
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: Synthesis of
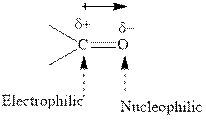
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
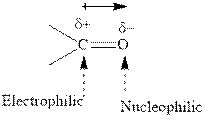
Grignard reagents are
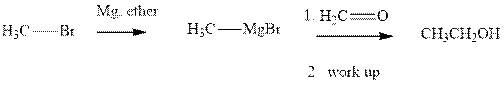
Methyl bromide reacts with magnesium ether to give Grignard reagent. This Grignard methyl magnesium bromide on treatment with formaldehyde gives corresponding alcohol. The mechanistic pathway for the latter reaction is as follows:

The polar carbonyl bond breaks and the polar Grignard reagent attack at electron-deficient carbon. Finally with the hydrolysis and work up the alcohol is formed.
(b)
Interpretation: Synthesis of
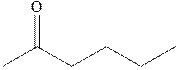
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. These reagents are useful precursors for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
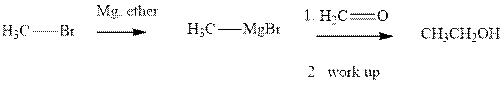
(c)
Interpretation: Synthesis of
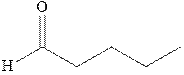
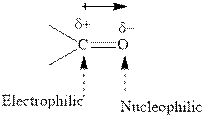
Concept introduction: The carbonyl bond is polar with the partial positive charge on carbon and partial negative charge on oxygen as illustrated below.
Grignard reagents are alkyl magnesium halides obtained from treatment of haloalkane with magnesium in presence of dried ether conditions. These reagents are useful precursors for quick synthesis of variety of organic compounds For example, the reaction of Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketone generates alcohol as illustrated below.
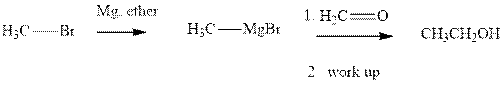
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Use the provided information to calculate Kc for the following reaction at 550 °C: H2(g) + CO2(g) ⇌ CO(g) + H2O(g) Kc = ?CoO(s) + CO(g) ⇌ Co(s) + CO2(g) Kc1 = 490CoO(s) + H2(g) ⇌ Co(s) + H2O(g) Kc2 = 67arrow_forwardCalculate Kc for the reaction: I2 (g) ⇋ 2 I (g) Kp = 6.26 x 10-22 at 298Karrow_forwardFor each scenario below, select the color of the solution using the indicator thymol blue during the titration. When you first add indicator to your Na2CO3solution, the solution is basic (pH ~10), and the color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . At the equivalence point for the titration, the moles of added HCl are equal to the moles of Na2CO3. One drop (or less!) past this is called the endpoint. The added HCl begins to titrate the thymol blue indicator itself. At the endpoint, the indicator color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . When you weren't paying attention and added too much HCl (~12 mL extra), the color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . When you really weren't paying attention and reached the second equivalence point of Na2CO3, the color isarrow_forward
- To convert cyclopentane-CH2-CHO to cyclopentane-CH2-CH3, compound A is added, followed by (CH3)3CO-K+, DMS at 100oC. Indicate which compound A is.arrow_forwardIndicate how to obtain the compound 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol.arrow_forwardIndicate the reagent needed to go from cyclopentane-CH2-CHO to cyclopentane-CH2-CH=CH-C6H5.arrow_forward
- esc Write the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure CH3 CH3-C=CH2 CH3-CH2-C-CH2-CH3 CH-CH3 CH3 ☐ ☐ ☐ CI-CH-CH=CH2 Explanation Check F1 F2 name 80 F3 F4 F5 F6 A 7 ! 2 # 3 4 % 5 6 & 7 Q W E R Y FT 2025 Mcarrow_forwardTwo reactants X and Z are required to convert the compound CH3-CH2-CH2Br to the compound CH3-CH2-CH=P(C6H5)3. State reactants X and Z.arrow_forward2. Write a reasonable mechanism that converts the reactants into the products. Avoid issues A-U from the previous page. You can use any number of steps (it does not have to be a one-step mechanism). Do not use any other chemicals (solvents, acids, bases, etc.) in your mechanism. 2 2 H ΗΘarrow_forward
- For the following reaction, the partial pressures were determined for the reaction components as shownbelow. Is the reaction at equilibrium? If not, in which direction will it proceed?I2 (g) + Cl2 (g) ⇋ 2 ICl (g) Kp = 81.9 partial pressures: I2 = 0.114 atm; Cl2 = 0.102 atm; ICl = 0.355 atmarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H3O+ + Oarrow_forwardWrite the law of mass action for the following quilibrium 2N2O5(g) --> 4 NO2(g) + O2(g).arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning



