a frictionless ramp, as...Ch. 8 - Suppose the ramp in Figure 8-40 is not motionless....Ch. 8 - BIO Compressing the Ground A running track at...Ch. 8 - BIO A Fleas Jump The resilin in the body of a flea...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate Tension at the Bottom A ball of...Ch. 8 - An ice cube is placed on top of an overturned...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate The two blocks shown in Figure...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate Loop-the-Loop (a) A block of...Ch. 8 - Figure 8-45 shows a 1.75-kg block at rest on a...Ch. 8 - In Figure 8-45 a 1.2-kg block is held at rest...Ch. 8 - BIO The Flight of the Dragonflies Of all the...Ch. 8 - BIO The Flight of the Dragonflies Of all the...Ch. 8 - BIO The Flight of the Dragonflies Of all the...Ch. 8 - BIO The Flight of the Dragonflies Of all the...Ch. 8 - Predict/Calculate Referring to Example 8-12...Ch. 8 - Referring to Example 8-12 Suppose the block is...Ch. 8 - Referring to Example 8-17 suppose we would like...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Fill in the blanks: The nose is to the mouth. The ankle is to the knee. The ring finger is to the inde...
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
There are 25 individuals in population 1, all with genotype AA, and there are 40 individuals in population 2, a...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
APPLY 1.2 Express the following quantities in scientific notation
using fundamental SI units of mass and lengt...
Chemistry (7th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. Whats the best explanation for the loc...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
1.1 Write a one-sentence definition for each of the following:
a. chemistry
b. chemical
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
18. SCIENTIFIC THINKING By measuring the fossil remains of Homo floresiensis, scientists have estimated its wei...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V) ammeter I =arrow_forwardsimple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart lawarrow_forwardA circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forward
- An L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forwardA long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forwardDescribe the motion of a charged particle entering a uniform magnetic field at an angle to the fieldlines. Include a diagram showing the velocity vector, magnetic field lines, and the path of the particle.arrow_forward
- Discuss the differences between the Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law in terms of their applicationsand the physical quantities they describe.arrow_forwardExplain why Ampere’s law can be used to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid but not outside.arrow_forward3. An Atwood machine consists of two masses, mA and m B, which are connected by an inelastic cord of negligible mass that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius RO and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and m B, and compare to the situation where the moment of inertia of the pulley is ignored. Ignore friction at the axle O. Use angular momentum and torque in this solutionarrow_forward
- A 0.850-m-long metal bar is pulled to the right at a steady 5.0 m/s perpendicular to a uniform, 0.650-T magnetic field. The bar rides on parallel metal rails connected through a 25-Ω, resistor (Figure 1), so the apparatus makes a complete circuit. Ignore the resistance of the bar and the rails. Please explain how to find the direction of the induced current.arrow_forwardFor each of the actions depicted, determine the direction (right, left, or zero) of the current induced to flow through the resistor in the circuit containing the secondary coil. The coils are wrapped around a plastic core. Immediately after the switch is closed, as shown in the figure, (Figure 1) in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? If the switch is then opened, as shown in the figure, in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? I have the answers to the question, but would like to understand the logic behind the answers. Please show steps.arrow_forwardWhen violet light of wavelength 415 nm falls on a single slit, it creates a central diffraction peak that is 8.60 cm wide on a screen that is 2.80 m away. Part A How wide is the slit? ΟΙ ΑΣΦ ? D= 2.7.10-8 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 8 attempts remaining marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanical work done (GCSE Physics); Author: Dr de Bruin's Classroom;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OapgRhYDMvw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY