
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The equation for the reaction that takes place to increase the solubility of
Concept Introduction: The solubility of a salt is defined as amount of salt dissolved in per 100 mL of the solvent at a constant temperature.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of aluminium ions and hydroxide ion forms aluminium hydroxide but it can also form
The precipitate is more soluble in very acidic and basic solutions.
The equations for reaction to increase the solubility of
The reaction in acidic solution is represented as follows:
The reaction in basic medium is represented as follows:
(b)
Interpretation: This is to be shown that the solubility of
Concept Introduction:
For a salt, the expression for solubility product can be written as follows:
The solubility product constant can be represented as follows:
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The relation between K,
Or,
The equilibrium constant expression can be represented as follows:
For the above reaction,
If ionization constant of water is used in this expression, the above expression can be rearranged as follows:
On rearranging,
Or,
The solubility product of
This can be rearranged as follows:
Also,
From equation (1) and (2),
(b)
Interpretation: The solubility of
Concept Introduction: The relation between solubility and hydrogen ion concentration can be represented as follows:
The relation between pH and hydrogen ion concentration can be represented as follows:
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The given value of K is 40.0 and solubility product constant is
The solubility of
Putting the value of K,
Or,
Now, for pH value 4, the hydrogen ion concentration will be
Similarly, for pH value 5, the hydrogen ion concentration will be
Thus, for pH value 6 -12, the solubility of
| pH | |
| 6 | |
| 7 | |
| 8 | |
| 9 | |
| 10 | |
| 11 | |
| 12 | |
| 13 | |
| 14 |
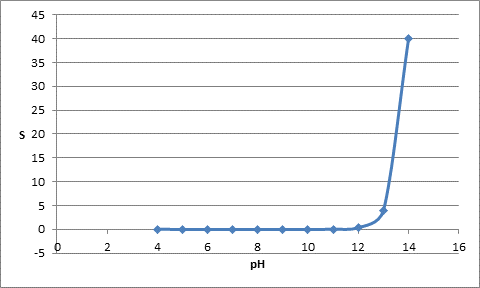
The table for pH and solubility can be represented as follows:
| pH | S |
| 4 | 0.02 |
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 7 | |
| 8 | |
| 9 | |
| 10 | |
| 11 | |
| 12 | 0.4 |
| 13 | 4 |
| 14 | 40 |
The plot can be represented as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES
- What is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forwardWhat would be the reagents and conditions above and below the arrow that will complete the proposed acetoacetic ester synthesis? If it cannot be done efficiently, then I will choose that answer. There could be 2 or 4 reagents involved. Please provide a detailed explanation and drawings showing how it would proceed with the correct reagents.arrow_forwardFor benzene, the ∆H° of vaporization is 30.72 kJ/mol and the ∆S° of vaporization is 86.97 J/mol・K. At 1.00 atm and 228.0 K, what is the ∆G° of vaporization for benzene, in kJ/mol?arrow_forward
- The reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reaction. it is spontaneous only at High T, it is spontaneous at low T it is nonspontaneous at all T it is spontanrous at all T. it is non spontaneous only at low T.arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reactionarrow_forwardWhich of the following has the largest standard molar entropy, S° (298.15 K) He H2 NaCl KBr Hgarrow_forward
- Which of the following is true for a particular reaction if ∆G° is -40.0 kJ/mol at 290 K and –20.0 kJ/mol at 390 K?arrow_forwardWhat is the major product of the following reaction? O O OH OH 1. BH 2. H₂O₂, NaOH OH OHarrow_forwardDraw the products formed when each ester is hydrolyzed with water and sulfuric acid.arrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





