
Classify each
(a)
Interpretation:
To classify the given alkyl halide as 1°, 2°, or 3°
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halides are organic molecules that contains a halogen atom X bonded to sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen.
Answer to Problem 7.1P
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2-Br---➜ primary (1°)
Explanation of Solution
Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen.
primary (1°) = one carbon attached to carbon with halogen
secondary (2°) = two carbon attached to carbon with halogen
tertiary (3°) = three carbon attached to carbon with halogen
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2-Br---➜ in this structure only one carbon attached to carbon with halogen so primary (1°)
Thus the given structure is primary (1°)
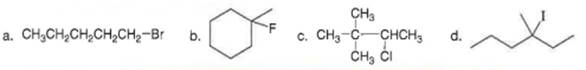
(b)
Interpretation:
To classify the given alkyl halide as 1°, 2°, or 3°
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halides are organic molecules that contains a halogen atom X bonded to sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen.
Answer to Problem 7.1P
 ------------➜ tertiary (3°)
------------➜ tertiary (3°)
Explanation of Solution
Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen.
primary (1°) = one carbon attached to carbon with halogen
secondary (2°) = two carbon attached to carbon with halogen
tertiary (3°) = three carbon attached to carbon with halogen
 ---➜ in this structure three carbons attached to carbon with halogen so primary (1°)
---➜ in this structure three carbons attached to carbon with halogen so primary (1°)
Thus the given structure is tertiary (3°)
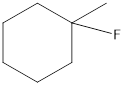
(c)
Interpretation:
To classify the given alkyl halide as 1°, 2°, or 3°
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halides are organic molecules that contains a halogen atom X bonded to sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen.
Answer to Problem 7.1P
 ------------➜ secondary (2°)
------------➜ secondary (2°)
Explanation of Solution
Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen.
primary (1°) = one carbon attached to carbon with halogen
secondary (2°) = two carbon attached to carbon with halogen
tertiary (3°) = three carbon attached to carbon with halogen

---➜ in this structure two carbons attached to carbon with halogen so secondary (2°)
Thus the given structure is secondary (2°)
(d)
Interpretation:
To classify the given alkyl halide as 1°, 2°, or 3°
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halides are organic molecules that contains a halogen atom X bonded to sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen.
Answer to Problem 7.1P
![]() ------------➜ tertiary (3°)
------------➜ tertiary (3°)
Explanation of Solution
Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen.
primary (1°) = one carbon attached to carbon with halogen
secondary (2°) = two carbon attached to carbon with halogen
tertiary (3°) = three carbon attached to carbon with halogen
![]()
---➜ in this structure three carbons attached to carbon with halogen so tertiary (3°)
Thus the given structure is tertiary (3°)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- molecule 0= OH ☐ ☐ type of molecule (check all that apply) fatty acid monoglyceride diglyceride triglyceride saturated unsaturated monounsaturated ☐ polyunsaturated ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐ 010 0 0 0 0 0 0 ☐ ☐ ☐ ☐☐☐☐ U omega-3 omega-6 fatty acid monoglyceride diglyceride triglyceride saturated unsaturated monounsaturated polyunsaturated omega-3 omega-6 fatty acid monoglyceride diglyceride triglyceride saturated unsaturated monounsaturated polyunsaturated omega-3 omega-6 OH OHarrow_forward'☐ : ☑ ด Suppose an alien life form has DNA just like human DNA remain the same.) - except that the alien DNA is made from deoxyarabinose instead of deoxyribose. (All other ingredients Draw the structure of a nucleotide containing thymine from which the alien DNA would be assembled. Note: be sure to draw the molecule as it would exist at physiological pH. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardPredict the products of the following biochemical reaction: CH2 CH-O + 3 KOH CH2-0 In particular, draw the structure of the product or products P in the drawing area below. If there are no products, because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. Note: if there is more than one product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. Also, just draw the structure of each product. You don't have to draw the complete right-hand side of the equation, including stoichiometric coefficients. No reaction Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : 5 èarrow_forward
- Name 1) 3-fluoro, 1-butene 2) 2-heptene 2,3-difluoro- 1-pentene 4) 6-iodo,4-methyl- 2-decyne 5) 4,4-dibromo- 1,2-butandiol Complete structural formula F -C=C-C-C- Line formula Condensed structural formula N F CH2=CHCHFCH3arrow_forward1. Part 1: Naming Organic Compounds он H₁C-C-CH3 CH3 Br CI CI 2. Br-CH-CH-CH₂ H₂C-CH-C= -CH-CH2-CH3 3. HC-CH-CH-C-OH 5. H₂C-CH-CH₂-OH 7. OH 4. CH CH₂-CH₂ 6. сно CH-CH-CH-CH₂-CH₂ H₁₂C-CH-CH-CH-CH₁₂-CH₁₂ 8. OHarrow_forward11 Organic Chemistry Organic Nomenclature Practice Name/Functional Group n-butane Formula Structural Formula (1) C4tt10 H3C C- (2) CH3CH2CH2 CH 3 H₂ -CH3 Н2 name & functional group (1) and (2) OH H₁₂C Н2 name only (1) and (2) name only (1) and (2) H₁C - = - CH₂ Н2 HC=C-C CH3arrow_forward
- Under aqueous basic conditions, nitriles will react to form a neutral organic intermediate 1 that has an N atom in it first, and then they will continue to react to form the final product 2: NC H₂O он- H₂O 1 2 OH Draw the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2 in the box below. You can draw the two structures in any arrangement you like. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardAssign these COSY Spectrumarrow_forwardAssign these C-NMR and H-NMR Spectrumarrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning



