
Principles of Cost Accounting
17th Edition
ISBN: 9781305087408
Author: Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 13E
Using
Last year, Wrigley Corp. adopted a
On June 30, the end of the current fiscal year, a partial
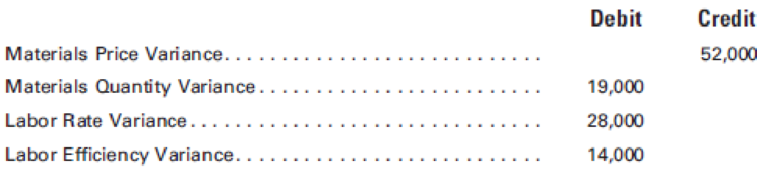
Standards set at the beginning of the year have remained unchanged. All inventories are priced at standard cost. What conclusions can be drawn from each of the four variances shown in Wrigley’s trial balance?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
I need assistance with this general accounting question using appropriate principles.
Please help me solve this general accounting question using the right accounting principles.
Can you solve this general accounting question with the appropriate accounting analysis techniques?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Principles of Cost Accounting
Ch. 8 - How does a standard cost accounting system work,...Ch. 8 - What is the difference between the standard cost...Ch. 8 - Prob. 3QCh. 8 - What are the specific procedures on which a...Ch. 8 - How are standards for materials and labor costs...Ch. 8 - What is a variance?Ch. 8 - How do price and quantity variances relate to...Ch. 8 - How do rate and efficiency variances relate to...Ch. 8 - Prob. 9QCh. 8 - How does a materials purchase price variance...
Ch. 8 - Prob. 11QCh. 8 - Prob. 12QCh. 8 - When a company uses a standard cost system, are...Ch. 8 - What two factors must be considered when breaking...Ch. 8 - What might cause the following materials...Ch. 8 - What might cause the following labor variances?
An...Ch. 8 - Prob. 17QCh. 8 - Prob. 18QCh. 8 - Prob. 19QCh. 8 - Prob. 20QCh. 8 - When does a flexible-budget variance occur?
Ch. 8 - Why is it important to determine flexible-budget...Ch. 8 - Prob. 23QCh. 8 - What is the significance of a production-volume...Ch. 8 - If production is more or less than the standard...Ch. 8 - At the end of the current fiscal year, the trial...Ch. 8 - What variances from the four-variance method are...Ch. 8 - What is the primary difference between the...Ch. 8 - What are the four variances in the four-variance...Ch. 8 - In all of the exercises involving variances, use F...Ch. 8 - Prob. 2ECh. 8 - Prob. 3ECh. 8 - Prob. 4ECh. 8 - Prob. 5ECh. 8 - Computing materials variances D-List Calendar Co....Ch. 8 - Computing labor variances LIFT Inc. manufactures...Ch. 8 - Standard cost summary; materials and labor cost...Ch. 8 - Computing labor variances Fill in the missing...Ch. 8 - Standard unit cost and journal entries The normal...Ch. 8 - Making journal entries Assume that during the...Ch. 8 - Using variance analysis and interpretation Last...Ch. 8 - Using variance analysis and interpretation Last...Ch. 8 - Journalizing standard costs in two departments...Ch. 8 - Calculating factory overhead The standard capacity...Ch. 8 - Determining Budgeted Overhead The overhead...Ch. 8 - Calculating factory overhead: two variances Munoz...Ch. 8 - Calculating factory overhead: two variances...Ch. 8 - The normal capacity of a manufacturing plant is...Ch. 8 - Calculating amount of factory overhead applied to...Ch. 8 - Georgia Gasket Co. budgets 8,000 direct labor...Ch. 8 - (Appendix) Calculating factory overhead: four...Ch. 8 - (Appendix) Calculating factory overhead: three...Ch. 8 - Materials and labor variances Branca Inspections...Ch. 8 - Materials and labor variances Fausto Fabricators...Ch. 8 - Zippy Inc. manufactures a fuel additive, Surge,...Ch. 8 - Calculation of materials and labor variances
Fritz...Ch. 8 - High-End Products Inc. uses a standard cost system...Ch. 8 - RDI Products Co. manufactures a variety of...Ch. 8 - The standard cost summary for the most popular...Ch. 8 - Carlo Lee Corp. has established the following...Ch. 8 - USD Inc. has established the following standard...Ch. 8 - Allocation of variances
Costa Brava Manufacturing...Ch. 8 - On May 1, Athens Inc. began the manufacture of a...Ch. 8 - The standard specifications for an electric motor...Ch. 8 - Cardiff Inc. manufactures men’s sport shirts for...Ch. 8 - Fargo Co. manufactures products in batches of 100...Ch. 8 - Prob. 15PCh. 8 - (Appendix) Overhead variances—four variance
Mobile...Ch. 8 - Shinto Corp. uses a standard cost system and...Ch. 8 - Kamen Manufacturing Co. estimates the following...Ch. 8 - Prob. 19PCh. 8 - Jillian Manufacturing Inc. manufactures a single...Ch. 8 - Cost and production data for Binghamton Beverages...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I am searching for the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the right approach.arrow_forwardWhat is the impact of inventory valuation method (FIFO vs. LIFO) on net income during inflation?no aiarrow_forwardCan you explain the correct methodology to solve this general accounting problem?arrow_forward
- What is the impact of inventory valuation method (FIFO vs. LIFO) on net income during inflation? Need helparrow_forwardWhat are index funds, and why are they popular among long-term investors in finance? need helparrow_forwardJoe and Ethan form JH Corporation. Joe transfers equipment (basis of $210,000 and fair market value of $180,000) while Ethan transfers land (basis of $15,000 and fair market value of $150,000) and $30,000 of cash. Each receives 50% of JH’s stock. As a result of these transfers: a. Joe has a recognized loss of $30,000, and Ethan has a recognized gain of $135,000. b. Neither Joe nor Ethan has any recognized gain or loss.c. Joe has no recognized loss, but Ethan has a recognized gain of $30,000. d. JH Corporation will have a basis in the land of $45,000.e. None of the above.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781305087408
Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...
Accounting
ISBN:9781337115773
Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337912020
Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:South-Western College Pub
What is Risk Management? | Risk Management process; Author: Educationleaves;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IP-E75FGFkU;License: Standard youtube license