
Concept explainers
7.13 through 7.16 For the given state of stress, determine the normal and shearing stresses after the element shown has been rotated through (a) 25° clockwise, (b) 10° counterclockwise.
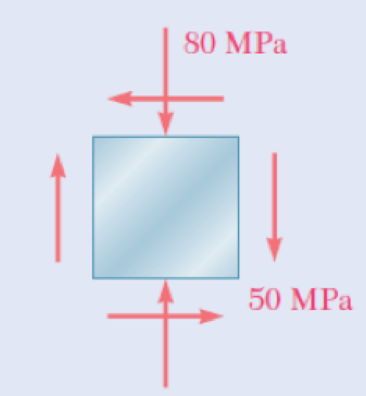
Fig. P7.16
(a)
The normal and shearing stresses after the element has been rotated through
Answer to Problem 16P
The normal stresses are
The shear stress is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The stress component along x direction as
The stress component along y direction as
The shear stress component as
The orientation of the principal plane as
Calculation:
Calculate the normal stress along x direction
Substitute
Hence, the normal stress as
Calculate the normal stress along y direction
Substitute
Hence, the normal stress as
Calculate the shear stress
Substitute
Therefore, the shear stress as
(b)
The normal and shearing stresses after the element has been rotated through
Answer to Problem 16P
The normal stresses are
The shear stress is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The stress component along x direction as
The stress component along y direction as
The shear stress component as
The orientation of the principal plane as
Calculation:
Calculate the normal stress along x direction
Substitute
Hence, the normal stress as
Calculate the normal stress along y direction
Substitute
Hence, the normal stress as
Calculate the shear stress
Substitute
Therefore, the shear stress as
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
- Correct answer only. I will upvote.arrow_forwardI really don't know how to approach this problem i've tried approaching it with some of the torsional stress equations I know but i'm comming up with awnsers that don't make any sence can you please help me with this?arrow_forwardI tried this problem and don't know what I did wrong or how else I could approach it can you please help me out?arrow_forward
- Q3: An engine produce 750 kW power and uses gaseous C12H26 as a fuel at 25 C; 200% theoretical air is used and air enters at 500 K. The products of combustion leave at 800 K. The heat loss from the engine is 175 kW. Determine the fuel consumption for complete combustion.arrow_forwardQu 5 Determine the carburizing time necessary to achieve a carbon concentration of 0.30 wt% at a position 4 mm into an iron carbon alloy that initially contains 0.10 wt% C. The surface concentration is to be maintained at 0.90 wt% C, and the treatment is to be conducted at 1100°C. Use the data for the diffusion of carbon into y-iron: Do = 2.3 x10-5 m2/s and Qd = 148,000 J/mol. Express your answer in hours to three significant figures. show all work step by step problems formula material sciencearrow_forward(Read Question)arrow_forward
- In figure A, the homogeneous rod of constant cross section is attached to unyielding supports. In figure B, a homogeneous bar with a cross-sectional area of 600 mm2 is attached to rigid supports. The bar carries the axial loads P1 = 20 kN and P2 = 60 kN, as shown.1. In figure A, derive the expression that calculates the reaction R1 in terms of P, and the given dimensions.2. In figure B, calculate the reaction (kN) at A.3. In figure B, calculate the maximum axial stress (MPa) in the rod.arrow_forward(Read image)arrow_forward(Read Image)arrow_forward
- M16x2 grade 8.8 bolts No. 25 C1- Q.2. The figure is a cross section of a grade 25 cast-iron pressure vessel. A total of N, M16x2.0 grade 8.8 bolts are to be used to resist a separating force of 160 kN. (a) Determine ks, km, and C. (b) Find the number of bolts required for a load factor of 2 where the bolts may be reused when the joint 19 mm is taken apart. (c) with the number of bolts obtained in (b), determine the realized load factor for overload, the yielding factor of safety, and the separation factor of safety. 19 mmarrow_forwardProblem4. The thin uniform disk of mass m = 1-kg and radius R = 0.1m spins about the bent shaft OG with the angular speed w2 = 20 rad/s. At the same time, the shaft rotates about the z-axis with the angular speed 001 = 10 rad/s. The angle between the bent portion of the shaft and the z-axis is ẞ = 35°. The mass of the shaft is negligible compared to the mass of the disk. a. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point G, based on the axis orientation as shown. Include an MVD in your solution. b. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point O, based on the axis orientation as shown. (Note: O is NOT the center of fixed-point rotation.) c. Find the kinetic energy of the assembly. z R R 002 2R x Answer: H = -0.046ĵ-0.040 kg-m²/sec Ho=-0.146-0.015 kg-m²/sec T 0.518 N-m =arrow_forwardProblem 3. The assembly shown consists of a solid sphere of mass m and the uniform slender rod of the same mass, both of which are welded to the shaft. The assembly is rotating with angular velocity w at a particular moment. Find the angular momentum with respect to point O, in terms of the axes shown. Answer: Ñ。 = ½mc²wcosßsinßĵ + (}{mr²w + 2mb²w + ½ mc²wcos²ß) k 3 m r b 2 C لا marrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





