
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The name of the given alcohol needs to be determined, the stereochemistry (if present) needs to be indicated and it needs to be labeled as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol.
Concept Introduction: An alcohol can be classified as primary, secondary and tertiary deepening on the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the C atom to which the hydroxyl group is attached. If the number of H atoms are two, the alcohol is primary in nature, if there is only 1 H atom attached, then the alcohol is secondary and if there is no H atom attached to the C atom then the alcohol is tertiary.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given organic compound is as follows:
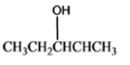
The name of the compound is 2-butanol.
Here, hydroxyl group is attached to the secondary carbon thus, it is a secondary alcohol.
(b)
Interpretation: The name of the given alcohol needs to be determined, the stereochemistry (if present) needs to be indicated and it needs to be labeled as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol.
Concept Introduction: An alcohol can be classified as primary, secondary and tertiary deepening on the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the C atom to which the hydroxyl group is attached. If the number of H atoms are two, the alcohol is primary in nature, if there is only 1 H atom attached, then the alcohol is secondary and if there is no H atom attached to the C atom then the alcohol is tertiary.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The given organic compound is as follows:
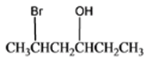
The name of the above compound is 5-bromo-3-hexanol.
Here, the hydroxyl group is at secondary carbon thus, it is a secondary alcohol.
(c)
Interpretation: The name of the given alcohol needs to be determined, the stereochemistry (if present) needs to be indicated and it needs to be labeled as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol.
Concept Introduction: An alcohol can be classified as primary, secondary and tertiary deepening on the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the C atom to which the hydroxyl group is attached. If the number of H atoms are two, the alcohol is primary in nature, if there is only 1 H atom attached, then the alcohol is secondary and if there is no H atom attached to the C atom then the alcohol is tertiary.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The given organic compound is as follows:
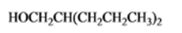
The name of the compound is 2-propyl-1-pentanol.
Now, there is hydroxyl group at primary position thus, it is a primary alcohol.
(d)
Interpretation: The name of the given alcohol needs to be determined, the stereochemistry (if present) needs to be indicated and it needs to be labeled as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol.
Concept Introduction: An alcohol can be classified as primary, secondary and tertiary deepening on the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the C atom to which the hydroxyl group is attached. If the number of H atoms are two, the alcohol is primary in nature, if there is only 1 H atom attached, then the alcohol is secondary and if there is no H atom attached to the C atom then the alcohol is tertiary.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The given organic compound is as follows:
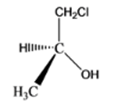
The name of the compound is (S)-1-chloro-2-propanol. There is a hydroxyl group at secondary carbon thus, it is a secondary alcohol.
(e)
Interpretation: The name of the given alcohol needs to be determined, the stereochemistry (if present) needs to be indicated and it needs to be labeled as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol.
Concept Introduction: An alcohol can be classified as primary, secondary and tertiary deepening on the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the C atom to which the hydroxyl group is attached. If the number of H atoms are two, the alcohol is primary in nature, if there is only 1 H atom attached, then the alcohol is secondary and if there is no H atom attached to the C atom then the alcohol is tertiary.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The given organic compound is as follows:
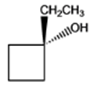
The name of the above compound is 1-ethylcyclobutanol. The hydroxyl group is at tertiary carbon thus, it is a tertiary alcohol.
(f)
Interpretation: The name of the given alcohol needs to be determined, the stereochemistry (if present) needs to be indicated and it needs to be labeled as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol.
Concept Introduction: An alcohol can be classified as primary, secondary and tertiary deepening on the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the C atom to which the hydroxyl group is attached. If the number of H atoms are two, the alcohol is primary in nature, if there is only 1 H atom attached, then the alcohol is secondary and if there is no H atom attached to the C atom then the alcohol is tertiary.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
The given organic compound is as follows:
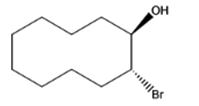
The name of the compound is (1R,2R)-2bromocyclodecanol.
In the above compound, the hydroxyl group is at secondary position thus, this is a secondary alcohol.
(g)
Interpretation: The name of the given alcohol needs to be determined, the stereochemistry (if present) needs to be indicated and it needs to be labeled as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol.
Concept Introduction: An alcohol can be classified as primary, secondary and tertiary deepening on the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the C atom to which the hydroxyl group is attached. If the number of H atoms are two, the alcohol is primary in nature, if there is only 1 H atom attached, then the alcohol is secondary and if there is no H atom attached to the C atom then the alcohol is tertiary.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
The given organic compound is as follows:
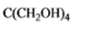
The name of the compound is 2, 2-bis(hydroxylmethyl)propane-1,3-
(h)
Interpretation: The name of the given alcohol needs to be determined, the stereochemistry (if present) needs to be indicated and it needs to be labeled as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol.
Concept Introduction: An alcohol can be classified as primary, secondary and tertiary deepening on the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the C atom to which the hydroxyl group is attached. If the number of H atoms are two, the alcohol is primary in nature, if there is only 1 H atom attached, then the alcohol is secondary and if there is no H atom attached to the C atom then the alcohol is tertiary.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
The given organic compound is as follows:
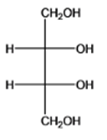
The name of the molecule is (2S,3R)-2,3-dihydroxybutane-1,2-diol. The hydroxyl group at first and fourth carbon atoms is primary and the other two hydroxyl groups are at second and third carbon atoms which are secondary.
(i)
Interpretation: The name of the given alcohol needs to be determined, the stereochemistry (if present) needs to be indicated and it needs to be labeled as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol.
Concept Introduction: An alcohol can be classified as primary, secondary and tertiary deepening on the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the C atom to which the hydroxyl group is attached. If the number of H atoms are two, the alcohol is primary in nature, if there is only 1 H atom attached, then the alcohol is secondary and if there is no H atom attached to the C atom then the alcohol is tertiary.
(i)
Explanation of Solution
The given organic compound is as follows:
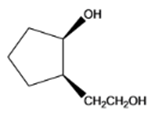
The name of the compound is cis-2-(2-hydroxylethyl)cyclopentanol. Here, the hydroxyl group is at secondary carbon atom of the cyclopentyl ring and the other hydroxyl group is attached to the primary carbon atom.
(j)
Interpretation: The name of the given alcohol needs to be determined, the stereochemistry (if present) needs to be indicated and it needs to be labeled as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol.
Concept Introduction: An alcohol can be classified as primary, secondary and tertiary deepening on the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the C atom to which the hydroxyl group is attached. If the number of H atoms are two, the alcohol is primary in nature, if there is only 1 H atom attached, then the alcohol is secondary and if there is no H atom attached to the C atom then the alcohol is tertiary.
(j)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is as follows:
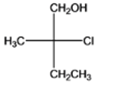
The name of the compound is (2R)-2-chloro-2-methyl-1-butanol. The hydroxyl group is at primary carbon atom thus, it is primary alcohol.
(k)
Interpretation: The name of the given alcohol and its all possible stereoisomers needs to be determined and it needs to be labeled as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol.
Concept Introduction: An alcohol can be classified as primary, secondary and tertiary deepening on the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the C atom to which the hydroxyl group is attached. If the number of H atoms are two, the alcohol is primary in nature, if there is only 1 H atom attached, then the alcohol is secondary and if there is no H atom attached to the C atom then the alcohol is tertiary.
(k)
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is as follows:
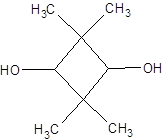
Since, there is no chiral center thus, there will be no possible stereoisomers.
The name of the given alcohol is 2, 2, 4, 4-tetramethylcyclobutane-1, 3-diol. Both the −OH groups are on the C atom with 1 H atom each thus, both are secondary alcohols.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Name the following molecules with IUpacarrow_forwardWhat is the molecular orbital for cyclopropenyl anion and is it aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic?arrow_forwardUsing the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid and its impact on the protein.arrow_forward
- How to get the predicted product of this reaction belowarrow_forwardPlease help me fill out the chart then using the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Then using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid.arrow_forwardWrite the Esterification reaction mechanism for acetic acid, and one propanol to make propanol ethanoate (molecule that gives peas its odor in flavor)arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





