
Concept explainers
Calculating factory
Munoz Manufacturing Co. normally produces 10,000 units of product X each month. Each unit requires 2 hours of direct labor, and factory overhead is applied on a direct labor hour basis. Fixed costs and variable costs in factory overhead at the normal capacity are $2.50 and $1.50 per direct labor hour, respectively. Cost and production data for May follow: 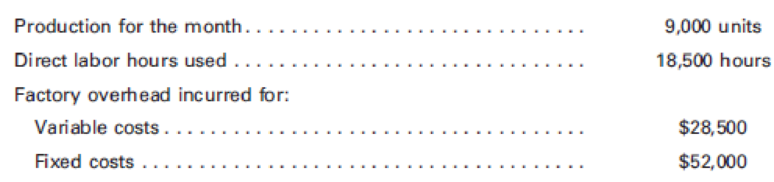
- a. Calculate the flexible-
budget variance . - b. Calculate the production-volume variance.
- c. Was the total factory overhead under- or overapplied? By what amount?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Principles of Cost Accounting
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Essentials of MIS (13th Edition)
Management (14th Edition)
Gitman: Principl Manageri Finance_15 (15th Edition) (What's New in Finance)
Intermediate Accounting (2nd Edition)
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains (12th Edition) (What's New in Operations Management)
- I need help with this general accounting problem using proper accounting guidelines.arrow_forwardCan you explain the process for solving this financial accounting question accurately?arrow_forwardI am looking for the correct answer to this financial accounting question with appropriate explanations.arrow_forward
- A business has accounts receivable of $180,000, an allowance for doubtful accounts balance of $7,200, and estimates that 5% of outstanding receivables will be uncollectible. What is the required adjustment to the allowance for doubtful accounts?arrow_forwardPlease explain this financial accounting problem with accurate financial standards.arrow_forwardHonda Company had beginning raw materials inventory of $32,000. During the period, the company purchased $127,000 of raw materials on account. If the ending balance in raw materials was $21,500, the amount of raw materials transferred to work in process inventory is?arrow_forward
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





