
(a)
To calculate: Under what condition on the coefficients of the system , a, b. c, d, e, and f the above system of linear equations has a one distinct solution.
(a)
Answer to Problem 71E
Condition to have a distinct solution of the above system of linear equations is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
In the question following general form of the system of linear equations is given
Calculation:
Given system of equations is
has a distinct solution if
(b)
To calculate: the solution of the given system of the linear equations by method of substitution and the graphical method.
(b)
Answer to Problem 71E
The solution of the given system of equations is
Explanation of Solution
- Method of Substitution
Given system of linear equations is
To solve the system of equation by the method of substitution take the following steps:
Step-1: Solve for y from the equation (1):
On subtracting ax from both sides of the above equation, it will give
Now, divide both sides by b to get the value of y :
Step-2: Substitute the above value of y in the second equation (2), and solve it for the value of x :
On multiplying both sides by b, it will give
Now, subtracting ec from both sides:
Now, on dividing both sides by (bd-ae), it will the value of x :
Or,
Notice that above value of x is meaningful only when
Step-3: (Back-substitution) Substitute the value of x in the value of y calculated in the step-1:
Or,
It gives the values of x and y by the method of substitution.
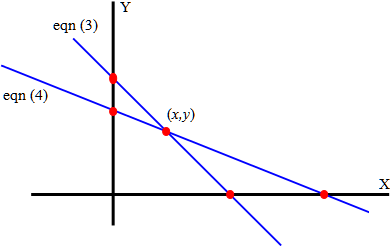
- Graphical Method:
To solve the given system of equation using graphical method, write the given linear equations in the following forms:
Equation (1)
And equation (2)
Notice that equation (3) and (4) are the equations of the straight lines. The system of linear equations (eqn (1)-(2)) has a solution if the straight lines (3) and (4) intersects. If the lines (3) and (4) intersects then the left hand sides of (3) and (4) are equal:
Now, solving the above equation for x ,
Or,
And, the corresponding y-coordinate of the intersection point can be calculate from the equation (3):
Notice that the point of intersection is equal to the solution of system of linear equations (1)-(2) determined by the method of substitutions. Point of intersection ( x,y ) in the following figure is given by the equations (5) and (6):
(c)
To write down the advantages of method of substitution compared to the graphical method.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
With graphical method, it is possible to locate or represent the solution as a point of intersection, but to actually find the solution one has to solve the equations using method of substitution. Sometimes in case of extremely large or small solutions it is not possible to draw a clear graph to represent the solution of the system of linear equations as the point of intersection. On the other hand, if the solution exists then it is always possible to find the solution using the method of substitution with a few calculation steps irrespective the size of solution.
Chapter 7 Solutions
EBK PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS
- Calculus III May I please have the example, definition semicolons, and all blanks completed and solved? Thank you so much,arrow_forwardA company estimates that the revenue (in dollars) from the sale of x doghouses is given by R(x) = 12,000 In (0.02x+1). Use the differential to approximate the change in revenue from the sale of one more doghouse if 80 doghouses have already been sold. The revenue will increase by $ if one more doghouse is made. (Round to the nearest cent as needed.)arrow_forwardThe population of bacteria (in millions) in a certain culture x hours after an experimental 20x nutrient is introduced into the culture is P(x) = - 2 Use the differential to approximate the changes in population for the following changes in x. 8+x a. 1 to 1.5 b. 3 to 3.25 a. Use the differential to approximate the change in population for x=1 to 1.5. Between 1 and 1.5 hours, the population of bacteria changes by million. (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
- The demand for grass seed (in thousands of pounds) at price p dollars is given by the following function. D(p) 3p³-2p² + 1460 Use the differential to approximate the changes in demand for the following changes in p. a. $4 to $4.11 b. $6 to $6.19arrow_forwardLet the region R be the area enclosed by the function f(x) = 3 ln (x) and g(x) = 3 x + 1. Write an integral in terms of x and also an integral in terms of y that would represent the area of the region R. If necessary, round limit values to the nearest thousandth. Answer Attempt 1 out of 2 y 7 10 6 5 4 3 2 -1 2 3 4 5 6 x2 dx x1 = x2 = x1 Y1 = Y2 = Y1 dyarrow_forwardA manufacturer of handcrafted wine racks has determined that the cost to produce x units per month is given by C = 0.3x² + 7,000. How fast is the cost per month changing when production is changing at the rate of 14 units per month and the production level is 80 units? Costs are increasing at the rate of $ (Round to the nearest dollar as needed.) per month at this production level.arrow_forward
- dy Assume x and y are functions of t. Evaluate for 2xy -3x+2y³ = - 72, with the conditions dt dx dt = -8, x=2, y = -3. dy dt (Type an exact answer in simplified form.)arrow_forwardConsider the sequence below: 1 1 1 (a) Express this sequence as a recurrence relation (b) Express this sequence in the form {a}=1 (c) Does this sequence converge or diverge? Justify your answer. Consider the sequence below: 1 1 1 1, 4' 9' 16' (a) Express this sequence in the form {ak}=1 (b) Does this sequence converge or diverge? Justify your answer. Consider the sequence below: 345 2. 4' 9' 16' ·} (a) Express this sequence in the form {a}1 (b) Does this sequence converge or diverge? Justify your answer.arrow_forwardUse the growth rate of sequences theorem to find the limit or state it divergesarrow_forward
- calculate the maximum value of the directional derivativearrow_forward2. A tank with a capacity of 650 gal. originally contains 200 gal of water with 100 lb. of salt in solution. Water containing 1 lb. of salt per gallon is entering at a rate of 4 gal/min, and the mixture is allowed to flow out of the tank at a rate of 3 gal/min. a. Find the amount of salt in the tank at any time prior to the instant when the tank begins to overflow (650 gallons). b. Find the concentration (in pounds per gallon) of salt in the tank when the tank hits 400 gallons. D.E. for mixture problems: dv dt=11-12 dA A(t) dtarrow_forward- Suppose that you have the differential equation: dy = (y - 2) (y+3) dx a. What are the equilibrium solutions for the differential equation? b. Where is the differential equation increasing or decreasing? Show how you know. Showing them on the drawing is not enough. c. Where are the changes in concavity for the differential equation? Show how you know. Showing them on the drawing is not enough. d. Consider the slope field for the differential equation. Draw solution curves given the following initial conditions: i. y(0) = -5 ii. y(0) = -1 iii. y(0) = 2arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





