
Concept explainers
A steel pipe of 12-in. outer diameter is fabricated from
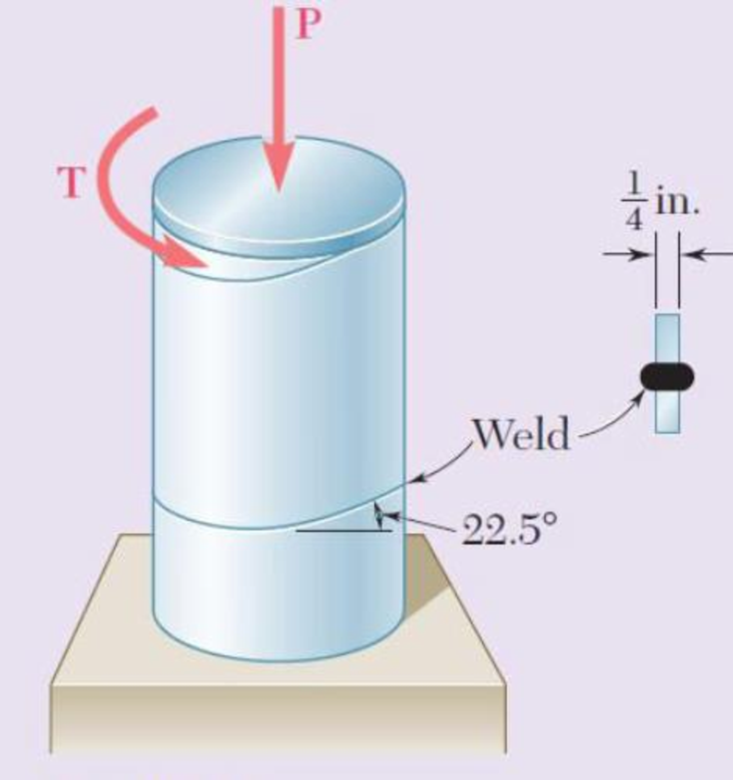
Fig. P7.158
Fund the normal and in-plane shearing stresses, normal and tangential stress to the weld.
Answer to Problem 158RP
The normal stress in x-axis is
The normal stress in y-axis is
The shearing stress in xy-plane is
The normal stress in the weld is
The tangential stress in the weld is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The outer diameter of the steel pipe is
The thickness of the plate is
The plate makes an angle with plane perpendicular to the pipe is
The magnitude of the axial force P is 40 kips.
The torque applied in the pipe T is 80 kip-in.
Calculation:
Find the inner diameter of the steel
Substitute 12 in. for
Find the area of the steel pipe (A) using the equation.
Substitute 12 in. for
Find the polar moment of inertia (J) of the steel pipe using the equation.
Substitute 12 in. for
Find the normal stress
Substitute 40 kips for P and
The normal stress in x-axis is
The normal stress in y-axis is
Find the shearing stress
Substitute 80 kip-in. for T, 12 in. for
The shearing stress in xy-plane is
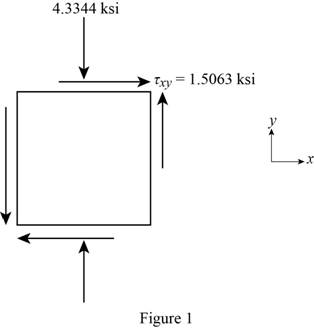
Show the stress element for pipe as in Figure 1.
Therefore,
The normal stress in x-axis is
The normal stress in y-axis is
The shearing stress in xy-plane is
Consider the axes
The normal stress in weld is
The shearing stress in weld is
Find the normal stress in the weld using the equation.
Substitute 0 for
Find the tangential stress in the weld using the equation.
Substitute 0 for
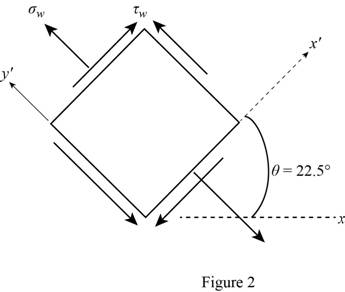
Show the stress element for weld as in Figure 2.
Therefore,
The normal stress in the weld is
The tangential stress in the weld is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
- Heat is generated uniformly in a 4 cm-diameter, 16-cm long solid bar (k=2.4 W/m-K). The temperaturesat the center and at the surface of the bar are measured to be 210 oC and 45 oC, respectively. Calculatethe rate of heat generation within the bar. Solve the relevant energy balance equation and the boundaryconditions to calculate the rate of heat generation within the bar. (6 pts)arrow_forwardA hot plane surface is maintained at 100°C, and it is exposed to air at 25°C. The combined heat transfercoefficient between the surface and the air is 25 W/m²·K. You are tasked with designing an insulatingmaterial to cover the surface in order to reduce the heat transfer rate by 90%, meaning only 10% of theheat transfer would occur compared to the situation without insulation. The available insulating materialhas a thermal conductivity of 0.093 W/m·K. Assuming that the heat transfer coefficient and the surface/airtemperatures remain constant, calculate the required thickness of the insulating material in centimeters.arrow_forwardThe euler parameter in the image describes the orientation of N in the reference frame of U. How do I find the euler parameters that describe the orientation of U in the reference frame of N from the given information in the image.arrow_forward
- Fpull Ө A person, weighing 155 lb, is being lifted by a rope thrown. over a tree branch as shown (drawing not to scale). If the static coefficient of friction between the rope and the tree branch is us = 0.67, and the 0 = 45°. Determine the pulling force required to start lifting the person and the pulling force required to keep the person from falling? Pulling force to lift the person: Pulling force to keep the person from falling: lb lbarrow_forwardThe car weighs 1630 lbs and drives up the hill at a constant speed. Assuming the static friction coefficient between the wheels and the road is μs = 0.64, determine the steepest angle that the car can climb without slipping if it is.... a.) rear wheel drive b.) front wheel drive c.) four wheel drive a C CC ①⑧ BY NC Dr. Jacob Moore Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 8.75 ft b 3.325 ft C 1.66 ft a.) The steepest angle for rear wheel drive is 0 max degrees. b.) The steepest angle for front wheel drive is Omax degrees. c.) The steepest angle for four wheel drive is Omax degrees. = = =arrow_forwardFor the structure below, each member of the truss will safely support a tensile force of 3 kN and a compressive force of 1 kN. Determine the largest mass m that can be safely suspended. Hint: First work through this algebraically to find the forces in each member terms of the mass "m" to determine the largest stress member. 1 m t 1 m 1 m 1m + 1m E B 1977 marrow_forward
- Block A has a mass of 34 kg and block B has a mass of 41 kg. The two blocks are stacked on the ramp with an incline of Ꮎ 0 = 15.4°. Determine the largest horizontal force F that can be applied to block B without either block moving for each of the following two cases: a.) The friction coefficient for the contact between blocks A and B is μs1 0.56 and the friction coefficient for the = contact between block A and the ramp is μs2 = 0.34. b.) The friction coefficient for the contact between blocks A and B is 1 = 0.56 and the friction coefficient for the contact between block A and the ramp is μs2 = 0.17. Ꮎ F B A Part a) The limiting slip condition occurs at Select an answer CC BY NC SA 2016 Eric Davishahl The maximum force before either block A or B slips is N Part b) The limiting slip condition occurs at Select an answer The maximum force before either block A or B slips is Narrow_forwardThe crane truck has a weight of 11000 lb and a center of gravity at point . The parking brake only locks the rear wheels of the truck, so the front wheels are free to rotate. Determine the maximum force F applied at the angle = 0 30.5° that can be exerted on the crane without it slipping or tipping for each of the following cases: Case 1: The static friction coefficient between the rear tires and the ground is μ. = 0.050. ა Case 2: The static friction coefficient between the rear tires and the ground is μα == 0.33. d CGD 口 BY NC SA F 2013 Michael Swanbom кажо с Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 5.5 ft b 9 ft C 4 ft 3 ft 10 ft d h For Case 1, the constraint is Select an answer F = lbs. шал For Case 2, the constraint is Select an answer F пал lbs. and andarrow_forwardYou are leaning your 5.0 ft, 15.0 lb ladder against the wall in your garage. There are 2 rubber foot paddles on the bottom of the ladder, and your garage floor is concrete. The static friction between the rubber and concrete is μs = 0.580. What is the maximum distance from the wall to the rubber foot paddles, which you can lean your ladder without it slipping? Assume the wall is smooth. S The maximum distance = ftarrow_forward
- Instructions. "I have written solutions in text form, but I need experts to rewrite them in handwriting from A to Z, exactly as I have written, without any changes."arrow_forwardPearson eText Study Area mylabmastering.pearson.com Access Pearson P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Problem 14.78 P Course Home b Answered: HW_02.pdf EE 213-01 > Assignments HW_#... 2 of 8 Document Sharing User Settings The spring has a stiffness k = 200 N/m and an unstretched length of 0.5 m. It is attached to the 4.6-kg smooth collar and the collar is released from rest at A. Neglect the size of the collar. (Figure 1) Part A Determine the speed of the collar when it reaches B. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 με VB = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? Review Next >arrow_forwardPearson eText Study Area Access Pearson mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Problem 15.79 P Course Home b Answered: HW_02.pdf EE 213-01 > Assignments HW_#... 6 of 8 > Document Sharing User Settings The two disks A and B have a mass of 4 kg and 5 kg, respectively. They collide with the initial velocities shown. The coefficient of restitution is e = 0.65. Suppose that (VA)1 = 6 m/s, (VB)1 = 8 m/s. (Figure 1) Part A Determine the magnitude of the velocity of A just after impact. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 μÅ (VA)2 = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B ? Review Determine the angle between the x axis and the velocity of A just after impact, measured clockwise from the negative x axis. Express your answer in degrees to three significant figures. ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ vec 01 Submit Request Answer Part C ? Determine the magnitude of the velocity of B just after impact. Express your answer to three significant…arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





