
Classify each
(a)
Interpretation:
To classify the given alkyl halide as 1°, 2°, or 3°
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halides are organic molecules that contains a halogen atom X bonded to sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen.
Answer to Problem 7.1P
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2-Br---➜ primary (1°)
Explanation of Solution
Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen.
primary (1°) = one carbon attached to carbon with halogen
secondary (2°) = two carbon attached to carbon with halogen
tertiary (3°) = three carbon attached to carbon with halogen
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2-Br---➜ in this structure only one carbon attached to carbon with halogen so primary (1°)
Thus the given structure is primary (1°)
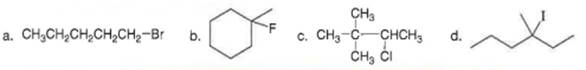
(b)
Interpretation:
To classify the given alkyl halide as 1°, 2°, or 3°
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halides are organic molecules that contains a halogen atom X bonded to sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen.
Answer to Problem 7.1P
 ------------➜ tertiary (3°)
------------➜ tertiary (3°)
Explanation of Solution
Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen.
primary (1°) = one carbon attached to carbon with halogen
secondary (2°) = two carbon attached to carbon with halogen
tertiary (3°) = three carbon attached to carbon with halogen
 ---➜ in this structure three carbons attached to carbon with halogen so primary (1°)
---➜ in this structure three carbons attached to carbon with halogen so primary (1°)
Thus the given structure is tertiary (3°)
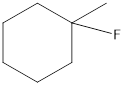
(c)
Interpretation:
To classify the given alkyl halide as 1°, 2°, or 3°
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halides are organic molecules that contains a halogen atom X bonded to sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen.
Answer to Problem 7.1P
 ------------➜ secondary (2°)
------------➜ secondary (2°)
Explanation of Solution
Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen.
primary (1°) = one carbon attached to carbon with halogen
secondary (2°) = two carbon attached to carbon with halogen
tertiary (3°) = three carbon attached to carbon with halogen

---➜ in this structure two carbons attached to carbon with halogen so secondary (2°)
Thus the given structure is secondary (2°)
(d)
Interpretation:
To classify the given alkyl halide as 1°, 2°, or 3°
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halides are organic molecules that contains a halogen atom X bonded to sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen.
Answer to Problem 7.1P
![]() ------------➜ tertiary (3°)
------------➜ tertiary (3°)
Explanation of Solution
Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen.
primary (1°) = one carbon attached to carbon with halogen
secondary (2°) = two carbon attached to carbon with halogen
tertiary (3°) = three carbon attached to carbon with halogen
![]()
---➜ in this structure three carbons attached to carbon with halogen so tertiary (3°)
Thus the given structure is tertiary (3°)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Construct a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for BeH2. Sketch the MO pictures (schematic representation) for the HOMO and LUMO of BeH2 [Orbital Potential Energies, H (1s): -13.6 eV; Be (2s): -9.3 eV, Be (2p): -6.0 eV]arrow_forwardIndicate the isomers of the A(H2O)6Cl3 complex. State the type of isomerism they exhibit and explain it briefly.arrow_forwardState the formula of the compound potassium μ-dihydroxydicobaltate (III) tetraoxalate.arrow_forward
- Consider the reaction of the cyclopentanone derivative shown below. i) NaOCH2CH3 CH3CH2OH, 25°C ii) CH3!arrow_forwardWhat constitutes a 'reference material', and why does its utilization play a critical role in the chemical analysis of food products? Provide examples.arrow_forwardExplain what calibration is and why it is essential in relation to food analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forward
- The cobalt mu-hydroxide complex cobaltate(III) of potassium is a dinuclear complex. Correct?arrow_forwardThe cobalt mi-hydroxide complex cobaltate(III) of potassium is a dinuclear complex. Correct?arrow_forward3. Arrange the different acids in Exercise B # 2 from the strongest (1) to the weakest acid (10). 1. 2. (strongest) 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10 10. (weakest)arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning



