
Concept explainers
a)
To determine: The break-even point quantity for the manual process.
Introduction:
Break-even point (BEP):
The break-even point is measured in units or in sales term to identify the point in a business which is required to cover the total investment costs. The total profit at break-even point is zero.
a)
Answer to Problem 25P
The break-even point quantity for the manual process is 50,000 bags.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Manual
Fixed costs= $37,500 / month
Variable costs = $1.75 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Mechanized process:
Fixed cost = $75,000 / month
Variable cost = $1.25 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Formula to calculate Break-even point (BEP) in units:
Calculation of Break-even point (BEP) in units:
The Break-even point is calculated by dividing the fixed cost with the difference of selling price and variable cost.
Hence, the Break-even point (BEP) in units is 50,000 bags.
b)
To determine: The revenue for the manual process at break-even point quantity.
Introduction:
Break-even point (BEP):
The break-even point is measured in units or in sales term to identify the point in a business which is required to cover the total investment costs. The total profit at break-even point is zero.
b)
Answer to Problem 25P
The revenue for the manual process at break-even point quantity is $125,000.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Manual process:
Fixed costs = $37,500 / month
Variable costs = $1.75 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Mechanized process:
Fixed cost = $75,000 / month
Variable cost = $1.25 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Formula to calculate Revenue for the manual process:
Calculation of Revenue
The revenue is calculated by dividing the fixed cost with the value obtained by dividing the resultant value obtained from dividing the difference between the selling price and variable cost divided by the selling price.
Hence, the revenue for the manual process at break-even point quantity is $125,000.
c)
To determine: The break-even point quantity for the mechanized process.
c)
Answer to Problem 25P
The break-even point quantity for the mechanized process is 60,000 bags.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Manual process:
Fixed costs = $37,500 / month
Variable costs = $1.75 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Mechanized process:
Fixed cost = $75,000 / month
Variable cost = $1.25 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Formula to calculate Break-even point (BEP) in units:
Calculation of Break-even point (BEP) in units:
The Break-even point is calculated by dividing the fixed cost with the difference of selling price and variable cost.
Hence, the Break-even point (BEP) in units is 60,000 bags.
d)
To determine: The revenue for the mechanized process at break-even point quantity.
d)
Answer to Problem 25P
The revenue for the mechanized process at break-even point quantity is $150,000.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Manual process:
Fixed costs = $37,500 / month
Variable costs = $1.75 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Mechanized process:
Fixed cost = $75,000 / month
Variable cost = $1.25 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Formula to calculate Revenue for the manual process:
Calculation of Revenue
The revenue is calculated by dividing the fixed cost with the value obtained by dividing the resultant value obtained from dividing the difference between the selling price and variable cost divided by the selling price.
Hence, the revenue for the manual process at break-even point quantity is $150,000.
e)
To determine: The monthly profit or loss for the manual process for the sale of 60,000 bags of lettuce per month.
e)
Answer to Problem 25P
The monthly profit for the manual process for the sale of 60,000 bags of lettuce per month is $7,500.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Manual process:
Fixed costs = $37,500 / month
Variable costs = $1.75 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Mechanized process:
Fixed cost = $75,000 / month
Variable cost = $1.25 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Formula to calculate Profit or loss:
Calculation of profit or loss for manual process:
The profit is calculated by multiplying number of bags of lettuce with selling price and the resultant value is subtracted from the fixed cost and the value obtained by multiplying number of bags of lettuce and variable cost.
The monthly profit for the manual process for the sale of 60,000 bags of lettuce per month is $7,500.
f)
To determine: The monthly profit or loss for the mechanized process for the sale of 60,000 bags of lettuce per month.
f)
Answer to Problem 25P
The monthly profit or lossfor the mechanized process for the sale of 60,000 bags of lettuce per month is $0which is the break-even point.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Manual process:
Fixed costs = $37,500 / month
Variable costs = $1.75 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Mechanized process:
Fixed cost = $75,000 / month
Variable cost = $1.25 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Formula to calculate Profit or loss:
Calculation of profit or loss for mechanized process:
The profit is calculated by multiplying number of bags of lettuce with selling price and the resultant value is subtracted from the fixed cost and the value obtained by multiplying number of bags of lettuce and variable cost.
Hence, the monthly profit or loss for the mechanized process for the sale of 60,000 bags of lettuce per month is $0 which is the break-even point.
g)
To determine: The point at which both the process will yield the same amount.
g)
Answer to Problem 25P
The point at which both the process will yield the same amount is 75,000 bags.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Manual process:
Fixed costs = $37,500 / month
Variable costs = $1.75 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Mechanized process:
Fixed cost = $75,000 / month
Variable cost = $1.25 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Formation of equation 1 for manual process:
Formation of equation 2 for mechanized process:
Calculation of the point at which both process yields the same amount:
The point is calculated by substituting all the known values in equation (1) and (2) and equating each other.
Hence, the point at which both the process will yield the same amount is 75,000 bags.
h)
To determine: The range of demand at which the manual process will be preferred over the mechanized process and the range of demand at which the mechanized will be preferred over the manual process.
Introduction:
Indifference point:
The indifference point in a business is a point where two different types of alternatives will not have any difference in the output they yield.
h)
Answer to Problem 25P
The manual process will be preferred over the mechanized process for the volume below 75,000 bags. The mechanized process will be preferred over the manual process for the volume above 75,000 bags.
Figure for showing the range at which one process will be better than the other:
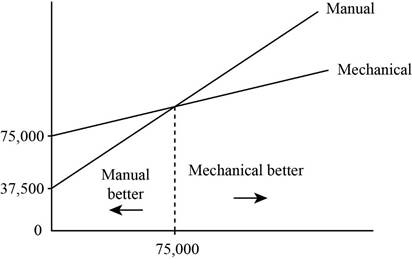
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Manual process:
Fixed costs = $37,500 / month
Variable costs = $1.75 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Mechanized process:
Fixed cost = $75,000 / month
Variable cost = $1.25 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Formation of equation 1 for manual process:
Formation of equation 2 for mechanized process:
Calculation of the point at which both process yields the same amount:
The point is calculated by substituting all the known values in equation (1) and (2) and equating each other.
The fixed costs of both the processes are plotted as shown in the graph. The intersection point in the graph is the point where both process will have no advantage over the other. It is also known as the indifference point. The indifference point is 75, 000 bags.
Hence, the manual process will be preferred over the mechanized process for the volume below 75,000 bags. The mechanized process will be preferred over the manual process for the volume above 75,000 bags.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Pearson eText Principles of Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
- Assess what led to such logistical inefficiencies / collapse of a previously world class freight networkarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements concerning the evaluation of training programs is true? Most companies thoroughly evaluate the return on investment of their training programs It is relatively easy to establish a control group and a treatment group for evaluation Results level of evaluation measures how well participants liked the program Behavior level criteria measure whether skills learned in training result in behavior changes back on the jobarrow_forwardEligibility testing is an disparate impact validation method none of the above a method to validate promotions and progressive discipline activity a test an employee administers to ensure that the potential employee is capable and qualified to perform the requirements of the positionarrow_forward
- A no-strike pledge by a union in a collective bargaining agreement is given in return for management’s agreement to: a grievance procedure a union shop a wage increase a fringe benefit increase binding arbitration of grievancesarrow_forwardWhich is the major OD technique that is used for increasing the communication, cooperation, and cohesiveness of work units? Leadership analysis Developing objectives Groupthink Strategic Planning team Buildingarrow_forwardAn American multinational firm usually is less than fully successful in adapting itself to local practices in each country because: American managers are often ignorant of local conditions None of the above management direction may be centralized in the home office All of the above Foreign subsidiaries often have American managersarrow_forward
- When salary increases are based on inputs, or performance, companies are following: agency theory equality theory equity theory compliance theory need theoryarrow_forwardThe most frequently used techniques for measuring job satisfaction involves Direct observation Questionnaires Interviews Psychological testsarrow_forwardWhich of the following is not an advantage of on-the-job training? Transfer is less difficult Transfer is less difficult The training is inexpensive Any organizational member can be the trainer without preparation It is relatively easy to use this methodarrow_forward
- Diversimilarity is characterized by A systematic and dual emphasis and appreciation of both the differences and the similarities that members of an organization have Everyone is either the same or different Attempting to change the values of minority groups to make them conform with the views of the dominant group Emotional intelligence of everyone involvedarrow_forwardCultural environment includes all of the following components except: religious beliefs values/ideologies corporate structure education/human capitalarrow_forwardSearch firms _____________. All of the above place consultants onsite for their clients are outsourced to search and place full-time employees for their clients place contract employees for the clientsarrow_forward
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage LearningMarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage LearningMarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub





